Change Over Time. Big Ideas. Inquiry. Enduring Outcomes
|
|
|
- Sybil Potter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Content Certain factors lead to the development of new species and the extinction of other species. Change Over Time Big Ideas Inquiry Natural selection is the mechanism of evolution Nature of Science All living things change over time. Enduring Outcomes (What will students need to recall, know or do to demonstrate understanding of the Big Idea? Include a connected set of Analytical, Creative & Practical Outcomes for this Big Idea Students should be able to: Analytical and Practical: Compare DNA of multiple organisms to determine relatedness. Creative: Design a new species with specific traits and adaptations that enable it to live in a particular environment. Analytical, Creative, Practical: Simulate how specific traits can help an organism survive or lead to extinction. Include a connected set of Analytical, Creative & Practical Outcomes for this Big Idea Students should be able to: Practical: Connect the genetic make up of an individual to a physical trait. Analytical and Practical: Simulate natural selection to show how a species can change over time depending on it s adaptations and the environment in which it lives. Analytical, Creative and Practical: Experiment with a model of how certain adaptations can be an advantage or disadvantage and relate the experience to real life examples. Include a connected set of Analytical, Creative & Practical Outcomes for this Big Idea Students should be able to: Analytical: Compare fossil evidence in an area over time. Practical: Use fossil evidence to infer what a past environment was like. Creative and Practical: Predict human impact on extinction of a species and give real life examples.
2 Certain factors lead to the development of new species and the extinction of other species. Enduring Outcomes Evidence Tasks Recall Analytical the and terms Practical: diversity and variation Compare DNA of multiple organisms to determine Classify organisms that are closely related and relatedness compare variations. Creative: Compare DNA of multiple organisms to determine Design a new relatedness species with specific traits and adaptations that enable it to live in a particular Model environment. a gene pool Design Analytical, a new Creative species and with Practical: specific traits and adaptations that enable it to live in a particular Simulate how specific traits can help an organism environment. survive or lead to extinction. Simulate how specific traits can help an organism survive or lead to extinction. Tell Tale Molecules Activity. Designer Animal Activity Bird Beak Buffet Activity To look at a sequence of DNA from each of the following: Horse, Donkey, Rabbit, Snake, Turtle, and a Whale to help reveal evolutionary relationships. Students will be given four specific environments and will be required to design an animal that will fit into the environment they choose, meeting the needs of food, water, protection, shelter and caring for their young. Student will use various tools to represent beaks. Multiple stations will exist and at each station a specific method for obtaining food will be described. Students will have a specified time to feed, record how much food was obtained, graph results and compile class results to complete an analysis.
3 Natural selection is the mechanism of evolution. Enduring Outcomes Evidence Tasks Practical: Connect the genetic make up of an individual to a physical trait. Analytical and Practical: Simulate natural selection to show how a species can change over time depending on its adaptations and the environment in which it lives. Analytical, Creative and Practical: Experiment with a model of how certain adaptations can be an advantage or disadvantage and relate the experience to real life examples. Data from Nature at Work Activity. Nature at Work Activity Pepper Moth Natural Selection Activity Woolly Booger Natural Selection Students will choose two mouse cards, all cards having a W or a w to represent the genes for fur color in mice. Student will identify WW as white, Ww as white and ww as brown in the data section. Predict how changing environmental conditions will affect natural selection in the model. Make a dynamic model of natural selection in mice. Student will participate in a model where two types of moths (newspaper moths and white paper moths) are hunted in a specific amount of time. Data will be collected and interpreted. In Woolly booger Natural Selection, students will use different tools to represent how Woollyboogers feed. With one food source, students will collect data to see which mouth type was most successful at feeding and which mouth type lead to starvation.
4 All living Things Change Over Time. Enduring Outcomes Evidence Tasks Analytical: Compare fossil evidence in an area over time. Practical and Creative: Use fossil evidence to infer what a past environment was like. Arrange 9 rock samples containing fossils in order from oldest to youngest according to their fossil content using the process of relative dating. Extinction and Fossils Group Project Dating the Fossil Record Activity. Students will research and select an extinct organism from California s fossil record. They will research the environment in which it lived and will prepare a report for the possible causes of extinction.
5 Essential Questions What Essential Question is arguable and important to argue about? Is it valuable to have differences among living things? What Essential Question lies at the heart of the subject and helps provide purpose for learning? Are natural selection and evolution synonymous? What Essential Question raises more questions provoking and sustaining engaged inquiry? What impact do humans have on change over time? Instructional Blueprint What Essential Question raises important conceptual or philosophical issues? When protecting an environment or species, are we interfering with natural selection? Lesson Topics Content Standards Measurable/Observable Learning Objectives (What should students know, understand and/or be able to do?) Instructional Strategies/Tasks to Support Differentiation (Include a balance of analytical, creative, and practical activities) Assessments that match objectives 1. Pre Test 2 Dating the Fossil Record 3a, 3b, 3c, 3e, 4e, Students will take a pre test on the content standards taught in this unit to have a baseline to assess growth 3c, 4e, 7c 1. Students will use various rock samples embedded with fossils to correctly sort and sequence the relative order of the layers. 2. Students will identify the relative ages of the fossils and hypothesize about the environment in which the Pre test on major concepts taught in this unit (fossils, natural selection, Darwin s evidence, variation, etc ) 1. Students will arrange 9 rock samples containing fossils in order from oldest to youngest according to their fossil content using the process of relative dating. (groups of 2) 2. Students will use the correctly sequenced layers to determine relative age of fossils (Part 1) and will then form a timeline showing absolute ages (Part 2 given the dates of the samples). Actual test to be used as a baseline to gauge understanding prior to the unit being taught. 1. Teacher check and okay correct order of rock layers. 2. Analysis questions, throughout the activity that students may work on together in their pairs.
6 fossil lived. Lesson Topics Content Standards Measurable/Observable Learning Objectives (What should students know, understand and/or be able to do?) 3 Types of Fossils 3c, 4e Students will review the different types of fossils and how they form and will simulate the creation of two types of fossils. Instructional Strategies/Tasks to Support Differentiation (Include a balance of analytical, creative, and practical activities) 1. Content reading on types of fossils 2. Whole group notes on types of fossils 3. Lab activity creating both a cast and a mold. Assessments that match objectives Directed reading worksheets Check for understanding during notes and lab activity. Follow up lab questions. 4 Extinction and Fossils Group Project 3a, 3c, 3e, 4e, 7b 1. Students will find examples of organism that lived in CA and that no longer exist. 2. Students will create a presentation to share their findings on where the fossil has been found, its characteristics, when it lived, the environment in which it lived, and a possible cause of extinction. 1. Students will be put into groups of five and will individually research an extinct organism whose fossils have been found in CA. 2. Students will meet with group to determine which ONE extinct organism they will research and present to the class. 3. Research tasks will be divided up, with one person taking each of 5 questions: where fossils have been found, when fossil lived, characteristics of organism, environment in which it lived, possible causes of extinction. Journal question related to lab. Built in teacher checks on due dates for various parts (requiring initials) along the way Worksheet questions regarding planning, individual research and presenting. (written by individuals in the group) Group presentation/ rubric for grading. 4. Decide how group will present findings and prepare written and visual parts to the presentation and present to class.
