TASKS DESIGN: A CHALLENGE FOR LANGUAGE TEACHERS
|
|
|
- Nora Francis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TASKS DESIGN: A CHALLENGE FOR LANGUAGE TEACHERS Ramiaida Darmi 1 *, Haliza Harun 2, Rosni Samah 3, Fariza Puteh-Behak 4, Noor Saazai Mat Saad 5, Suraini Mohd Ali 6 1 Dr., Universiti Sains Islam Malaysia, MALAYSIA, ramiaida@usim.edu.my 2 Dr., Universiti Sains Islam Malaysia, MALAYSIA, haliza@usim.edu.my 3 Assoc. Prof. Dr., Universiti Sains Islam Malaysia, MALAYSIA, rosni@usim.edu.my 4 Dr., Universiti Sains Islam Malaysia, MALAYSIA, fariza@usim.edu.my 5 Dr., Universiti Sains Islam Malaysia, MALAYSIA, noorsaazai@usim.edu.my 6 Dr., Universiti Sains Islam Malaysia, MALAYSIA, suraini@usim.edu.my *Corresponding author Abstract Creating tasks may sound simple, however, it is one of the challenging jobs for language teachers. In teaching language, teachers need to consider many things such as learners social background, learner s language proficiency, learners ability, learners attitude and many more. Thus, creating tasks can be a challenge for them. Cummins (1981) suggests 2 main elements in designing materials contextual relevance and cognitive difficulty which are formed into a matrix to show four levels to consider in tasks design. Based on Cummins matrix, tasks can be easy for some, and difficult for some. One task may not suit all learners, and thus make task design a challenge for language teachers. This study looks at the use of tasks, developed based on Cummins matrix, for low proficiency English language learners. Five types of tasks are used, and learners views are gathered to understand what they think of the tasks. The aim of the study is to explore learners perceptions towards tasks prepared for an English language class, and aligning them with the teacher s understanding of the tasks. Fourteen learners were involved in the study. Using qualitative approach, data is gathered through interviews, which are then transcribed verbatim, and analysed using thematic analysis. Results show that learners have different views of tasks, which may be due to many factors within learners experience and knowledge. This shows that although learners are of the same proficiency level, the difficulty of tasks may not be equal for all learners as it is affected by the contextual relevance of the tasks to learners, as well as the cognitive level of learners in their ability to perform the tasks. Therefore, understanding learners is important for teachers in planning suitable tasks for their learners. By doing this, learners will have more enjoyment in language learning, and able to associate tasks more to their life. Keywords: Tasks, contextual relevance, cognitive difficulty, language learning. ISBN:
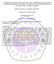
2 1 INTRODUCTION Tasks design is a part of language teaching and learning. Some people may say that creating tasks is simple, yet, it may be challenging for some language teachers. As each learner is different in his own ways, the language teacher will need to consider many things to suit the learner s differences. Studies on the use of tasks in second language (L2) classroom has been widely researched in the area of second language (L2) teaching. As task-based syllabus aims to facilitate L2 learning (Richards and Rodgers, 2001), it is actively incorporated into language classrooms. According to Richards and Rodgers (2001), it is best to use pedagogical tasks in the classroom as the activities have non-linguistic goal, clear outcome, use any of the four language skills, and convey meaning that reflects real-world language use (Willis & Willis, 2007). According to Castillo (2008), classroom tasks and materials should be designed to resemble actual use of language for communication, and thus teachers should propose tasks and texts that activate previous knowledge and provide enough background information in order for learners to be able to grasp the key concepts in the tasks. 1.1 Task-based language teaching According to Ellis (2003) and Willis (1996), task-based language teaching (TBLT) is a current approach to L2 teaching that represents a strong version of Communicative Language Teaching. It started in the 1970s when scholars argued that language interaction should teach both grammar and meaning (Skehan, 2003). Ellis (2009) states that task-based approach is beneficial as it offers the opportunity for natural learning inside the classroom, emphasizes meaning over form, provides learners a rich input of target language, is intrinsically motivating and learner-centered, develops communication, and can be used with other approach. According to Ellis (2009), in TBLT, language learning will progress most successfully if teaching aims to create contexts that consider learners natural language learning ability. This is supported by Samuda and Bygate (2008), who suggest classroom learning to be connected to students personal experiences, or classroom teaching to be authentic. Because tasks focus on meaning, there is a need for learners to convey information, express an opinion or infer meaning, using their own linguistic and nonlinguistic knowledge in order to complete the activity (Ellis, 2009). According to Carless (2008), task-based approaches involve a complex teacher role. The tasks must suit the proficiency levels of the students and result in appropriate L2 use (Ellis, 2009). Therefore, teachers need a clear understanding of what a task is, and be involved in the development of the task materials. Studies on tasks have explored a variety of areas such as from a theoretical (language processing) and a methodological (instructional design) perspective (Bygate, Skehan & Swain, 2001; Ellis, 2000; Foster & Skehan, 1996; Robinson, 2001; Skehan & Foster, 1997, 1999; Swain & Lapkin, 2000; Willis, 1996). However, there are few studies that investigate how tasks need to be designed. According to Castillo (2008), to ensure learners achieve successful L2 learning, teachers should consider learners background knowledge and include it in the task. This means that teachers should start language teaching by activating learners background knowledge first. To do this, teachers should not neglect what learners have in their minds so that L2 learning can become a memorable experience for L2 learners (Darmi, 2014). To add, Castillo (2008) considers context and cognitive demands as important elements for teachers to consider when choosing the types of tasks for learners. 1.2 Contextual support and cognitive demands of tasks According to Cummins (1981, 2000), there is a relationship between contextual support and cognitive demands in communicative tasks. This is differentiated by the extent to which the meaning being communicated is supported by contextual or interpersonal cues (such as gestures, facial expressions, and intonation present in face-to-face interaction) or is dependent on the amount of information that must be processed immediately through the communicative context (Cummins, 2000, 2001, 2008). Cummins (2008) refers to context as what we bring to a task (internal), and the range of supports that may be incorporated in the task itself (external). Context-embedded communication is more typical of the everyday world outside the classroom, but context-reduced communication reflects tasks with many linguistic demands of the classroom (Cummins, 2008; Darmi, 2014). Cognitively undemanding tasks consist of words that are familiar to learners, and thus require little active cognitive involvement; while cognitively demanding tasks are very open ended and subjective, and require learners to process information (Cummins, 2008; Darmi, 2014). In cognitively demanding tasks, L2 learners are expected to be fluent in their academic language. They should be able to express and support opinions, formulate hypotheses, propose different solutions, describe, generalize, ask and answer informational and clarifying questions, classify, relate information, compare and contrast, explain cause and effect, interpret, infer, draw conclusions, summarize, evaluate, critique, justify ISBN:
3 analyze, and persuade (Dutro & Moran, 2003; Williams, 2001; Zwiers, 2008). This means that they are able to use academic language to describe higher order thinking, complexity, and abstraction as clearly as possible. Cummins (1981) proposed a model (Figure 1) for designing tasks based on the range of contextual support and degree of cognitive involvement in communicative activities. Figure 1: Range of contextual support and degree of cognitive involvement in The model is represented in four quadrants. Quadrant A involves tasks that reflect face-to-face social conversation i.e. greeting someone. Quadrant B are tasks that require learners to process information based on the contextual support provided i.e. comparing and contrasting, seeking solutions or explaining and justifying. Quadrant C involves tasks that have less contextual support but do not involve learners in too much information processing i.e. listening to a story, copying information from a text and retelling a story. Quadrant D activities require learners to master academic functions (Cummins, 2000) by carrying out tasks that are minimally supported by familiar contextual or interpersonal cues, and require high levels of cognitive involvement for successful task completion i.e. arguing a case, interpreting evidence and evaluating and analyzing critically. According to Cummins (2001), because some context-embedded activities are clearly just as cognitivelydemanding as context-reduced activities, it is important to distinguish the dimensions of contextualembeddedness and cognitive demand. Learners may have different interpretation of what is contextembedded or cognitively demanding in the tasks, due to the differences in internal attributes such as prior knowledge or interest (Cummins, 1984). The more students know and understand, the easier it is for them to make sense of academic language, since there is internal support for understanding the messages (Garcia, 2009). This is also important for the language teachers as it would help them in designing tasks that are suitable for their learners. 2 THE STUDY Many learners nowadays seem to have limited enjoyment in their learning as many tasks used in the classroom are unsuitable for them. Thus, it is important for teachers to understand the tasks that they design to be used in their lessons. As teachers, they have to be up-to-date with changes in pedagogy, and also their learners needs. The aim of this paper is to explore learners perceptions towards the tasks prepared in the English language class, and aligning them with the teacher s understanding of the tasks. The data from this study is taken from a bigger study that used quantitative data to look at learners perceptions on task difficulty in task-based lessons (Darmi, 2016). This study, however, reports part of the qualitative data and links it to teacher s understanding of the tasks. 3 METHODOLOGY Using a qualitative approach, the study involved fourteen learners who participated in an English language class designed for the study, and the researcher as the teacher in the class. Learners worked in pairs in completing the twenty tasks prepared. The tasks are of different task types jigsaw task (JT), information gap task (IG), problem solving task (PS), decision making task (DM) and opinion exchange task (OE) each constructed in relation to Cummins (1981) context and cognitive dimensions. Learners were involved in semi-structured pair interviews, which were conducted at the end of the English language class of the study. The interview aimed at gathering learners perceptions of the tasks used in the language class. This was categorized into the easiest task and the most difficult task, as the researcher ISBN:
4 wanted to understand how learners identification of the tasks relate to teacher s understanding of the tasks. This would hopefully provide insights into the variation in contextual support and cognitive demands of the tasks prepared. Interviews were then transcribed verbatim, and analysed using thematic analysis. 4 RESULTS The data on learners perceptions of task difficulty is discussed in relation to teacher s understanding of tasks. Learners responses in relation to the difficulty or ease of the tasks were categorized according to their perceptions of (1) contextual support and (2) cognitive demands. The following section is divided into two parts: the first part deals with individual learners perceptions of the easiest tasks, and the second part deals with individual learners perceptions of the most difficult tasks. 4.1 The easiest tasks When designing the tasks for the English language class, the teacher had intended the first task (out of the four individual tasks in each task type) to be the easiest. However, result from the interviews show that not all pairs shared the teacher s view of the easiest tasks. Two pairs agreed with the teacher for Jigsaw Task (JT), and three pairs agreed with the teacher for Decision Making (DM) tasks. However, for Opinion Exchange (OE) and Problem Solving (PS) tasks, only a few pairs of learners also viewed the first tasks as the easiest tasks. This disagreement between learners perceptions of the easiest tasks in the interviews was also reflected in some other pairs e.g. Pairs B, D and G for task 4 in Information Gap (IG) task, and task 3 for Problem Solving (PS) task. This shows that there are differences not only between learners and the teacher, but also among learners themselves in their view of the easiest tasks. This provides evidence of learner variation in their perceptions of the tasks which may be related to the contextual and cognitive factors involved in the tasks. Further data from the interviews show the reasons for learners choice of the easiest task. A majority of learners mentioned that they regarded the task as the easiest task due to its high-context. This means that learners were able to associate the tasks to their background knowledge. A few learners regarded the task as the easiest as the cognitive challenge was low. When tasks are regarded as high-context, learners related them to their everyday life, which is the most frequent association for the easiest tasks. Other associations of the easiest tasks are content familiarity and pictures. Some of the interview excerpts to support these findings are provided below. ISBN:
5 The findings show that pairs perceptions of the easiest tasks fit closely with Cummins (1981) contextembedded dimension. However, the data gathered was limited to show a strong link to their perceptions to the low-cognitive challenge of tasks. 4.2 The most difficult tasks Compared to the identification of the easiest task, the teacher designed task 3 and 4 of different task types as the most difficult tasks. However, similar to the easiest tasks discussed above, the learners view of the most difficult tasks did not fully align with the teacher s. From the questions asked in the interviews, I was able to gather learners reasons for their view of the most difficult task, which allowed me to relate to Cummins (2008) claim about the influences of task difficulty in language learning. In designing these tasks, the teacher assumed tasks as the most difficult when there was low-contextual support and high-cognitive demand (Darmi, 2013). In designing the tasks, the teacher intended one task from each task type to be the most difficult tasks, either task 3 or task 4. Overall, learners viewed thirteen tasks as the most difficult. For Information Gap (IG) task, most learners viewed task 2 as the most difficult. However, there was less consensus among learners for the other four task types. Although one task from each task type dominates others in its group, at least one or more other tasks were also viewed by two or more pairs as the most difficult in all task types. Three pairs viewed PS4; and two pairs viewed OE4 and DM1 respectively as the most difficult tasks. One pair each viewed JT2, OE1 and DM3 as the most difficult. The rating for the JT group is possibly less reliable since three of the seven pairs did not complete the tasks. Further data from the interviews show the reasons for learners choice of the most difficult task. Most of learners responses for their choice of the most difficult task linked to Cummins (1981) description of highcognitive demand, while half of the responses linked to reduced contextual support. Tasks are regarded as ISBN:
6 highly-cognitive when learners come across unknown English words, and that which involved them in more thinking and the need for use of the L2 to explain content. Learners viewed tasks as the most difficult when contextual support is low, and associated to lack of clarity, lack of familiarity with or lack of relation to previous experiences, and no prior experience of the task. Some sample interview excerpts that support these findings are: ISBN:
7 This shows that learners perception of task difficulty is influenced by both the contextual and the cognitive dimensions. This means that the level of ease of tasks was associated to contextual-embeddedness, and that the cognitive demands played only a minor role. 4.3 Learners perceptions of task difficulty In this section, I compare learners ratings within task types and the teacher s perceptions of task difficulty, based on how the learners identified the easiest tasks and the most difficult tasks. Figure 4.3 illustrates learners perceptions of both levels of task difficulty. These tasks are compared to the teacher s interpretation of the tasks in Cummins (1981) matrix. Learners perceptions of task difficulty in the interviews are presented in relation to Cummins (1981) matrix. This is shown in Figure 2. Figure 2: Learners perceptions of task difficulty in relation to Cummins (1981) matrix In Figure 2, we see that pairs perceptions of the easiest and the most difficult tasks occur all over the matrix, showing no relationship between overall relationships between task difficulty and the contextual support and cognitive demands of tasks. When learners interpretation of task difficulty is compared to that of the teacher (see Fig. 2), we see that the result differs. As mentioned earlier, the teacher s interpretation of task difficulty was based on Cummins (1981) framework, and the learners interpretation of task difficulty was based on their view of the easiest and the most difficult task of each task type. This finding shows that although the teacher s perception of the difficulty of the tasks connects to learners perceptions in most ways, the variability in learners perceptions of task difficulty shows that the teacher s judgement may not always match that of the learners. Learners comments in the interviews provide further understanding of how they interpret the tasks. The data shows that there is a connection between the easiest task and contextual support, and the most difficult task with cognitive demands. This shows that learners perceptions of the level of task difficulty provide a dominant connection between both contextual support and cognitive demands. ISBN:
8 5 CONCLUSIONS Results show that learners have different views of tasks, which may be due to many factors within learners experience and knowledge. This shows that although learners are of the same proficiency level, the difficulty of tasks may not be equal for all learners as it is affected by the contextual relevance of the tasks to learners, as well as the cognitive level of learners in their ability to perform the tasks. The way that learners in this study perceived the easiest and the most difficult tasks allowed me to understand how they viewed the level of difficulty of tasks, which enabled me to link to other studies on task difficulty (Robinson, 2001; Tavakoli, 2009; Tavakoli & Skehan, 2005). These researchers have identified lack of familiarity with task types, the cognitive demand of the tasks, the clarity of pictures or story and the amount of information as factors that contribute to task difficulty and easiness. The findings have also revealed that the teacher and the learners may have similar interpretation of tasks, but that there is a higher possibility of differences in perceptions as learners are different in their own ways, which makes it complex for teachers to design exactly the same tasks to suit all learners in the same class. It is also important to highlight the differences that was found between the teacher s and the learners perception of task difficulty. Although there is a mismatch among their perceptions within tasks and among task types, the teacher s and the learners perceptions seem to show some connection: the easiest tasks were linked to context-embedded and cognitively demanding and undemanding tasks, while the most difficult tasks were linked to context-reduced and cognitively demanding tasks. This shows differences in the learners and teacher s interpretation of the cognitive and contextual level of the tasks. This finding generally shows that a teacher s perception of task difficulty may not always match those of the learners. REFERENCE LIST Bygate, M., Skehan, P, & Swain, M. (2001). Researching pedagogic tasks, second language learning, teaching and testing. Harlow, UK: Longman. Carless, D. (2008). Implementing task-based learning with young learners. ELT Journal, 56 (4), Castillo, R. (2008). Issues involved in context, comprehension and content. Latin American Journal of Content and Language Integrated Learning, 1 (1), Cummins, J. (2008). BICS and CALP: Empirical and theoretical status of the distinction. In B. A. Street, Encyclopedia of Language and Education, (2nd ed.).(vol. 2: Literacy, pp ). New York: Springer Science + Business Media LLC. Cummins, J. (1984). Bilingualism and special education: Issues in assessment and pedagogy. San Diego, CA: College Hill Press. Cummins, J. (2000). Language, power and pedagogy: Bilingual children in the crossfire. Great Britain.: Multilingual Matters Ltd. Cummins, J. (2001). Negotiating identities: Education for empowerment in a diverse society (2nd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: California Association for Bilingual Education. Cummins, J. (1981). The role of primary language development in promoting educational success for language minority students. In C. S. (Ed.), Schooling and language minority students: A theoretical framework. Los Angeles: Evaluation, Dissemination and Assessment Center. Darmi, R., Harun, H., Samah, R., Puteh-Behak, F., Mat Saad, N.S. & Mohd Ali, S. (2016). Learners perceptions on task difficulty in task-based lessons. In International Conference on Education and Regional Development 2016 (ICERD 2016) Proceeding. Universiti Pendidikan Indonesia, Bandung, Indonesia, pp Darmi, R. (2014). The Effects of the Application of Cummins Model on Learners Language Use. In International Journal of Language Education and Applied Linguistics, Vol. 1, 1-8, Penerbit Universiti Malaysia Pahang (ISSN: print). Darmi, R. (2013). Exploring teacher-learner perceptions of first language use and tasks, and their relationship to task types and task difficulty in a Malaysian tertiary context. Phd Thesis. La Trobe University, Melbourne. Dutro, S. & Moran, C. (2003). Rethinking English language instruction: An architectural. In G. G. (Eds.), English learners: Reaching the highest level of (pp ). Newark, DE: International Reading ISBN:
9 Association. Ellis, R. (2009). Task-based language teaching: sorting out the misunderstandings. International Journal of Applied Linguistics, 19 (3), Ellis, R. (2003). Task-based language teaching and learning. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. Ellis, R. (2000). Task-based research and language pedagogy. Language Teaching Research, 4, Foster, P. & Skehan, P. (1996). The influence of planning and task type on second language performance. Studies in Second Language Acquisition, 18, Garcia, O. (2009). Bilingual education in the 21st century a global perspective.singapore: Wiley-Blackwell. Richards, J. & Rodgers, T. S. (2001). Approaches and methods in language teaching (2nd Ed.). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. Robinson, P. (2001). Task complexity, task difficulty, and task production: Exploring interactions in a componential framework. Applied Linguistics, 22 (1), Samuda, V. & Bygate, M. (2008). Tasks in second language learning. New York: Palgrave Macmillan. Skehan, P. & Foster, P. (1997). Task type and task processing conditions as influences on foreign language performance. Language Teaching Research, 1 (3), Skehan, P. & Foster, P. (1999). The influence of task structure and processing conditions on narrative retellings. Language Teaching Research, 49, Skehan, P. (2003). Task-based instruction. Language Teaching, 36, Swain, M. &. Lapkin, S. (2000). Task-based second language learning: The uses of the first language. Language Teaching Research, 4 (3), Willis, J. (1996). A framework for task-based learning. Harlow, Essex: Addison Wesley Longman. Longman. Willis, D. & Willis, J. (2007). Doing task-based teaching. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Zwiers, J. (2008). Building academic language: Essential practices for content. Newark, DE: International Reading Association. ISBN:
THE EFFECTS OF TASK COMPLEXITY ALONG RESOURCE-DIRECTING AND RESOURCE-DISPERSING FACTORS ON EFL LEARNERS WRITTEN PERFORMANCE
 THE EFFECTS OF TASK COMPLEXITY ALONG RESOURCE-DIRECTING AND RESOURCE-DISPERSING FACTORS ON EFL LEARNERS WRITTEN PERFORMANCE Zahra Talebi PhD candidate in TEFL, Faculty of Humanities, University of Payame
THE EFFECTS OF TASK COMPLEXITY ALONG RESOURCE-DIRECTING AND RESOURCE-DISPERSING FACTORS ON EFL LEARNERS WRITTEN PERFORMANCE Zahra Talebi PhD candidate in TEFL, Faculty of Humanities, University of Payame
Ohio s New Learning Standards: K-12 World Languages
 COMMUNICATION STANDARD Communication: Communicate in languages other than English, both in person and via technology. A. Interpretive Communication (Reading, Listening/Viewing) Learners comprehend the
COMMUNICATION STANDARD Communication: Communicate in languages other than English, both in person and via technology. A. Interpretive Communication (Reading, Listening/Viewing) Learners comprehend the
I. INTRODUCTION. for conducting the research, the problems in teaching vocabulary, and the suitable
 1 I. INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the background of the problem which includes the reasons for conducting the research, the problems in teaching vocabulary, and the suitable activity which is needed
1 I. INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the background of the problem which includes the reasons for conducting the research, the problems in teaching vocabulary, and the suitable activity which is needed
THE ORAL PROFICIENCY OF ESL TEACHER TRAINEES IN DIFFERENT DISCOURSE DOMAINS
 THE ORAL PROFICIENCY OF ESL TEACHER TRAINEES IN DIFFERENT DISCOURSE DOMAINS Abstract C.E.Olivier, Language Centre, University of Namibia This article reports on a study that investigated the oral proficiency
THE ORAL PROFICIENCY OF ESL TEACHER TRAINEES IN DIFFERENT DISCOURSE DOMAINS Abstract C.E.Olivier, Language Centre, University of Namibia This article reports on a study that investigated the oral proficiency
Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences 8 (2010)
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences 8 (2010) 312 316 International Conference on Mathematics Education Research 2010 (ICMER 2010) Teachers Choice and Use of
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences 8 (2010) 312 316 International Conference on Mathematics Education Research 2010 (ICMER 2010) Teachers Choice and Use of
Laporan Penelitian Unggulan Prodi
 Nama Rumpun Ilmu : Ilmu Sosial Laporan Penelitian Unggulan Prodi THE ROLE OF BAHASA INDONESIA IN FOREIGN LANGUAGE TEACHING AT THE LANGUAGE TRAINING CENTER UMY Oleh: Dedi Suryadi, M.Ed. Ph.D NIDN : 0504047102
Nama Rumpun Ilmu : Ilmu Sosial Laporan Penelitian Unggulan Prodi THE ROLE OF BAHASA INDONESIA IN FOREIGN LANGUAGE TEACHING AT THE LANGUAGE TRAINING CENTER UMY Oleh: Dedi Suryadi, M.Ed. Ph.D NIDN : 0504047102
Maximizing Learning Through Course Alignment and Experience with Different Types of Knowledge
 Innov High Educ (2009) 34:93 103 DOI 10.1007/s10755-009-9095-2 Maximizing Learning Through Course Alignment and Experience with Different Types of Knowledge Phyllis Blumberg Published online: 3 February
Innov High Educ (2009) 34:93 103 DOI 10.1007/s10755-009-9095-2 Maximizing Learning Through Course Alignment and Experience with Different Types of Knowledge Phyllis Blumberg Published online: 3 February
Language Acquisition Chart
 Language Acquisition Chart This chart was designed to help teachers better understand the process of second language acquisition. Please use this chart as a resource for learning more about the way people
Language Acquisition Chart This chart was designed to help teachers better understand the process of second language acquisition. Please use this chart as a resource for learning more about the way people
Approaches to Teaching Second Language Writing Brian PALTRIDGE, The University of Sydney
 Approaches to Teaching Second Language Writing Brian PALTRIDGE, The University of Sydney This paper presents a discussion of developments in the teaching of writing. This includes a discussion of genre-based
Approaches to Teaching Second Language Writing Brian PALTRIDGE, The University of Sydney This paper presents a discussion of developments in the teaching of writing. This includes a discussion of genre-based
TEACHERS ATTITUDES TOWARDS THE USE OF FIRST LANGUAGE IN ARABIC CLASSROOM
 TEACHERS ATTITUDES TOWARDS THE USE OF FIRST LANGUAGE IN ARABIC CLASSROOM Mohamad Azrien Mohamed Adnan, Academy of Islamic Studies University of Malaya Nilam Puri, Kelantan, Malaysia. Mohd Alwee Yusoff,
TEACHERS ATTITUDES TOWARDS THE USE OF FIRST LANGUAGE IN ARABIC CLASSROOM Mohamad Azrien Mohamed Adnan, Academy of Islamic Studies University of Malaya Nilam Puri, Kelantan, Malaysia. Mohd Alwee Yusoff,
Table of Contents. Introduction Choral Reading How to Use This Book...5. Cloze Activities Correlation to TESOL Standards...