7 Lesson Topics 5 Modeling a Gene Pool Content Standards 3a Measurable/Observable Learning Objectives (What should students know, understand and/or be able to do?) To show, using a model, that a gene pool is all the genes in a population, not just the genes in an individual. Instructional Strategies/Tasks to Support Differentiation (Include a balance of analytical, creative, and practical activities) 1. Students will be drawing two disks out of each of two bags and recording the gene pairs either two red alleles, two black alleles, or one red and one black allele. Assessments that match objectives Follow Up Lab Question: Which gene pool the first bag or the second bag shows the most diversity? 6 Tell Tale Molecules 3a, 7b, Students will use the amino acid sequence of a protein to determine evolutionary the evolutionary relationship of several animals. Students will draw conclusions about how close the species are related. 7 Nature at Work 3a, 3b, 3e, 7c, 7e 1. Predict how changing environmental conditions will affect the natural selection model. 2. Make a dynamic model of natural selection in mice. 2. Students will compare the diversity of organisms produced by the gene pairs in each bag. 1. Students will examine the sequence of amino acids in on region of protein for six different animals (horse, donkey, rabbit, snake, turtle, and whale). 2. Students will compare the amino acid sequences, make observations and answer some analysis and conclusion questions. 1. Students will simulate natural selection in mice by choosing two mouse cards (each having an allele for the gene for fur color) and recording the color of the mouse they have. 2. They will then choose an event card (disease, predator that kills mice that contrast with environment, predator that kills mice of all color, or mouse survives) to Analysis and Conclusion Questions for Telltale Molecules (students can work together in partners to check their responses). Journal question the following day. CFU before starting How do you think variation of color in a species might affect natural selection? CFU during activity with individual lab groups to see that students assign the right phenotype (mouse color) to
8 8 Bird Beak Buffet 3a, 3b, 3e, 7c Students will simulate how specific traits can help an organism survive or lead to extinction. Students will simulate how adaptation can increase the chance for survival of organisms. 9 Designer Animal 3a, Students will design a new species with specific traits and adaptations that enable it to live in a particular environment. determine the fate of the mouse. 3. Mouse color and fate data is recorded. A mouse that dies leaves the population for the future generations. 4. Students will complete analysis questions with their partners for each step of the simulation, making attempts to apply to real life examples and to predict the outcome if this model extended beyond 3 generations. 1. Students will use various tools to represent beaks. 2. Multiple stations will exist and at each station a specific method for obtaining food will be described. 3. Students will have a specified time to feed, then will record how much food was obtained, graph results and compile class results to complete an analysis. 1. Students will be given 4 specific environments and will be required to design an animal that will fit into the environment they choose, meeting the needs of food, water, protection, shelter and caring for their young. each genotype (mouse cards drawn) Questions on worksheet to analyze data for Part 1 (White Sand environment) and then part 2 (Forest Floor Environment) Explain the point of this lab to Charles Darwin comparing the ways in which this model simulates natural selection and ways this model differs from natural selection. Analysis questions for lab including questions about data obtained, the tool that was able to collect the most food, pictures of real birds with different beaks, and a question asking them to apply what they learned to a different example and predict the outcome. Drawing of animal in its environment showing evidence of how the needs of food, water, shelter, protection and care of the young are addressed. 10 How Do Living 3a Students will observe that the 1. Students will use a ruler to measure the Informal teacher observation of
9 Things Vary? seeds in their sample differ in size, shape, color, or number of stripes. length and width of 10 sunflower seeds and will record each measurement. 2. Students will use a hand lens to carefully examine each seed, recording each seed s shape, color and number of stripes. student s data. Individual written reflection on the ways the seeds in the sample are similar and different. 11 Evolution. 3b, 3c, 7b, 7c 1. Students will describe the reasoning that led to Darwin s theory 12. Pepper Moth Natural Selection 2. Students will use a branching diagram of the to compare beak types, sizes and environments. 3a, 3e, 7b, 7c 1.Students will do a simulation and describe the importance of coloration in avoiding predation. 2. Students will relate environmental changes to change in organisms (Peppermoth in England between ) 1. Content reading to describe the observations that Darwin made. 2. Explain how Darwin explained the differences between similar species, using examples. 3. Use the branching diagram of the 13 species of finches found on the Galapagos Islands to compare and contrast their beak types, the food they eat, and the environment in which each lives. 1. Students will participate in a simulation where two types of moths (newspaper moths and white paper moths) are hunted for a specific amount of time. There will be two different environments in this model. Data will be collected and interpreted. Response to how seeds could be classified according to their similarities and differences. Directed reading worksheets. Notes on Evolution activity. Follow up questions from Branching Diagram of Finches Activity. Data table from simulation. Graph of real life data and interpretation of graph. Analysis and conclusion questions related to simulation, real life data, and a creative example of situation where this type of selection might occur. 3. Students will explain how natural selection causes populations to change. 13. Woolly Booger Natural Selection 3a, 3e, 7c Students will model natural selection by using various 1. Students will use different tools to represent how Woollyboogers feed. Class notes reviewing evolution, variation, mutation,
10 utensils to capture food. * please note this is a different activity than Bird Beak Buffet because the food source does NOT change in this activity. 2. With only one food source, students will feed for a specified amount of time, record data, and compile data from their entire group. 3. Students will graph group data for each tool type. 3. Students will analyze group data and class data and relate the experiment to reallife examples. and adaptation. Woollybooger data and analysis questions. Journal question the following day.
11 Attachments California Content Standards, Science, Grade 7 Standard 3: Evolution Biological evolution accounts for the diversity of species developed through gradual processes over many generations. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know both genetic variation and environmental factors are causes of evolution and diversity of organisms. b. Students know the reasoning used by Charles Darwin in reaching his conclusion that natural selection is the mechanism of evolution. c. Students know how independent lines of evidence from geology, fossils, and comparative anatomy provide the bases for the theory of evolution. e. Students know that extinction of a species occurs when the environment changes and the adaptive characteristics of a species are insufficient for its survival. Standard 4e: Students know fossils provide evidence of how life and environmental conditions have changed. Standard 7: Investigation and Experimentation b. Use a variety of print and electronic resources (including the World Wide Web) to collect information and evidence as part of a research project. c. Communicate the logical connection among hypotheses, science concepts, tests conducted, data collected, and conclusions drawn from the scientific evidence. d. Construct scale models, maps, and appropriately labeled diagrams to communicate scientific knowledge (e.g., motion of Earth s plates and cell structure). e. Communicate the steps and results from an investigation in written reports and oral presentations.
12 ASSESSMENT: EXTINCTION AND FOSSILS What organisms that once lived in California are now extinct? What environmental factors may have caused their extinction? In this investigation, you will select an extinct organism from California s fossil record. Then you will research the environment in which it lived, and the causes for its extinction. At the end of your investigation, you will prepare a report on your findings. In addition, your group will make a presentation to the class. Investigation Rules * First, everyone in your group should do some research on the California fossil record. Identify some extinct organisms that once lived in your state. Use references such as books and World Wide Web resources. Web sites of California natural history museums and California fossil sites may be especially useful. Select some extinct organisms that interest you and about which a lot of information is available. Your group will meet with your teacher after you have read Section 1 to discuss your choice. * After you decide which organism you will investigate, divide up the research tasks among group members. Make a list of group member responsibilities. If you find some information that would be useful to another member of the group, share it. Your group will meet with your teacher at the end of section 3 to review the progress of your investigations. * Meet regularly with your group to discuss your findings. Questions from other group members can help to focus your investigation. When your investigation is complete, you should write a report that answers your assigned question. The report should include a complete list of the sources of your information. * After group members finish their individual research, your group should decide how to organize the information for the presentation. Think about how much time you have for each part of the presentation. * When you have organized your information for your presentation, you need to decide how you will display it to the class. Presentations can include pictures and models. Think about the way museums make displays and explain them to visitors. Discuss which tasks each member will do to prepare the presentation. * After you have read Section 5, discuss your progress with your teacher. Let your teacher know if you need any special equipment. Practice your final presentation. Time it to see how it fits into the time your teacher set aside for you.
13 Investigation Timeline Task Due Date Teacher s Initials 1. Choose some possible extinct organism for your investigation. 2. Meet with your group members and choose an organism to research. 3. Divide up the research tasks among the members of the group. Make a list of group member responsibilities. 4. Decide how your group will present your findings. 5. Prepare and label any illustrations you are going to use. Write any parts of your presentation that need to be written. Set up and practice your presentation. 6. Make your presentation to the class.