 Table of Contents Introduction.... 4 How to Use This Book.....................5 Correlation to TESOL Standards... 6 ESL Terms.... 8 Levels of English Language Proficiency... 9 The Four Language Domains.............
Table of Contents Introduction.... 4 How to Use This Book.....................5 Correlation to TESOL Standards... 6 ESL Terms.... 8 Levels of English Language Proficiency... 9 The Four Language Domains.............
Text and task authenticity in the EFL classroom
 Text and task authenticity in the EFL classroom William Guariento and John Morley There is now a general consensus in language teaching that the use of authentic materials in the classroom is beneficial
Text and task authenticity in the EFL classroom William Guariento and John Morley There is now a general consensus in language teaching that the use of authentic materials in the classroom is beneficial
Assessing speaking skills:. a workshop for teacher development. Ben Knight
 Assessing speaking skills:. a workshop for teacher development Ben Knight Speaking skills are often considered the most important part of an EFL course, and yet the difficulties in testing oral skills
Assessing speaking skills:. a workshop for teacher development Ben Knight Speaking skills are often considered the most important part of an EFL course, and yet the difficulties in testing oral skills
Why PPP won t (and shouldn t) go away
 (and shouldn t) go IATEFL Birmingham 2016 jasonanderson1@gmail.com www.jasonanderson.org.uk speakinggames.wordpress.com Structure of my talk 1. Introduction 3. Why is it so enduring / popular? (i.e. Does
(and shouldn t) go IATEFL Birmingham 2016 jasonanderson1@gmail.com www.jasonanderson.org.uk speakinggames.wordpress.com Structure of my talk 1. Introduction 3. Why is it so enduring / popular? (i.e. Does
The Effects of Strategic Planning and Topic Familiarity on Iranian Intermediate EFL Learners Written Performance in TBLT
 ISSN 1799-2591 Theory and Practice in Language Studies, Vol. 2, No. 11, pp. 2308-2315, November 2012 Manufactured in Finland. doi:10.4304/tpls.2.11.2308-2315 The Effects of Strategic Planning and Topic
ISSN 1799-2591 Theory and Practice in Language Studies, Vol. 2, No. 11, pp. 2308-2315, November 2012 Manufactured in Finland. doi:10.4304/tpls.2.11.2308-2315 The Effects of Strategic Planning and Topic
Observing Teachers: The Mathematics Pedagogy of Quebec Francophone and Anglophone Teachers
 Observing Teachers: The Mathematics Pedagogy of Quebec Francophone and Anglophone Teachers Dominic Manuel, McGill University, Canada Annie Savard, McGill University, Canada David Reid, Acadia University,
Observing Teachers: The Mathematics Pedagogy of Quebec Francophone and Anglophone Teachers Dominic Manuel, McGill University, Canada Annie Savard, McGill University, Canada David Reid, Acadia University,
EQuIP Review Feedback
 EQuIP Review Feedback Lesson/Unit Name: On the Rainy River and The Red Convertible (Module 4, Unit 1) Content Area: English language arts Grade Level: 11 Dimension I Alignment to the Depth of the CCSS
EQuIP Review Feedback Lesson/Unit Name: On the Rainy River and The Red Convertible (Module 4, Unit 1) Content Area: English language arts Grade Level: 11 Dimension I Alignment to the Depth of the CCSS
Intensive Writing Class
 Intensive Writing Class Student Profile: This class is for students who are committed to improving their writing. It is for students whose writing has been identified as their weakest skill and whose CASAS
Intensive Writing Class Student Profile: This class is for students who are committed to improving their writing. It is for students whose writing has been identified as their weakest skill and whose CASAS
The role of the first language in foreign language learning. Paul Nation. The role of the first language in foreign language learning
 1 Article Title The role of the first language in foreign language learning Author Paul Nation Bio: Paul Nation teaches in the School of Linguistics and Applied Language Studies at Victoria University
1 Article Title The role of the first language in foreign language learning Author Paul Nation Bio: Paul Nation teaches in the School of Linguistics and Applied Language Studies at Victoria University
Linking the Common European Framework of Reference and the Michigan English Language Assessment Battery Technical Report
 Linking the Common European Framework of Reference and the Michigan English Language Assessment Battery Technical Report Contact Information All correspondence and mailings should be addressed to: CaMLA
Linking the Common European Framework of Reference and the Michigan English Language Assessment Battery Technical Report Contact Information All correspondence and mailings should be addressed to: CaMLA
To appear in The TESOL encyclopedia of ELT (Wiley-Blackwell) 1 RECASTING. Kazuya Saito. Birkbeck, University of London
 To appear in The TESOL encyclopedia of ELT (Wiley-Blackwell) 1 RECASTING Kazuya Saito Birkbeck, University of London Abstract Among the many corrective feedback techniques at ESL/EFL teachers' disposal,
To appear in The TESOL encyclopedia of ELT (Wiley-Blackwell) 1 RECASTING Kazuya Saito Birkbeck, University of London Abstract Among the many corrective feedback techniques at ESL/EFL teachers' disposal,
The Effect of Discourse Markers on the Speaking Production of EFL Students. Iman Moradimanesh
 The Effect of Discourse Markers on the Speaking Production of EFL Students Iman Moradimanesh Abstract The research aimed at investigating the relationship between discourse markers (DMs) and a special
The Effect of Discourse Markers on the Speaking Production of EFL Students Iman Moradimanesh Abstract The research aimed at investigating the relationship between discourse markers (DMs) and a special
Perception of Lecturer on Intercultural Competence and Culture Teaching Time (Case Study)
 Perception of Lecturer on Intercultural Competence and Culture Teaching Time (Case Study) Enkeleda Jata PhD Cand. European University of Tirana, Albania, enki_jata@yahoo.it Abstract Of all the changes
Perception of Lecturer on Intercultural Competence and Culture Teaching Time (Case Study) Enkeleda Jata PhD Cand. European University of Tirana, Albania, enki_jata@yahoo.it Abstract Of all the changes
Developing Students Research Proposal Design through Group Investigation Method
 IOSR Journal of Research & Method in Education (IOSR-JRME) e-issn: 2320 7388,p-ISSN: 2320 737X Volume 7, Issue 1 Ver. III (Jan. - Feb. 2017), PP 37-43 www.iosrjournals.org Developing Students Research
IOSR Journal of Research & Method in Education (IOSR-JRME) e-issn: 2320 7388,p-ISSN: 2320 737X Volume 7, Issue 1 Ver. III (Jan. - Feb. 2017), PP 37-43 www.iosrjournals.org Developing Students Research
Analyzing Linguistically Appropriate IEP Goals in Dual Language Programs
 Analyzing Linguistically Appropriate IEP Goals in Dual Language Programs 2016 Dual Language Conference: Making Connections Between Policy and Practice March 19, 2016 Framingham, MA Session Description
Analyzing Linguistically Appropriate IEP Goals in Dual Language Programs 2016 Dual Language Conference: Making Connections Between Policy and Practice March 19, 2016 Framingham, MA Session Description
Professional Development Guideline for Instruction Professional Practice of English Pre-Service Teachers in Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University
 Professional Development Guideline for Instruction Professional Practice of English Pre-Service Teachers in Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University Pintipa Seubsang and Suttipong Boonphadung, Member, IEDRC Abstract
Professional Development Guideline for Instruction Professional Practice of English Pre-Service Teachers in Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University Pintipa Seubsang and Suttipong Boonphadung, Member, IEDRC Abstract
ADDIE MODEL THROUGH THE TASK LEARNING APPROACH IN TEXTILE KNOWLEDGE COURSE IN DRESS-MAKING EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM OF STATE UNIVERSITY OF MEDAN
 International Journal of GEOMATE, Feb., 217, Vol. 12, Issue, pp. 19-114 International Journal of GEOMATE, Feb., 217, Vol.12 Issue, pp. 19-114 Special Issue on Science, Engineering & Environment, ISSN:2186-299,
International Journal of GEOMATE, Feb., 217, Vol. 12, Issue, pp. 19-114 International Journal of GEOMATE, Feb., 217, Vol.12 Issue, pp. 19-114 Special Issue on Science, Engineering & Environment, ISSN:2186-299,
DOES RETELLING TECHNIQUE IMPROVE SPEAKING FLUENCY?
 DOES RETELLING TECHNIQUE IMPROVE SPEAKING FLUENCY? Noor Rachmawaty (itaw75123@yahoo.com) Istanti Hermagustiana (dulcemaria_81@yahoo.com) Universitas Mulawarman, Indonesia Abstract: This paper is based
DOES RETELLING TECHNIQUE IMPROVE SPEAKING FLUENCY? Noor Rachmawaty (itaw75123@yahoo.com) Istanti Hermagustiana (dulcemaria_81@yahoo.com) Universitas Mulawarman, Indonesia Abstract: This paper is based
Communicative Language Teaching (CLT): A Critical and Comparative Perspective
 ISSN 1799-2591 Theory and Practice in Language Studies, Vol. 3, No. 9, pp. 1579-1583, September 2013 Manufactured in Finland. doi:10.4304/tpls.3.9.1579-1583 Communicative Language Teaching (CLT): A Critical
ISSN 1799-2591 Theory and Practice in Language Studies, Vol. 3, No. 9, pp. 1579-1583, September 2013 Manufactured in Finland. doi:10.4304/tpls.3.9.1579-1583 Communicative Language Teaching (CLT): A Critical
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND USING A MULTILITERACIES APPROACH IN A MALAYSIAN POLYTECHNIC CLASSROOM: A PARTICIPATORY ACTION RESEARCH PROJECT A dissertation submitted by: Fariza Puteh-Behak For the
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND USING A MULTILITERACIES APPROACH IN A MALAYSIAN POLYTECHNIC CLASSROOM: A PARTICIPATORY ACTION RESEARCH PROJECT A dissertation submitted by: Fariza Puteh-Behak For the
Second Language Acquisition in Adults: From Research to Practice
 Second Language Acquisition in Adults: From Research to Practice Donna Moss, National Center for ESL Literacy Education Lauren Ross-Feldman, Georgetown University Second language acquisition (SLA) is the
Second Language Acquisition in Adults: From Research to Practice Donna Moss, National Center for ESL Literacy Education Lauren Ross-Feldman, Georgetown University Second language acquisition (SLA) is the
IMPROVING SPEAKING SKILL OF THE TENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMK 17 AGUSTUS 1945 MUNCAR THROUGH DIRECT PRACTICE WITH THE NATIVE SPEAKER
 IMPROVING SPEAKING SKILL OF THE TENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMK 17 AGUSTUS 1945 MUNCAR THROUGH DIRECT PRACTICE WITH THE NATIVE SPEAKER Mohamad Nor Shodiq Institut Agama Islam Darussalam (IAIDA) Banyuwangi
IMPROVING SPEAKING SKILL OF THE TENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMK 17 AGUSTUS 1945 MUNCAR THROUGH DIRECT PRACTICE WITH THE NATIVE SPEAKER Mohamad Nor Shodiq Institut Agama Islam Darussalam (IAIDA) Banyuwangi
5. UPPER INTERMEDIATE
 Triolearn General Programmes adapt the standards and the Qualifications of Common European Framework of Reference (CEFR) and Cambridge ESOL. It is designed to be compatible to the local and the regional
Triolearn General Programmes adapt the standards and the Qualifications of Common European Framework of Reference (CEFR) and Cambridge ESOL. It is designed to be compatible to the local and the regional
Differences in Perceived Fluency and Utterance Fluency across Speech Elicitation Tasks: A Pilot Study
 Differences in Perceived Fluency and Utterance Fluency across Speech Elicitation Tasks: A Pilot Study Yvonne Préfontaine Lancaster University, Lancaster Abstract This pilot study focuses on whether analysis
Differences in Perceived Fluency and Utterance Fluency across Speech Elicitation Tasks: A Pilot Study Yvonne Préfontaine Lancaster University, Lancaster Abstract This pilot study focuses on whether analysis
Assessment System for M.S. in Health Professions Education (rev. 4/2011)
 Assessment System for M.S. in Health Professions Education (rev. 4/2011) Health professions education programs - Conceptual framework The University of Rochester interdisciplinary program in Health Professions
Assessment System for M.S. in Health Professions Education (rev. 4/2011) Health professions education programs - Conceptual framework The University of Rochester interdisciplinary program in Health Professions
An Assessment of the Dual Language Acquisition Model. On Improving Student WASL Scores at. McClure Elementary School at Yakima, Washington.
 An Assessment of the Dual Language Acquisition Model On Improving Student WASL Scores at McClure Elementary School at Yakima, Washington. ------------------------------------------------------ A Special
An Assessment of the Dual Language Acquisition Model On Improving Student WASL Scores at McClure Elementary School at Yakima, Washington. ------------------------------------------------------ A Special
Curriculum and Assessment Guide (CAG) Elementary California Treasures First Grade
 Curriculum and Assessment Guide (CAG) Elementary 2012-2013 California Treasures First Grade 1 2 English Language Arts CORE INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS 2012-2013 Grade 1 Macmillan/McGraw-Hill California Treasures
Curriculum and Assessment Guide (CAG) Elementary 2012-2013 California Treasures First Grade 1 2 English Language Arts CORE INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS 2012-2013 Grade 1 Macmillan/McGraw-Hill California Treasures
The Effectiveness of Realistic Mathematics Education Approach on Ability of Students Mathematical Concept Understanding
 International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR) ISSN 2307-4531 (Print & Online) http://gssrr.org/index.php?journal=journalofbasicandapplied ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR) ISSN 2307-4531 (Print & Online) http://gssrr.org/index.php?journal=journalofbasicandapplied ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 141 ( 2014 ) WCLTA Using Corpus Linguistics in the Development of Writing
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 141 ( 2014 ) 124 128 WCLTA 2013 Using Corpus Linguistics in the Development of Writing Blanka Frydrychova
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 141 ( 2014 ) 124 128 WCLTA 2013 Using Corpus Linguistics in the Development of Writing Blanka Frydrychova
Reducing Spoon-Feeding to Promote Independent Thinking
 Reducing Spoon-Feeding to Promote Independent Thinking Janice T. Blane This paper was completed and submitted in partial fulfillment of the Master Teacher Program, a 2-year faculty professional development
Reducing Spoon-Feeding to Promote Independent Thinking Janice T. Blane This paper was completed and submitted in partial fulfillment of the Master Teacher Program, a 2-year faculty professional development
English for Specific Purposes World ISSN Issue 34, Volume 12, 2012 TITLE:
 TITLE: The English Language Needs of Computer Science Undergraduate Students at Putra University, Author: 1 Affiliation: Faculty Member Department of Languages College of Arts and Sciences International
TITLE: The English Language Needs of Computer Science Undergraduate Students at Putra University, Author: 1 Affiliation: Faculty Member Department of Languages College of Arts and Sciences International
Correspondence between the DRDP (2015) and the California Preschool Learning Foundations. Foundations (PLF) in Language and Literacy
 1 Desired Results Developmental Profile (2015) [DRDP (2015)] Correspondence to California Foundations: Language and Development (LLD) and the Foundations (PLF) The Language and Development (LLD) domain
1 Desired Results Developmental Profile (2015) [DRDP (2015)] Correspondence to California Foundations: Language and Development (LLD) and the Foundations (PLF) The Language and Development (LLD) domain
Kaufman Assessment Battery For Children
 Kaufman Assessment Battery For Children Read Book Online: Kaufman Assessment Battery For Children Download or read online ebook kaufman assessment battery for children in any format for any devices. Kaufman
Kaufman Assessment Battery For Children Read Book Online: Kaufman Assessment Battery For Children Download or read online ebook kaufman assessment battery for children in any format for any devices. Kaufman
Professional Learning Suite Framework Edition Domain 3 Course Index