14 DOING THE RESEARCH Worksheet 1 This worksheet will help you select an extinct organism and find out about it. 1. What are some extinct organisms that are found in the California fossil record? Find the names of at least five extinct California organisms. 2. After you meet with your group members, choose the extinct organism that your group will investigate. Write its name here. 3. What resources are you using in your research about an extinct organism? List books and magazines and the URLs of any promising Web sites. Use a separate sheet of paper. 4. Do more research to find detailed information about the organism you have chosen. Assign group members to answer the following questions: a. Where in California have fossils of this organism been found? b. When did the organism live? c. Describe the characteristics of the organism in detail. d. What kind of environment did the organism probably live in? e. What might have caused the organism to become extinct? 5. What other important information might be included in your presentation?
15 SETTING UP THE PRESENTATION Worksheet 2 This worksheet will help you organize and prepare your presentation. 1. How will you present your findings to the class? Will you use a Power Point presentation, overhead projector poster, booklet, computer display, presentation board, or some other method? Discuss this with your teacher to make sure your plans are practical. 2. What kind of visuals (drawings and photographs) do you plan to use? Will your presentation include other things, such as models and displays? Who will be responsible for preparing these items? ORGANIZE THE PRESENTATION 3. How will your group introduce the presentation? What do you want to tell your audience to get them interested? Write a short introduction. 4. What will be the order of your presentation? Who will deliver each part? 5. How will you wrap up your presentation? Write a brief conclusion. 6. How will you conduct the question and answer part of the presentation? Will there be a group leader? Or will group members jump in when they know the answer? FINALIZING THE PRESENTATION 7. How much time will you allow for each part?
16 Doing Research/Preparing a Report. * Developing/Using Visuals Presenting the Investigation to the Class Participating in the Group EXTINCTION AND FOSSILS SCORING RUBRIC (Attachment 3B) Student writes a thorough report that includes a clear, accurate answers his/her assigned question*: (where in CA fossil was found, when it lived, characteristics of organism, environment, or possible cause of extinction), and a complete source list with several varied sources. Student develops attractive and relevant visuals (poster, media, pictures) that enhance and clarify the presentation. Student makes a thorough and interesting presentation that includes a clear, accurate answer to the assigned question*. Student takes a lead in planning, researching, developing, and making the presentation. Student writes a report that includes a mostly accurate answer to his/her assigned question *(where in CA fossil was found, when it lived, characteristics of organism, environment, possible cause of extinction), but something is missing in the answer, and a source list with several sources. Student develops relevant visuals (poster, media, pictures) that clarify the presentation. Student makes a thorough presentation that includes a satisfactory answer to the assigned question*, but there is something missing. Student participates in all aspects of planning, researching, developing, and making the presentation. Student writes a report that includes an answer to his/her assigned question *(where in CA fossil was found, when it lived, characteristics of organism, environment, possible cause of extinction), but there is important information missing, and an incomplete source list. Student develops visuals (poster, media, pictures) and uses them in the presentation. Student makes a presentation that includes a partial answer to the assigned question*,and leaves out something important. Student participates in most aspects of planning, researching, developing, and making the presentation. Student writes a report that includes an inaccurate answer to his/her assigned question*, and no source list. Student does not develop or use visuals in the presentation, or the visuals are inaccurate. Student makes a presentation that includes an incomplete and/or inaccurate answer to the assigned question*. Student plays a minor role in planning, researching, developing, and making the presentation. * Each student in the group is assigned ONE of the questions that needs to be in the presentation and is responsible for writing a report for his/her question.
Adaptations and Survival: The Story of the Peppered Moth
 Adaptations and Survival: The Story of the Peppered Moth Teacher: Rachel Card Subject Areas: Science/ELA Grade Level: Fourth Unit Title: Animal Adaptations Lesson Title: Adaptations and Survival: The Story
Adaptations and Survival: The Story of the Peppered Moth Teacher: Rachel Card Subject Areas: Science/ELA Grade Level: Fourth Unit Title: Animal Adaptations Lesson Title: Adaptations and Survival: The Story
What can I learn from worms?
 What can I learn from worms? Stem cells, regeneration, and models Lesson 7: What does planarian regeneration tell us about human regeneration? I. Overview In this lesson, students use the information that
What can I learn from worms? Stem cells, regeneration, and models Lesson 7: What does planarian regeneration tell us about human regeneration? I. Overview In this lesson, students use the information that
Simbio Virtual Labs Answers Finches And Evolution
 Simbio Virtual Labs Answers Finches And Free PDF ebook Download: Simbio Virtual Labs Answers Finches And Download or Read Online ebook simbio virtual labs answers finches and evolution in PDF Format From
Simbio Virtual Labs Answers Finches And Free PDF ebook Download: Simbio Virtual Labs Answers Finches And Download or Read Online ebook simbio virtual labs answers finches and evolution in PDF Format From
Airplane Rescue: Social Studies. LEGO, the LEGO logo, and WEDO are trademarks of the LEGO Group The LEGO Group.
 Airplane Rescue: Social Studies LEGO, the LEGO logo, and WEDO are trademarks of the LEGO Group. 2010 The LEGO Group. Lesson Overview The students will discuss ways that people use land and their physical
Airplane Rescue: Social Studies LEGO, the LEGO logo, and WEDO are trademarks of the LEGO Group. 2010 The LEGO Group. Lesson Overview The students will discuss ways that people use land and their physical
Content Language Objectives (CLOs) August 2012, H. Butts & G. De Anda
 Content Language Objectives (CLOs) Outcomes Identify the evolution of the CLO Identify the components of the CLO Understand how the CLO helps provide all students the opportunity to access the rigor of
Content Language Objectives (CLOs) Outcomes Identify the evolution of the CLO Identify the components of the CLO Understand how the CLO helps provide all students the opportunity to access the rigor of
Grade 5: Module 2A: Unit 1: Lesson 6 Analyzing an Interview with a Rainforest Scientist Part 1
 Grade 5: Module 2A: Unit 1: Lesson 6 Analyzing an Interview with a Rainforest Scientist Part 1 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Grade 5: Module 2A: Unit 1: Lesson 6 Analyzing an Interview with a Rainforest Scientist Part 1 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
How the Guppy Got its Spots:
 This fall I reviewed the Evobeaker labs from Simbiotic Software and considered their potential use for future Evolution 4974 courses. Simbiotic had seven labs available for review. I chose to review the
This fall I reviewed the Evobeaker labs from Simbiotic Software and considered their potential use for future Evolution 4974 courses. Simbiotic had seven labs available for review. I chose to review the
Heredity In Plants For 2nd Grade
 In Plants For 2nd Grade Free PDF ebook Download: In Plants For 2nd Grade Download or Read Online ebook heredity in plants for 2nd grade in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database I Write the letter
In Plants For 2nd Grade Free PDF ebook Download: In Plants For 2nd Grade Download or Read Online ebook heredity in plants for 2nd grade in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database I Write the letter
Critical Analysis of Evolution Grade 10
 Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark H Describe a foundation of biological evolution as the change in gene frequency of a population over time. Explain the historical and current scientific
Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark H Describe a foundation of biological evolution as the change in gene frequency of a population over time. Explain the historical and current scientific
SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE
 FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York Le REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION LIVING ENVIRONMENT Wednesday, June 19, 2002 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Directions
FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York Le REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION LIVING ENVIRONMENT Wednesday, June 19, 2002 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Directions
Program Alignment Worksheet High School
 Program Alignment Worksheet High School Publisher Name Pearson Program Title Prentice Hall Biology (Miler/Levine) 2010; Event Based Science 2005 Computer Based? Requires Internet? Target Grades 9 12 Steps
Program Alignment Worksheet High School Publisher Name Pearson Program Title Prentice Hall Biology (Miler/Levine) 2010; Event Based Science 2005 Computer Based? Requires Internet? Target Grades 9 12 Steps
GOING VIRAL. Viruses are all around us and within us. They replicate
 GOING VIRAL Using laptops, flash drives, and YouTube videos to model the structure and function of viruses Christina Crawford, Beth Beason-Abmayr, Elizabeth Eich, Jamie Scott, and Carolyn Nichol Copyright
GOING VIRAL Using laptops, flash drives, and YouTube videos to model the structure and function of viruses Christina Crawford, Beth Beason-Abmayr, Elizabeth Eich, Jamie Scott, and Carolyn Nichol Copyright
MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm
 MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm Why participate in the Science Fair? Science fair projects give students
MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm Why participate in the Science Fair? Science fair projects give students
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15
 Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments Plants Are Producers... 17 Producing a Producer... 19 The Part Plants Play...
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments Plants Are Producers... 17 Producing a Producer... 19 The Part Plants Play...
Scientific Inquiry Test Questions
 Test Questions Free PDF ebook Download: Test Questions Download or Read Online ebook scientific inquiry test questions in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Understandings about scientific inquiry
Test Questions Free PDF ebook Download: Test Questions Download or Read Online ebook scientific inquiry test questions in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Understandings about scientific inquiry
Biome I Can Statements
 Biome I Can Statements I can recognize the meanings of abbreviations. I can use dictionaries, thesauruses, glossaries, textual features (footnotes, sidebars, etc.) and technology to define and pronounce
Biome I Can Statements I can recognize the meanings of abbreviations. I can use dictionaries, thesauruses, glossaries, textual features (footnotes, sidebars, etc.) and technology to define and pronounce
What is this species called? Generation Bar Graph
 Name: Date: What is this species called? Color Count Blue Green Yellow Generation Bar Graph 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Blue Green Yellow Name: Date: What is this species called? Color Count Blue Green
Name: Date: What is this species called? Color Count Blue Green Yellow Generation Bar Graph 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Blue Green Yellow Name: Date: What is this species called? Color Count Blue Green
Evolution in Paradise
 Evolution in Paradise Engaging science lessons for middle and high school brought to you by BirdSleuth K-12 and the most extravagant birds in the world! The Evolution in Paradise lesson series is part
Evolution in Paradise Engaging science lessons for middle and high school brought to you by BirdSleuth K-12 and the most extravagant birds in the world! The Evolution in Paradise lesson series is part
Planting Seeds, Part 1: Can You Design a Fair Test?
 Planting Seeds, Part 1: Can You Design a Fair Test? In this investigation, your team will choose 2 or 3 seeds in order to design an investigation to learn something more about them. First, you will need
Planting Seeds, Part 1: Can You Design a Fair Test? In this investigation, your team will choose 2 or 3 seeds in order to design an investigation to learn something more about them. First, you will need
Unit: Human Impact Differentiated (Tiered) Task How Does Human Activity Impact Soil Erosion?
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Biological Sciences, BS and BA
 Student Learning Outcomes Assessment Summary Biological Sciences, BS and BA College of Natural Science and Mathematics AY 2012/2013 and 2013/2014 1. Assessment information collected Submitted by: Diane
Student Learning Outcomes Assessment Summary Biological Sciences, BS and BA College of Natural Science and Mathematics AY 2012/2013 and 2013/2014 1. Assessment information collected Submitted by: Diane
Create A City: An Urban Planning Exercise Students learn the process of planning a community, while reinforcing their writing and speaking skills.
 Create A City: An Urban Planning Exercise Students learn the process of planning a community, while reinforcing their writing and speaking skills. Author Gale Ekiss Grade Level 4-8 Duration 3 class periods
Create A City: An Urban Planning Exercise Students learn the process of planning a community, while reinforcing their writing and speaking skills. Author Gale Ekiss Grade Level 4-8 Duration 3 class periods
OUTLINE OF ACTIVITIES
 Exploring Plant Hormones In class, we explored a few analyses that have led to our current understanding of the roles of hormones in various plant processes. This lab is your opportunity to carry out your
Exploring Plant Hormones In class, we explored a few analyses that have led to our current understanding of the roles of hormones in various plant processes. This lab is your opportunity to carry out your
Prerequisite: General Biology 107 (UE) and 107L (UE) with a grade of C- or better. Chemistry 118 (UE) and 118L (UE) or permission of instructor.
 Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology BIOL 499-02 Fall 2017 Class time: Lectures: Tuesday, Thursday 8:30 am 9:45 am Location: Name of Faculty: Contact details: Laboratory: 2:00 pm-4:00 pm; Monday
Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology BIOL 499-02 Fall 2017 Class time: Lectures: Tuesday, Thursday 8:30 am 9:45 am Location: Name of Faculty: Contact details: Laboratory: 2:00 pm-4:00 pm; Monday
People: Past and Present
 People: Past and Present Field Trip Grade Level: 1 Process Skills: Observation Connections Enduring understanding: There are similarities and differences across cultures. Alignment to Utah Core Curriculum
People: Past and Present Field Trip Grade Level: 1 Process Skills: Observation Connections Enduring understanding: There are similarities and differences across cultures. Alignment to Utah Core Curriculum
Case study Norway case 1
 Case study Norway case 1 School : B (primary school) Theme: Science microorganisms Dates of lessons: March 26-27 th 2015 Age of students: 10-11 (grade 5) Data sources: Pre- and post-interview with 1 teacher
Case study Norway case 1 School : B (primary school) Theme: Science microorganisms Dates of lessons: March 26-27 th 2015 Age of students: 10-11 (grade 5) Data sources: Pre- and post-interview with 1 teacher
Lab 1 - The Scientific Method
 Lab 1 - The Scientific Method As Biologists we are interested in learning more about life. Through observations of the living world we often develop questions about various phenomena occurring around us.
Lab 1 - The Scientific Method As Biologists we are interested in learning more about life. Through observations of the living world we often develop questions about various phenomena occurring around us.
DEVELOPING AN INTERACTIVE METHOD TO MAP THE STUDENT PERSPECTIVES ON EVOLUTION
 DEVELOPING AN INTERACTIVE METHOD TO MAP THE STUDENT PERSPECTIVES ON EVOLUTION Florian Koslowski and Jörg Zabel Universität Leipzig, Institut für Biologie (Leipzig Germany) florian.koslowski@uni-leipzig.de;
DEVELOPING AN INTERACTIVE METHOD TO MAP THE STUDENT PERSPECTIVES ON EVOLUTION Florian Koslowski and Jörg Zabel Universität Leipzig, Institut für Biologie (Leipzig Germany) florian.koslowski@uni-leipzig.de;
A method to teach or reinforce concepts of restriction enzymes, RFLPs, and gel electrophoresis. By: Heidi Hisrich of The Dork Side
 A method to teach or reinforce concepts of restriction enzymes, RFLPs, and gel electrophoresis. By: Heidi Hisrich of The Dork Side My students STRUGGLE with the concepts of restriction enzymes, PCR and
A method to teach or reinforce concepts of restriction enzymes, RFLPs, and gel electrophoresis. By: Heidi Hisrich of The Dork Side My students STRUGGLE with the concepts of restriction enzymes, PCR and
WHAT ARE VIRTUAL MANIPULATIVES?