 Domain 3: Instruction Professional Learning Suite Framework Edition Domain 3 Course Index Courses included in the Professional Learning Suite Framework Edition related to Domain 3 of the Framework for
Domain 3: Instruction Professional Learning Suite Framework Edition Domain 3 Course Index Courses included in the Professional Learning Suite Framework Edition related to Domain 3 of the Framework for
Author: Justyna Kowalczys Stowarzyszenie Angielski w Medycynie (PL) Feb 2015
 Author: Justyna Kowalczys Stowarzyszenie Angielski w Medycynie (PL) www.angielskiwmedycynie.org.pl Feb 2015 Developing speaking abilities is a prerequisite for HELP in order to promote effective communication
Author: Justyna Kowalczys Stowarzyszenie Angielski w Medycynie (PL) www.angielskiwmedycynie.org.pl Feb 2015 Developing speaking abilities is a prerequisite for HELP in order to promote effective communication
Developing a Language for Assessing Creativity: a taxonomy to support student learning and assessment
 Investigations in university teaching and learning vol. 5 (1) autumn 2008 ISSN 1740-5106 Developing a Language for Assessing Creativity: a taxonomy to support student learning and assessment Janette Harris
Investigations in university teaching and learning vol. 5 (1) autumn 2008 ISSN 1740-5106 Developing a Language for Assessing Creativity: a taxonomy to support student learning and assessment Janette Harris
The Use of Drama and Dramatic Activities in English Language Teaching
 The Crab: Journal of Theatre and Media Arts (Number 7/June 2012, 151-159) The Use of Drama and Dramatic Activities in English Language Teaching Chioma O.C. Chukueggu Abstract The purpose of this paper
The Crab: Journal of Theatre and Media Arts (Number 7/June 2012, 151-159) The Use of Drama and Dramatic Activities in English Language Teaching Chioma O.C. Chukueggu Abstract The purpose of this paper
EDUCATING TEACHERS FOR CULTURAL AND LINGUISTIC DIVERSITY: A MODEL FOR ALL TEACHERS
 New York State Association for Bilingual Education Journal v9 p1-6, Summer 1994 EDUCATING TEACHERS FOR CULTURAL AND LINGUISTIC DIVERSITY: A MODEL FOR ALL TEACHERS JoAnn Parla Abstract: Given changing demographics,
New York State Association for Bilingual Education Journal v9 p1-6, Summer 1994 EDUCATING TEACHERS FOR CULTURAL AND LINGUISTIC DIVERSITY: A MODEL FOR ALL TEACHERS JoAnn Parla Abstract: Given changing demographics,
Express, an International Journal of Multi Disciplinary Research ISSN: , Vol. 1, Issue 3, March 2014 Available at: journal.
 The Role of Teacher in the Postmethod Era by Mahshad Tasnimi Department of English, Qazvin Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran E-mail: mtasnimi@yahoo.com Abstract In the postmethod era, the role
The Role of Teacher in the Postmethod Era by Mahshad Tasnimi Department of English, Qazvin Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran E-mail: mtasnimi@yahoo.com Abstract In the postmethod era, the role
Rubric for Scoring English 1 Unit 1, Rhetorical Analysis
 FYE Program at Marquette University Rubric for Scoring English 1 Unit 1, Rhetorical Analysis Writing Conventions INTEGRATING SOURCE MATERIAL 3 Proficient Outcome Effectively expresses purpose in the introduction
FYE Program at Marquette University Rubric for Scoring English 1 Unit 1, Rhetorical Analysis Writing Conventions INTEGRATING SOURCE MATERIAL 3 Proficient Outcome Effectively expresses purpose in the introduction
Integrating culture in teaching English as a second language
 Book of Proceedings 52 Integrating culture in teaching English as a second language Dr. Anita MUHO Department of Foreign Languages Faculty of Education Aleksandër Moisiu University Durrës, Albania E mail:
Book of Proceedings 52 Integrating culture in teaching English as a second language Dr. Anita MUHO Department of Foreign Languages Faculty of Education Aleksandër Moisiu University Durrës, Albania E mail:
Is There a Role for Tutor in Group Work: Peer Interaction in a Hong Kong EFL Classroom
 HKBU Papers in Applied Language Studies Vol. 13, 2009 Is There a Role for Tutor in Group Work: Peer Interaction in a Hong Kong EFL Classroom LI Danli English Department, Wuhan University Abstract This
HKBU Papers in Applied Language Studies Vol. 13, 2009 Is There a Role for Tutor in Group Work: Peer Interaction in a Hong Kong EFL Classroom LI Danli English Department, Wuhan University Abstract This
ACADEMIC AFFAIRS GUIDELINES
 ACADEMIC AFFAIRS GUIDELINES Section 8: General Education Title: General Education Assessment Guidelines Number (Current Format) Number (Prior Format) Date Last Revised 8.7 XIV 09/2017 Reference: BOR Policy
ACADEMIC AFFAIRS GUIDELINES Section 8: General Education Title: General Education Assessment Guidelines Number (Current Format) Number (Prior Format) Date Last Revised 8.7 XIV 09/2017 Reference: BOR Policy
UCLA Issues in Applied Linguistics
 UCLA Issues in Applied Linguistics Title An Introduction to Second Language Acquisition Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3165s95t Journal Issues in Applied Linguistics, 3(2) ISSN 1050-4273 Author
UCLA Issues in Applied Linguistics Title An Introduction to Second Language Acquisition Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3165s95t Journal Issues in Applied Linguistics, 3(2) ISSN 1050-4273 Author
Different Requirements Gathering Techniques and Issues. Javaria Mushtaq
 835 Different Requirements Gathering Techniques and Issues Javaria Mushtaq Abstract- Project management is now becoming a very important part of our software industries. To handle projects with success
835 Different Requirements Gathering Techniques and Issues Javaria Mushtaq Abstract- Project management is now becoming a very important part of our software industries. To handle projects with success
ESL Curriculum and Assessment
 ESL Curriculum and Assessment Terms Syllabus Content of a course How it is organized How it will be tested Curriculum Broader term, process Describes what will be taught, in what order will it be taught,
ESL Curriculum and Assessment Terms Syllabus Content of a course How it is organized How it will be tested Curriculum Broader term, process Describes what will be taught, in what order will it be taught,
National Standards for Foreign Language Education
 A Correlation of Prentice Hall Ecce Romani I To the ACTFL American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language National Standards for Foreign Language Education A Correlation of Statement of Philosophy
A Correlation of Prentice Hall Ecce Romani I To the ACTFL American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language National Standards for Foreign Language Education A Correlation of Statement of Philosophy
Textbook Evalyation:
 STUDIES IN LITERATURE AND LANGUAGE Vol. 1, No. 8, 2010, pp. 54-60 www.cscanada.net ISSN 1923-1555 [Print] ISSN 1923-1563 [Online] www.cscanada.org Textbook Evalyation: EFL Teachers Perspectives on New
STUDIES IN LITERATURE AND LANGUAGE Vol. 1, No. 8, 2010, pp. 54-60 www.cscanada.net ISSN 1923-1555 [Print] ISSN 1923-1563 [Online] www.cscanada.org Textbook Evalyation: EFL Teachers Perspectives on New
Academic Language: Equity for ELs
 Academic Language: Equity for ELs NCSU Annual ESL Symposium May 19, 2017 Glenda Harrell, ESL Director Amanda Miller, ESL Coordinating Teacher Includes information from Title III/ESL Update to WCPSS Board
Academic Language: Equity for ELs NCSU Annual ESL Symposium May 19, 2017 Glenda Harrell, ESL Director Amanda Miller, ESL Coordinating Teacher Includes information from Title III/ESL Update to WCPSS Board
TEXT FAMILIARITY, READING TASKS, AND ESP TEST PERFORMANCE: A STUDY ON IRANIAN LEP AND NON-LEP UNIVERSITY STUDENTS
 The Reading Matrix Vol.3. No.1, April 2003 TEXT FAMILIARITY, READING TASKS, AND ESP TEST PERFORMANCE: A STUDY ON IRANIAN LEP AND NON-LEP UNIVERSITY STUDENTS Muhammad Ali Salmani-Nodoushan Email: nodushan@chamran.ut.ac.ir
The Reading Matrix Vol.3. No.1, April 2003 TEXT FAMILIARITY, READING TASKS, AND ESP TEST PERFORMANCE: A STUDY ON IRANIAN LEP AND NON-LEP UNIVERSITY STUDENTS Muhammad Ali Salmani-Nodoushan Email: nodushan@chamran.ut.ac.ir
Explaining: a central discourse function in instruction. Christiane Dalton-Puffer University of Vienna
 Explaining: a central discourse function in instruction Christiane Dalton-Puffer University of Vienna Learning as interaction. Locke Vygotsky (1930s; 1978) Tomasello (1999) language as a special instrument
Explaining: a central discourse function in instruction Christiane Dalton-Puffer University of Vienna Learning as interaction. Locke Vygotsky (1930s; 1978) Tomasello (1999) language as a special instrument
Implementation of a Western-based Multiliteracies Pedagogy in Malaysia: A Socio-cultural Perspective
 GEMA Online Journal of Language Studies 1 Implementation of a Western-based Multiliteracies Pedagogy in Malaysia: A Socio-cultural Perspective Fariza Puteh-Behak fariza@usim.edu.my Universiti Sains Islam
GEMA Online Journal of Language Studies 1 Implementation of a Western-based Multiliteracies Pedagogy in Malaysia: A Socio-cultural Perspective Fariza Puteh-Behak fariza@usim.edu.my Universiti Sains Islam
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 98 ( 2014 ) International Conference on Current Trends in ELT
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 98 ( 2014 ) 852 858 International Conference on Current Trends in ELT Analyzing English Language Learning
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 98 ( 2014 ) 852 858 International Conference on Current Trends in ELT Analyzing English Language Learning
Learning and Retaining New Vocabularies: The Case of Monolingual and Bilingual Dictionaries
 Learning and Retaining New Vocabularies: The Case of Monolingual and Bilingual Dictionaries Mohsen Mobaraki Assistant Professor, University of Birjand, Iran mmobaraki@birjand.ac.ir *Amin Saed Lecturer,
Learning and Retaining New Vocabularies: The Case of Monolingual and Bilingual Dictionaries Mohsen Mobaraki Assistant Professor, University of Birjand, Iran mmobaraki@birjand.ac.ir *Amin Saed Lecturer,
Running head: METACOGNITIVE STRATEGIES FOR ACADEMIC LISTENING 1. The Relationship between Metacognitive Strategies Awareness
 Running head: METACOGNITIVE STRATEGIES FOR ACADEMIC LISTENING 1 The Relationship between Metacognitive Strategies Awareness and Listening Comprehension Performance Valeriia Bogorevich Northern Arizona
Running head: METACOGNITIVE STRATEGIES FOR ACADEMIC LISTENING 1 The Relationship between Metacognitive Strategies Awareness and Listening Comprehension Performance Valeriia Bogorevich Northern Arizona
A Decent Proposal for Bilingual Education at International Standard Schools/SBI in Indonesia
 A Decent Proposal for Bilingual Education at International Standard Schools/SBI in Indonesia Harits Masduqi Universitas Negeri Malang Paper presented at The 57 th TEFLIN International Conference: Revitalizing
A Decent Proposal for Bilingual Education at International Standard Schools/SBI in Indonesia Harits Masduqi Universitas Negeri Malang Paper presented at The 57 th TEFLIN International Conference: Revitalizing
CLASSIFICATION OF PROGRAM Critical Elements Analysis 1. High Priority Items Phonemic Awareness Instruction
 CLASSIFICATION OF PROGRAM Critical Elements Analysis 1 Program Name: Macmillan/McGraw Hill Reading 2003 Date of Publication: 2003 Publisher: Macmillan/McGraw Hill Reviewer Code: 1. X The program meets
CLASSIFICATION OF PROGRAM Critical Elements Analysis 1 Program Name: Macmillan/McGraw Hill Reading 2003 Date of Publication: 2003 Publisher: Macmillan/McGraw Hill Reviewer Code: 1. X The program meets
THE INFLUENCE OF ENGLISH SONG TOWARD STUDENTS VOCABULARY MASTERY AND STUDENTS MOTIVATION
 77 THE INFLUENCE OF ENGLISH SONG TOWARD STUDENTS VOCABULARY MASTERY AND STUDENTS MOTIVATION By Eva Faliyanti Muhammadiyah University of Metro evafaliyanti1980@gmail.com Abstract Learning vocabulary is
77 THE INFLUENCE OF ENGLISH SONG TOWARD STUDENTS VOCABULARY MASTERY AND STUDENTS MOTIVATION By Eva Faliyanti Muhammadiyah University of Metro evafaliyanti1980@gmail.com Abstract Learning vocabulary is
LANGUAGE IN INDIA Strength for Today and Bright Hope for Tomorrow Volume 11 : 12 December 2011 ISSN
 LANGUAGE IN INDIA Strength for Today and Bright Hope for Tomorrow Volume ISSN 1930-2940 Managing Editor: M. S. Thirumalai, Ph.D. Editors: B. Mallikarjun, Ph.D. Sam Mohanlal, Ph.D. B. A. Sharada, Ph.D.
LANGUAGE IN INDIA Strength for Today and Bright Hope for Tomorrow Volume ISSN 1930-2940 Managing Editor: M. S. Thirumalai, Ph.D. Editors: B. Mallikarjun, Ph.D. Sam Mohanlal, Ph.D. B. A. Sharada, Ph.D.
Monticello Community School District K 12th Grade. Spanish Standards and Benchmarks
 Monticello Community School District K 12th Grade Spanish Standards and Benchmarks Developed by the Monticello Community High School Spanish Department Primary contributors to the 9 12 Spanish Standards
Monticello Community School District K 12th Grade Spanish Standards and Benchmarks Developed by the Monticello Community High School Spanish Department Primary contributors to the 9 12 Spanish Standards
Improving Student s Listening Skill Using Task- Based Approach in EFL Classroom Setting
 4th Asia Pacific Education Conference (AECON 2017) Improving Student s Listening Skill Using Task- Based Approach in EFL Classroom Setting Heri Kuswoyo, S.S., M.Hum Faculty of Arts and Education Universitas
4th Asia Pacific Education Conference (AECON 2017) Improving Student s Listening Skill Using Task- Based Approach in EFL Classroom Setting Heri Kuswoyo, S.S., M.Hum Faculty of Arts and Education Universitas
Did they acquire? Or were they taught?
 ISLL, Vitoria-Gasteiz, 13/05/2011 Did they acquire? Or were they taught? A Framework for Investigating the Effects and Effect(ivenes)s of Instruction in Second Language Acquisition Alex Housen University
ISLL, Vitoria-Gasteiz, 13/05/2011 Did they acquire? Or were they taught? A Framework for Investigating the Effects and Effect(ivenes)s of Instruction in Second Language Acquisition Alex Housen University
1 Copyright Texas Education Agency, All rights reserved.
 Lesson Plan-Diversity at Work Course Title: Business Information Management II Session Title: Diversity at Work Performance Objective: Upon completion of this lesson, students will understand diversity
Lesson Plan-Diversity at Work Course Title: Business Information Management II Session Title: Diversity at Work Performance Objective: Upon completion of this lesson, students will understand diversity
International Conference on Current Trends in ELT
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scien ce s 98 ( 2014 ) 52 59 International Conference on Current Trends in ELT Pragmatic Aspects of English for
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scien ce s 98 ( 2014 ) 52 59 International Conference on Current Trends in ELT Pragmatic Aspects of English for
Degree Qualification Profiles Intellectual Skills
 Degree Qualification Profiles Intellectual Skills Intellectual Skills: These are cross-cutting skills that should transcend disciplinary boundaries. Students need all of these Intellectual Skills to acquire
Degree Qualification Profiles Intellectual Skills Intellectual Skills: These are cross-cutting skills that should transcend disciplinary boundaries. Students need all of these Intellectual Skills to acquire
Oakland Unified School District English/ Language Arts Course Syllabus
 Oakland Unified School District English/ Language Arts Course Syllabus For Secondary Schools The attached course syllabus is a developmental and integrated approach to skill acquisition throughout the
Oakland Unified School District English/ Language Arts Course Syllabus For Secondary Schools The attached course syllabus is a developmental and integrated approach to skill acquisition throughout the
The Effects of Jigsaw and GTM on the Reading Comprehension Achievement of the Second Grade of Senior High School Students.