 by SCOTT PIERSON AA, Community College of the Air Force, 1992 BS, Eastern Connecticut State University, 2010 A VIRTUAL MANIPULATIVES PROJECT SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR TECHNOLOGY
by SCOTT PIERSON AA, Community College of the Air Force, 1992 BS, Eastern Connecticut State University, 2010 A VIRTUAL MANIPULATIVES PROJECT SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR TECHNOLOGY
H EALTHCARE S CIENCE
 H EALTHCARE S CIENCE COURSE: UNIT: 25.552 Applications of Therapeutic Services 9.1 Overview of Human Body Structure Anatomy & Physiology Annotation: INTRODUCTION In this unit students will be able to apply
H EALTHCARE S CIENCE COURSE: UNIT: 25.552 Applications of Therapeutic Services 9.1 Overview of Human Body Structure Anatomy & Physiology Annotation: INTRODUCTION In this unit students will be able to apply
All Systems Go! Using a Systems Approach in Elementary Science
 All Systems Go! CAST November Tracey Ramirez Professional Learning Facilitator The Charles A. Dana Center What we do and how we do it The Dana Center collaborates with others locally and nationally to
All Systems Go! CAST November Tracey Ramirez Professional Learning Facilitator The Charles A. Dana Center What we do and how we do it The Dana Center collaborates with others locally and nationally to
Biology 1 General Biology, Lecture Sections: 47231, and Fall 2017
 Instructor: Rana Tayyar, Ph.D. Email: rana.tayyar@rcc.edu Website: http://websites.rcc.edu/tayyar/ Office: MTSC 320 Class Location: MTSC 401 Lecture time: Tuesday and Thursday: 2:00-3:25 PM Biology 1 General
Instructor: Rana Tayyar, Ph.D. Email: rana.tayyar@rcc.edu Website: http://websites.rcc.edu/tayyar/ Office: MTSC 320 Class Location: MTSC 401 Lecture time: Tuesday and Thursday: 2:00-3:25 PM Biology 1 General
Food Chain Cut And Paste Activities
 Cut And Paste Activities Free PDF ebook Download: Cut And Paste Activities Download or Read Online ebook food chain cut and paste activities in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database CO #3: Organise
Cut And Paste Activities Free PDF ebook Download: Cut And Paste Activities Download or Read Online ebook food chain cut and paste activities in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database CO #3: Organise
level 5 (6 SCQF credit points)
 Biology: Life on Earth (National 5) SCQF: level 5 (6 SCQF credit points) Unit code: H209 75 Unit outline The general aim of this Unit is to develop skills of scientific inquiry, investigation and analytical
Biology: Life on Earth (National 5) SCQF: level 5 (6 SCQF credit points) Unit code: H209 75 Unit outline The general aim of this Unit is to develop skills of scientific inquiry, investigation and analytical
Physical Features of Humans
 Grade 1 Science, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Physical Features of Humans Overview Number of instructional days: 11 (1 day = 20 30 minutes) Content to be learned Observe, identify, and record the external features
Grade 1 Science, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Physical Features of Humans Overview Number of instructional days: 11 (1 day = 20 30 minutes) Content to be learned Observe, identify, and record the external features
Lesson Plan Title Aquatic Ecology
 Lesson Plan Title Aquatic Ecology Name (last, first): Larson, Don Scientific Theme(s): C-2: develop an understanding of the structure, function, behavior, development, life cycles, and diversity of living
Lesson Plan Title Aquatic Ecology Name (last, first): Larson, Don Scientific Theme(s): C-2: develop an understanding of the structure, function, behavior, development, life cycles, and diversity of living
Contents. Foreword... 5
 Contents Foreword... 5 Chapter 1: Addition Within 0-10 Introduction... 6 Two Groups and a Total... 10 Learn Symbols + and =... 13 Addition Practice... 15 Which is More?... 17 Missing Items... 19 Sums with
Contents Foreword... 5 Chapter 1: Addition Within 0-10 Introduction... 6 Two Groups and a Total... 10 Learn Symbols + and =... 13 Addition Practice... 15 Which is More?... 17 Missing Items... 19 Sums with
Teaching NGSS in Elementary School Third Grade
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Teaching NGSS in Elementary School Third Grade Presented by: Ted Willard, Carla Zembal-Saul, Mary Starr, and Kathy Renfrew December 17, 2014 6:30 p.m. ET / 5:30
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Teaching NGSS in Elementary School Third Grade Presented by: Ted Willard, Carla Zembal-Saul, Mary Starr, and Kathy Renfrew December 17, 2014 6:30 p.m. ET / 5:30
Unit 14 Dangerous animals
 Unit 14 Dangerous About this unit In this unit, the pupils will look at some wild living in Africa at how to keep safe from them, at the sounds they make and at their natural habitats. The unit links with
Unit 14 Dangerous About this unit In this unit, the pupils will look at some wild living in Africa at how to keep safe from them, at the sounds they make and at their natural habitats. The unit links with
Going to School: Measuring Schooling Behaviors in GloFish
 Name Period Date Going to School: Measuring Schooling Behaviors in GloFish Objective The learner will collect data to determine if schooling behaviors are exhibited in GloFish fluorescent fish. The learner
Name Period Date Going to School: Measuring Schooling Behaviors in GloFish Objective The learner will collect data to determine if schooling behaviors are exhibited in GloFish fluorescent fish. The learner
Rendezvous with Comet Halley Next Generation of Science Standards
 Next Generation of Science Standards 5th Grade 6 th Grade 7 th Grade 8 th Grade 5-PS1-3 Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties. MS-PS1-4 Develop a model that
Next Generation of Science Standards 5th Grade 6 th Grade 7 th Grade 8 th Grade 5-PS1-3 Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties. MS-PS1-4 Develop a model that
Science Olympiad Competition Model This! Event Guidelines
 Science Olympiad Competition Model This! Event Guidelines These guidelines should assist event supervisors in preparing for and setting up the Model This! competition for Divisions B and C. Questions should
Science Olympiad Competition Model This! Event Guidelines These guidelines should assist event supervisors in preparing for and setting up the Model This! competition for Divisions B and C. Questions should
Ocean Exploration: Diving Deep into Ocean Science. Developed by: Sierra Tobiason, Lynn Fujii and Noe Taum
 Ocean Exploration: Diving Deep into Ocean Science Grade Level: Sixth Grade Developed by: Sierra Tobiason, Lynn Fujii and Noe Taum Purpose: This curriculum is designed to communicate: I. Methods scientist
Ocean Exploration: Diving Deep into Ocean Science Grade Level: Sixth Grade Developed by: Sierra Tobiason, Lynn Fujii and Noe Taum Purpose: This curriculum is designed to communicate: I. Methods scientist
Statewide Framework Document for:
 Statewide Framework Document for: 260102 Standards may be added to this document prior to submission, but may not be removed from the framework to meet state credit equivalency requirements. Performance
Statewide Framework Document for: 260102 Standards may be added to this document prior to submission, but may not be removed from the framework to meet state credit equivalency requirements. Performance
For information only, correct responses are listed in the chart below. Question Number. Correct Response
 THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK 4GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST JUNE 207 WRITTEN TEST FOR TEACHERS ONLY SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Note: All schools (public, nonpublic, and charter) administering
THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK 4GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST JUNE 207 WRITTEN TEST FOR TEACHERS ONLY SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Note: All schools (public, nonpublic, and charter) administering
The lab is designed to remind you how to work with scientific data (including dealing with uncertainty) and to review experimental design.
 Name: Partner(s): Lab #1 The Scientific Method Due 6/25 Objective The lab is designed to remind you how to work with scientific data (including dealing with uncertainty) and to review experimental design.
Name: Partner(s): Lab #1 The Scientific Method Due 6/25 Objective The lab is designed to remind you how to work with scientific data (including dealing with uncertainty) and to review experimental design.
End-of-Module Assessment Task
 Student Name Date 1 Date 2 Date 3 Topic E: Decompositions of 9 and 10 into Number Pairs Topic E Rubric Score: Time Elapsed: Topic F Topic G Topic H Materials: (S) Personal white board, number bond mat,
Student Name Date 1 Date 2 Date 3 Topic E: Decompositions of 9 and 10 into Number Pairs Topic E Rubric Score: Time Elapsed: Topic F Topic G Topic H Materials: (S) Personal white board, number bond mat,
Grade 3 Science Life Unit (3.L.2)
 Grade 3 Science Life Unit (3.L.2) Decision 1: What will students learn in this unit? Standards Addressed: Science 3.L.2 Understand how plants survive in their environments. Ask and answer questions to
Grade 3 Science Life Unit (3.L.2) Decision 1: What will students learn in this unit? Standards Addressed: Science 3.L.2 Understand how plants survive in their environments. Ask and answer questions to
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Trophies Grade 5
 Unit 6/Week 2 Title: The Golden Lion Tamarin Comes Home Suggested Time: 5 days (45 minutes per day) Common Core ELA Standards: RI.5.1, RI.5.3, RL.5.4, RI.5.8; RF.5.3, RF.5.4; W.5.2, W.5.4, W.5.9; SL.5.1,
Unit 6/Week 2 Title: The Golden Lion Tamarin Comes Home Suggested Time: 5 days (45 minutes per day) Common Core ELA Standards: RI.5.1, RI.5.3, RL.5.4, RI.5.8; RF.5.3, RF.5.4; W.5.2, W.5.4, W.5.9; SL.5.1,
Facing our Fears: Reading and Writing about Characters in Literary Text
 Facing our Fears: Reading and Writing about Characters in Literary Text by Barbara Goggans Students in 6th grade have been reading and analyzing characters in short stories such as "The Ravine," by Graham
Facing our Fears: Reading and Writing about Characters in Literary Text by Barbara Goggans Students in 6th grade have been reading and analyzing characters in short stories such as "The Ravine," by Graham
First and Last Name School District School Name School City, State
 Unit Plan - Fractions Unit Author First and Last Name School District School Name School City, State Allison Cooper (King) Putnam County Rock Branch Elementary School Rock Branch, WV Unit Overview Unit
Unit Plan - Fractions Unit Author First and Last Name School District School Name School City, State Allison Cooper (King) Putnam County Rock Branch Elementary School Rock Branch, WV Unit Overview Unit
Timeline. Recommendations
 Introduction Advanced Placement Course Credit Alignment Recommendations In 2007, the State of Ohio Legislature passed legislation mandating the Board of Regents to recommend and the Chancellor to adopt
Introduction Advanced Placement Course Credit Alignment Recommendations In 2007, the State of Ohio Legislature passed legislation mandating the Board of Regents to recommend and the Chancellor to adopt
TEACHING Simple Tools Set II
 TEACHING GUIDE TEACHING Simple Tools Set II Kindergarten Reading Level ISBN-10: 0-8225-6880-2 Green ISBN-13: 978-0-8225-6880-3 2 TEACHING SIMPLE TOOLS SET II Standards Science Mathematics Language Arts
TEACHING GUIDE TEACHING Simple Tools Set II Kindergarten Reading Level ISBN-10: 0-8225-6880-2 Green ISBN-13: 978-0-8225-6880-3 2 TEACHING SIMPLE TOOLS SET II Standards Science Mathematics Language Arts
Maximizing Learning Through Course Alignment and Experience with Different Types of Knowledge
 Innov High Educ (2009) 34:93 103 DOI 10.1007/s10755-009-9095-2 Maximizing Learning Through Course Alignment and Experience with Different Types of Knowledge Phyllis Blumberg Published online: 3 February
Innov High Educ (2009) 34:93 103 DOI 10.1007/s10755-009-9095-2 Maximizing Learning Through Course Alignment and Experience with Different Types of Knowledge Phyllis Blumberg Published online: 3 February
Mongoose On The Loose/ Larry Luxner/ Created by SAP District
 Unit 2 /Week 2 Title: Mongoose on the Loose Suggested Time: 3 days (45 minutes per day) Common Core ELA Standards: RI.7.1, RI.7.2, RI.7.3; W.7.2, W.7.4, W.7.7, W.7.8, W.7.9; SL.7.1, SL.7.3, SL.7.4, SL.7.5;
Unit 2 /Week 2 Title: Mongoose on the Loose Suggested Time: 3 days (45 minutes per day) Common Core ELA Standards: RI.7.1, RI.7.2, RI.7.3; W.7.2, W.7.4, W.7.7, W.7.8, W.7.9; SL.7.1, SL.7.3, SL.7.4, SL.7.5;
Introduction to Forensics: Preventing Fires in the First Place. A Distance Learning Program Presented by the FASNY Museum of Firefighting
 Introduction to Forensics: A Distance Learning Program Presented by the FASNY Museum of Firefighting Educators Overview Introduction to Forensics This Distance Learning Program is a part of the education
Introduction to Forensics: A Distance Learning Program Presented by the FASNY Museum of Firefighting Educators Overview Introduction to Forensics This Distance Learning Program is a part of the education
CHAPTER V IMPLEMENTATION OF A LEARNING CONTRACT AND THE MODIFICATIONS TO THE ACTIVITIES Instructional Space The atmosphere created by the interaction
 CHAPTER V IMPLEMENTATION OF A LEARNING CONTRACT AND THE MODIFICATIONS TO THE ACTIVITIES Instructional Space The atmosphere created by the interaction of the physical organization of space and the students
CHAPTER V IMPLEMENTATION OF A LEARNING CONTRACT AND THE MODIFICATIONS TO THE ACTIVITIES Instructional Space The atmosphere created by the interaction of the physical organization of space and the students
Statistical Analysis of Climate Change, Renewable Energies, and Sustainability An Independent Investigation for Introduction to Statistics
 5/22/2012 Statistical Analysis of Climate Change, Renewable Energies, and Sustainability An Independent Investigation for Introduction to Statistics College of Menominee Nation & University of Wisconsin
5/22/2012 Statistical Analysis of Climate Change, Renewable Energies, and Sustainability An Independent Investigation for Introduction to Statistics College of Menominee Nation & University of Wisconsin
Text: envisionmath by Scott Foresman Addison Wesley. Course Description
 Ms. Burr 4B Mrs. Hession 4A Math Syllabus 4A & 4B Text: envisionmath by Scott Foresman Addison Wesley In fourth grade we will learn and develop in the acquisition of different mathematical operations while
Ms. Burr 4B Mrs. Hession 4A Math Syllabus 4A & 4B Text: envisionmath by Scott Foresman Addison Wesley In fourth grade we will learn and develop in the acquisition of different mathematical operations while
SOCIAL STUDIES GRADE 1. Clear Learning Targets Office of Teaching and Learning Curriculum Division FAMILIES NOW AND LONG AGO, NEAR AND FAR
 SOCIAL STUDIES FAMILIES NOW AND LONG AGO, NEAR AND FAR GRADE 1 Clear Learning Targets 2015-2016 Aligned with Ohio s Learning Standards for Social Studies Office of Teaching and Learning Curriculum Division
SOCIAL STUDIES FAMILIES NOW AND LONG AGO, NEAR AND FAR GRADE 1 Clear Learning Targets 2015-2016 Aligned with Ohio s Learning Standards for Social Studies Office of Teaching and Learning Curriculum Division
Indiana Collaborative for Project Based Learning. PBL Certification Process
 Indiana Collaborative for Project Based Learning ICPBL Certification mission is to PBL Certification Process ICPBL Processing Center c/o CELL 1400 East Hanna Avenue Indianapolis, IN 46227 (317) 791-5702
Indiana Collaborative for Project Based Learning ICPBL Certification mission is to PBL Certification Process ICPBL Processing Center c/o CELL 1400 East Hanna Avenue Indianapolis, IN 46227 (317) 791-5702
Table of Contents. Introduction Choral Reading How to Use This Book...5. Cloze Activities Correlation to TESOL Standards...
 Table of Contents Introduction.... 4 How to Use This Book.....................5 Correlation to TESOL Standards... 6 ESL Terms.... 8 Levels of English Language Proficiency... 9 The Four Language Domains.............
Table of Contents Introduction.... 4 How to Use This Book.....................5 Correlation to TESOL Standards... 6 ESL Terms.... 8 Levels of English Language Proficiency... 9 The Four Language Domains.............
Extraordinary Eggs (Life Cycle of Animals)
 General Information Extraordinary Eggs (Life Cycle of Animals) Class: CI-5055 Subject: Science Lesson Title: Extraordinary Eggs (Life Cycle of Animals) Grade Level: Second Grade Purpose The purpose of
General Information Extraordinary Eggs (Life Cycle of Animals) Class: CI-5055 Subject: Science Lesson Title: Extraordinary Eggs (Life Cycle of Animals) Grade Level: Second Grade Purpose The purpose of
Person Centered Positive Behavior Support Plan (PC PBS) Report Scoring Criteria & Checklist (Rev ) P. 1 of 8
 Scoring Criteria & Checklist (Rev. 3 5 07) P. 1 of 8 Name: Case Name: Case #: Rater: Date: Critical Features Note: The plan needs to meet all of the critical features listed below, and needs to obtain
Scoring Criteria & Checklist (Rev. 3 5 07) P. 1 of 8 Name: Case Name: Case #: Rater: Date: Critical Features Note: The plan needs to meet all of the critical features listed below, and needs to obtain
Evolution of Symbolisation in Chimpanzees and Neural Nets
 Evolution of Symbolisation in Chimpanzees and Neural Nets Angelo Cangelosi Centre for Neural and Adaptive Systems University of Plymouth (UK) a.cangelosi@plymouth.ac.uk Introduction Animal communication
Evolution of Symbolisation in Chimpanzees and Neural Nets Angelo Cangelosi Centre for Neural and Adaptive Systems University of Plymouth (UK) a.cangelosi@plymouth.ac.uk Introduction Animal communication
Lecturing Module
 Lecturing: What, why and when www.facultydevelopment.ca Lecturing Module What is lecturing? Lecturing is the most common and established method of teaching at universities around the world. The traditional
Lecturing: What, why and when www.facultydevelopment.ca Lecturing Module What is lecturing? Lecturing is the most common and established method of teaching at universities around the world. The traditional
Mathematics Scoring Guide for Sample Test 2005
 Mathematics Scoring Guide for Sample Test 2005 Grade 4 Contents Strand and Performance Indicator Map with Answer Key...................... 2 Holistic Rubrics.......................................................
Mathematics Scoring Guide for Sample Test 2005 Grade 4 Contents Strand and Performance Indicator Map with Answer Key...................... 2 Holistic Rubrics.......................................................
WebQuest - Student Web Page
 WebQuest - Student Web Page On the Home Front WW2 A WebQuest for Grade 9 American History Allyson Ayres - May 15, 2014 Children pointing at movie poster for Uncle Sam at Work at the Auditorium Theater
WebQuest - Student Web Page On the Home Front WW2 A WebQuest for Grade 9 American History Allyson Ayres - May 15, 2014 Children pointing at movie poster for Uncle Sam at Work at the Auditorium Theater
It s News to Me! Teaching with Colorado s Historic Newspaper Collection Model Lesson Format
 It s News to Me! Teaching with Colorado s Historic Newspaper Collection Model Lesson Format Lesson Title: Colorado Irrigation Methods and Water Rights Disputes in the Late 1800s and Early 1900s Subject(s)
It s News to Me! Teaching with Colorado s Historic Newspaper Collection Model Lesson Format Lesson Title: Colorado Irrigation Methods and Water Rights Disputes in the Late 1800s and Early 1900s Subject(s)
Instructional Supports for Common Core and Beyond: FORMATIVE ASSESMENT
 Instructional Supports for Common Core and Beyond: FORMATIVE ASSESMENT Defining Date Guiding Question: Why is it important for everyone to have a common understanding of data and how they are used? Importance
Instructional Supports for Common Core and Beyond: FORMATIVE ASSESMENT Defining Date Guiding Question: Why is it important for everyone to have a common understanding of data and how they are used? Importance
George Mason University Graduate School of Education Program: Special Education
 George Mason University Graduate School of Education Program: Special Education 1 EDSE 590: Research Methods in Special Education Instructor: Margo A. Mastropieri, Ph.D. Assistant: Judy Ericksen Section
George Mason University Graduate School of Education Program: Special Education 1 EDSE 590: Research Methods in Special Education Instructor: Margo A. Mastropieri, Ph.D. Assistant: Judy Ericksen Section
Learning Fields Unit and Lesson Plans
 Learning Fields Unit and Lesson Plans UNIT INTRODUCTION Learning Fields seeks to connect people with agriculture and rural life today. The lessons in this unit will help students to understand how agriculture
Learning Fields Unit and Lesson Plans UNIT INTRODUCTION Learning Fields seeks to connect people with agriculture and rural life today. The lessons in this unit will help students to understand how agriculture
Grade 4. Common Core Adoption Process. (Unpacked Standards)
 Grade 4 Common Core Adoption Process (Unpacked Standards) Grade 4 Reading: Literature RL.4.1 Refer to details and examples in a text when explaining what the text says explicitly and when drawing inferences
Grade 4 Common Core Adoption Process (Unpacked Standards) Grade 4 Reading: Literature RL.4.1 Refer to details and examples in a text when explaining what the text says explicitly and when drawing inferences
Summarize The Main Ideas In Nonfiction Text
 Summarize The Main Ideas In Free PDF ebook Download: Summarize The Main Ideas In Download or Read Online ebook summarize the main ideas in nonfiction text in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database
Summarize The Main Ideas In Free PDF ebook Download: Summarize The Main Ideas In Download or Read Online ebook summarize the main ideas in nonfiction text in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database
ABSTRACT. A major goal of human genetics is the discovery and validation of genetic polymorphisms
 ABSTRACT DEODHAR, SUSHAMNA DEODHAR. Using Grammatical Evolution Decision Trees for Detecting Gene-Gene Interactions in Genetic Epidemiology. (Under the direction of Dr. Alison Motsinger-Reif.) A major
ABSTRACT DEODHAR, SUSHAMNA DEODHAR. Using Grammatical Evolution Decision Trees for Detecting Gene-Gene Interactions in Genetic Epidemiology. (Under the direction of Dr. Alison Motsinger-Reif.) A major
Handouts and Resources
 Handouts and Resources 6 th Grade MELD Culminating Task: Compare the information presented in the articles and interview regarding the effect or purpose of activist groups in influencing society. You will
Handouts and Resources 6 th Grade MELD Culminating Task: Compare the information presented in the articles and interview regarding the effect or purpose of activist groups in influencing society. You will
Stacks Teacher notes. Activity description. Suitability. Time. AMP resources. Equipment. Key mathematical language. Key processes
 Stacks Teacher notes Activity description (Interactive not shown on this sheet.) Pupils start by exploring the patterns generated by moving counters between two stacks according to a fixed rule, doubling
Stacks Teacher notes Activity description (Interactive not shown on this sheet.) Pupils start by exploring the patterns generated by moving counters between two stacks according to a fixed rule, doubling
Smiley Face Self Assessment Template
 Smiley Face Self Assessment Template Free PDF ebook Download: Smiley Face Self Assessment Template Download or Read Online ebook smiley face self assessment template in PDF Format From The Best User Guide
Smiley Face Self Assessment Template Free PDF ebook Download: Smiley Face Self Assessment Template Download or Read Online ebook smiley face self assessment template in PDF Format From The Best User Guide
We will use the text, Lehninger: Principles of Biochemistry, as the primary supplement to topics presented in lecture.
 Biochemical Pathways Biology 361, Spring 2014 Instructor: Office: Office Time: Email: Lecture: Text: Lecture Notes: Course Website: Gregory Johnson, Ph.D. Thompson 257d W, 10:00-11:30 and 1:00-2:00 pm
Biochemical Pathways Biology 361, Spring 2014 Instructor: Office: Office Time: Email: Lecture: Text: Lecture Notes: Course Website: Gregory Johnson, Ph.D. Thompson 257d W, 10:00-11:30 and 1:00-2:00 pm
2016/17 Big History: Sample Semester-Long Course Plan Content Pacing Guide
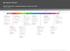 2016/17 Big History: Sample Semester-Long Course Plan Content Pacing Guide August September October November December UNIT 1 UNIT 2 UNIT 3 UNIT 4 UNIT 5 UNIT 6 UNIT 7 UNIT 8 UNIT 9 UNIT 10 What Is Big
2016/17 Big History: Sample Semester-Long Course Plan Content Pacing Guide August September October November December UNIT 1 UNIT 2 UNIT 3 UNIT 4 UNIT 5 UNIT 6 UNIT 7 UNIT 8 UNIT 9 UNIT 10 What Is Big
1. READING ENGAGEMENT 2. ORAL READING FLUENCY
 Teacher Observation Guide Animals Can Help Level 28, Page 1 Name/Date Teacher/Grade Scores: Reading Engagement /8 Oral Reading Fluency /16 Comprehension /28 Independent Range: 6 7 11 14 19 25 Book Selection
Teacher Observation Guide Animals Can Help Level 28, Page 1 Name/Date Teacher/Grade Scores: Reading Engagement /8 Oral Reading Fluency /16 Comprehension /28 Independent Range: 6 7 11 14 19 25 Book Selection
NCSC Alternate Assessments and Instructional Materials Based on Common Core State Standards
 NCSC Alternate Assessments and Instructional Materials Based on Common Core State Standards Ricki Sabia, JD NCSC Parent Training and Technical Assistance Specialist ricki.sabia@uky.edu Background Alternate
NCSC Alternate Assessments and Instructional Materials Based on Common Core State Standards Ricki Sabia, JD NCSC Parent Training and Technical Assistance Specialist ricki.sabia@uky.edu Background Alternate
Stakeholder Debate: Wind Energy
 Activity ENGAGE For Educator Stakeholder Debate: Wind Energy How do stakeholder interests determine which specific resources a community will use? For the complete activity with media resources, visit:
Activity ENGAGE For Educator Stakeholder Debate: Wind Energy How do stakeholder interests determine which specific resources a community will use? For the complete activity with media resources, visit:
BIOS 104 Biology for Non-Science Majors Spring 2016 CRN Course Syllabus
 BIOS 104 Biology for Non-Science Majors Spring 2016 CRN 21348 Course Syllabus INTRODUCTION This course is an introductory course in the biological sciences focusing on cellular and organismal biology as
BIOS 104 Biology for Non-Science Majors Spring 2016 CRN 21348 Course Syllabus INTRODUCTION This course is an introductory course in the biological sciences focusing on cellular and organismal biology as
(I couldn t find a Smartie Book) NEW Grade 5/6 Mathematics: (Number, Statistics and Probability) Title Smartie Mathematics
 (I couldn t find a Smartie Book) NEW Grade 5/6 Mathematics: (Number, Statistics and Probability) Title Smartie Mathematics Lesson/ Unit Description Questions: How many Smarties are in a box? Is it the
(I couldn t find a Smartie Book) NEW Grade 5/6 Mathematics: (Number, Statistics and Probability) Title Smartie Mathematics Lesson/ Unit Description Questions: How many Smarties are in a box? Is it the
Word Segmentation of Off-line Handwritten Documents
 Word Segmentation of Off-line Handwritten Documents Chen Huang and Sargur N. Srihari {chuang5, srihari}@cedar.buffalo.edu Center of Excellence for Document Analysis and Recognition (CEDAR), Department
Word Segmentation of Off-line Handwritten Documents Chen Huang and Sargur N. Srihari {chuang5, srihari}@cedar.buffalo.edu Center of Excellence for Document Analysis and Recognition (CEDAR), Department
1 Copyright Texas Education Agency, All rights reserved.
 Lesson Plan-Diversity at Work Course Title: Business Information Management II Session Title: Diversity at Work Performance Objective: Upon completion of this lesson, students will understand diversity
Lesson Plan-Diversity at Work Course Title: Business Information Management II Session Title: Diversity at Work Performance Objective: Upon completion of this lesson, students will understand diversity
Abc Of Science 8th Grade
 Abc Of 8th Grade Free PDF ebook Download: Abc Of 8th Grade Download or Read Online ebook abc of science 8th grade in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database In addition, some courses such as 7th grade
Abc Of 8th Grade Free PDF ebook Download: Abc Of 8th Grade Download or Read Online ebook abc of science 8th grade in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database In addition, some courses such as 7th grade
STANDARDS AND RUBRICS FOR SCHOOL IMPROVEMENT 2005 REVISED EDITION
 Arizona Department of Education Tom Horne, Superintendent of Public Instruction STANDARDS AND RUBRICS FOR SCHOOL IMPROVEMENT 5 REVISED EDITION Arizona Department of Education School Effectiveness Division
Arizona Department of Education Tom Horne, Superintendent of Public Instruction STANDARDS AND RUBRICS FOR SCHOOL IMPROVEMENT 5 REVISED EDITION Arizona Department of Education School Effectiveness Division
Fourth Grade. Reporting Student Progress. Libertyville School District 70. Fourth Grade
 Fourth Grade Libertyville School District 70 Reporting Student Progress Fourth Grade A Message to Parents/Guardians: Libertyville Elementary District 70 teachers of students in kindergarten-5 utilize a
Fourth Grade Libertyville School District 70 Reporting Student Progress Fourth Grade A Message to Parents/Guardians: Libertyville Elementary District 70 teachers of students in kindergarten-5 utilize a
LA1 - High School English Language Development 1 Curriculum Essentials Document
 LA1 - High School English Language Development 1 Curriculum Essentials Document Boulder Valley School District Department of Curriculum and Instruction April 2012 Access for All Colorado English Language
LA1 - High School English Language Development 1 Curriculum Essentials Document Boulder Valley School District Department of Curriculum and Instruction April 2012 Access for All Colorado English Language
EGRHS Course Fair. Science & Math AP & IB Courses
 EGRHS Course Fair Science & Math AP & IB Courses Science Courses: AP Physics IB Physics SL IB Physics HL AP Biology IB Biology HL AP Physics Course Description Course Description AP Physics C (Mechanics)
EGRHS Course Fair Science & Math AP & IB Courses Science Courses: AP Physics IB Physics SL IB Physics HL AP Biology IB Biology HL AP Physics Course Description Course Description AP Physics C (Mechanics)
4th Grade Science Test Ecosystems
 4th Grade Science Free PDF ebook Download: 4th Grade Science Download or Read Online ebook 4th grade science test ecosystems in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database 4th Grade--LIFE SCIENCE. Unit
4th Grade Science Free PDF ebook Download: 4th Grade Science Download or Read Online ebook 4th grade science test ecosystems in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database 4th Grade--LIFE SCIENCE. Unit
Inquiry and scientific explanations: Helping students use evidence and reasoning. Katherine L. McNeill Boston College
 Inquiry and scientific explanations: Helping students use evidence and reasoning Katherine L. McNeill Boston College Joseph S. Krajcik University of Michigan contact info: Lynch School of Education, Boston
Inquiry and scientific explanations: Helping students use evidence and reasoning Katherine L. McNeill Boston College Joseph S. Krajcik University of Michigan contact info: Lynch School of Education, Boston
Becoming Herodotus. Objectives: Task Description: Background or Instructional Context/Curriculum Connections: Time:
 Becoming Herodotus Content Area: : Visual Arts Grades: 9-12 Advanced Task Description: Students are to be introduced to the life and histories of Herodotus, giving specific attention to his recollections
Becoming Herodotus Content Area: : Visual Arts Grades: 9-12 Advanced Task Description: Students are to be introduced to the life and histories of Herodotus, giving specific attention to his recollections
Mapping the Assets of Your Community:
 Mapping the Assets of Your Community: A Key component for Building Local Capacity Objectives 1. To compare and contrast the needs assessment and community asset mapping approaches for addressing local
Mapping the Assets of Your Community: A Key component for Building Local Capacity Objectives 1. To compare and contrast the needs assessment and community asset mapping approaches for addressing local
2015 Educator Workshops
 2015 Educator Workshops PROJECT LEARNING TREE AND PROJECT WET Saturday, April 25, 2015 9:00 am - 4:00 pm John Heinz National Wildlife Refuge 8601 Lindbergh Boulevard Philadelphia, PA 19153 Presented by
2015 Educator Workshops PROJECT LEARNING TREE AND PROJECT WET Saturday, April 25, 2015 9:00 am - 4:00 pm John Heinz National Wildlife Refuge 8601 Lindbergh Boulevard Philadelphia, PA 19153 Presented by
Rubric For California Mission Project
 For California Free PDF ebook Download: For Project Download or Read Online ebook rubric for california mission project in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Report 4th grade project. Each student
For California Free PDF ebook Download: For Project Download or Read Online ebook rubric for california mission project in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Report 4th grade project. Each student
ASTEN Fellowship report Priscilla Gaff Program Coordinator Life Science
 ASTEN Fellowship report 2012 Priscilla Gaff Program Coordinator Life Science ASTEN FELLOWSHIP REPORT 2012 In March 2012, I was fortunate to receive an ASTEN Professional Development Fellowship to visit
ASTEN Fellowship report 2012 Priscilla Gaff Program Coordinator Life Science ASTEN FELLOWSHIP REPORT 2012 In March 2012, I was fortunate to receive an ASTEN Professional Development Fellowship to visit