 The Effects of Jigsaw and GTM on the Reading Comprehension Achievement of the Second Grade of Senior High School Students Yullia Rossiana Abstract. The aim of this study is to compare the effectiveness
The Effects of Jigsaw and GTM on the Reading Comprehension Achievement of the Second Grade of Senior High School Students Yullia Rossiana Abstract. The aim of this study is to compare the effectiveness
The Influence of Affective Variables on the Complexity, Accuracy, and Fluency in L2 Oral Production: The Contribution of Task Repetition*
 Journal of English Language Teaching and Learning Tabriz University No. 17, 2016 The Influence of Affective Variables on the Complexity, Accuracy, and Fluency in L2 Oral Production: The Contribution of
Journal of English Language Teaching and Learning Tabriz University No. 17, 2016 The Influence of Affective Variables on the Complexity, Accuracy, and Fluency in L2 Oral Production: The Contribution of
Analysis of Students Incorrect Answer on Two- Dimensional Shape Lesson Unit of the Third- Grade of a Primary School
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Analysis of Students Incorrect Answer on Two- Dimensional Shape Lesson Unit of the Third- Grade of a Primary School To cite this article: Ulfah and
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Analysis of Students Incorrect Answer on Two- Dimensional Shape Lesson Unit of the Third- Grade of a Primary School To cite this article: Ulfah and
CELTA. Syllabus and Assessment Guidelines. Third Edition. University of Cambridge ESOL Examinations 1 Hills Road Cambridge CB1 2EU United Kingdom
 CELTA Syllabus and Assessment Guidelines Third Edition CELTA (Certificate in Teaching English to Speakers of Other Languages) is accredited by Ofqual (the regulator of qualifications, examinations and
CELTA Syllabus and Assessment Guidelines Third Edition CELTA (Certificate in Teaching English to Speakers of Other Languages) is accredited by Ofqual (the regulator of qualifications, examinations and
A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN NATURAL APPROACH AND QUANTUM LEARNING METHOD IN TEACHING VOCABULARY TO THE STUDENTS OF ENGLISH CLUB AT SMPN 1 RUMPIN
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN NATURAL APPROACH AND QUANTUM LEARNING METHOD IN TEACHING VOCABULARY TO THE STUDENTS OF ENGLISH CLUB AT SMPN 1 RUMPIN REZZA SANJAYA, DR. RITA SUTJIATI Undergraduate Program,
A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN NATURAL APPROACH AND QUANTUM LEARNING METHOD IN TEACHING VOCABULARY TO THE STUDENTS OF ENGLISH CLUB AT SMPN 1 RUMPIN REZZA SANJAYA, DR. RITA SUTJIATI Undergraduate Program,
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 146 ( 2014 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 146 ( 2014 ) 456 460 Third Annual International Conference «Early Childhood Care and Education» Different
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 146 ( 2014 ) 456 460 Third Annual International Conference «Early Childhood Care and Education» Different
PAGE(S) WHERE TAUGHT If sub mission ins not a book, cite appropriate location(s))
 Ohio Academic Content Standards Grade Level Indicators (Grade 11) A. ACQUISITION OF VOCABULARY Students acquire vocabulary through exposure to language-rich situations, such as reading books and other
Ohio Academic Content Standards Grade Level Indicators (Grade 11) A. ACQUISITION OF VOCABULARY Students acquire vocabulary through exposure to language-rich situations, such as reading books and other
MYP Language A Course Outline Year 3
 Course Description: The fundamental piece to learning, thinking, communicating, and reflecting is language. Language A seeks to further develop six key skill areas: listening, speaking, reading, writing,
Course Description: The fundamental piece to learning, thinking, communicating, and reflecting is language. Language A seeks to further develop six key skill areas: listening, speaking, reading, writing,
Intercultural communicative competence past and future
 Intercultural communicative competence past and future Michael Byram Visiting Professor School of Education and Social Work, University of Sussex m.s.byram@dur.ac.uk Overview Defining the concept of ICC
Intercultural communicative competence past and future Michael Byram Visiting Professor School of Education and Social Work, University of Sussex m.s.byram@dur.ac.uk Overview Defining the concept of ICC
Inside the mind of a learner
 Inside the mind of a learner - Sampling experiences to enhance learning process INTRODUCTION Optimal experiences feed optimal performance. Research has demonstrated that engaging students in the learning
Inside the mind of a learner - Sampling experiences to enhance learning process INTRODUCTION Optimal experiences feed optimal performance. Research has demonstrated that engaging students in the learning
Derivational and Inflectional Morphemes in Pak-Pak Language
 Derivational and Inflectional Morphemes in Pak-Pak Language Agustina Situmorang and Tima Mariany Arifin ABSTRACT The objectives of this study are to find out the derivational and inflectional morphemes
Derivational and Inflectional Morphemes in Pak-Pak Language Agustina Situmorang and Tima Mariany Arifin ABSTRACT The objectives of this study are to find out the derivational and inflectional morphemes
Quality Framework for Assessment of Multimedia Learning Materials Version 1.0
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 67 ( 2012 ) 571 579 The 3 rd International Conference on e-learning ICEL2011, 23-24 November 2011, Bandung, Indonesia
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 67 ( 2012 ) 571 579 The 3 rd International Conference on e-learning ICEL2011, 23-24 November 2011, Bandung, Indonesia
CHAPTER II REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE. together and language learning is supposed to happen. As stated by
 A. Review of Related Literature 1. Classroom Interaction CHAPTER II REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE The classroom is the place where lecturers and learners come together and language learning is supposed
A. Review of Related Literature 1. Classroom Interaction CHAPTER II REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE The classroom is the place where lecturers and learners come together and language learning is supposed
Task-Based Language Teaching: An Insight into Teacher Practice
 International Journal of Education, Culture and Society 2017; 2(4): 126-131 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijecs doi: 10.11648/j.ijecs.20170204.14 ISSN: 2575-3460 (Print); ISSN: 2575-3363 (Online)
International Journal of Education, Culture and Society 2017; 2(4): 126-131 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijecs doi: 10.11648/j.ijecs.20170204.14 ISSN: 2575-3460 (Print); ISSN: 2575-3363 (Online)
Using Team-based learning for the Career Research Project. Francine White. LaGuardia Community College
 Team Based Learning and Career Research 1 Using Team-based learning for the Career Research Project Francine White LaGuardia Community College Team Based Learning and Career Research 2 Discussion Paper
Team Based Learning and Career Research 1 Using Team-based learning for the Career Research Project Francine White LaGuardia Community College Team Based Learning and Career Research 2 Discussion Paper
Students Understanding of Graphical Vector Addition in One and Two Dimensions
 Eurasian J. Phys. Chem. Educ., 3(2):102-111, 2011 journal homepage: http://www.eurasianjournals.com/index.php/ejpce Students Understanding of Graphical Vector Addition in One and Two Dimensions Umporn
Eurasian J. Phys. Chem. Educ., 3(2):102-111, 2011 journal homepage: http://www.eurasianjournals.com/index.php/ejpce Students Understanding of Graphical Vector Addition in One and Two Dimensions Umporn
Learning Objectives by Course Matrix Objectives Course # Course Name Psyc Know ledge
 APPENDICES Learning Objectives by Course Matrix Objectives Course # Course Name 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Psyc Know ledge Integration across domains Psyc as Science Critical Thinking Diversity Ethics Applying
APPENDICES Learning Objectives by Course Matrix Objectives Course # Course Name 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Psyc Know ledge Integration across domains Psyc as Science Critical Thinking Diversity Ethics Applying
Model of Lesson Study Approach during Micro Teaching
 International Education Studies; Vol. 7, No. 13; 2014 ISSN 1913-9020 E-ISSN 1913-9039 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Model of Lesson Study Approach during Micro Teaching Zanaton
International Education Studies; Vol. 7, No. 13; 2014 ISSN 1913-9020 E-ISSN 1913-9039 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Model of Lesson Study Approach during Micro Teaching Zanaton
A Critique of Running Records
 Critique of Running Records 1 A Critique of Running Records Ken E. Blaiklock UNITEC Institute of Technology Auckland New Zealand Paper presented at the New Zealand Association for Research in Education/
Critique of Running Records 1 A Critique of Running Records Ken E. Blaiklock UNITEC Institute of Technology Auckland New Zealand Paper presented at the New Zealand Association for Research in Education/
A Minimalist Approach to Code-Switching. In the field of linguistics, the topic of bilingualism is a broad one. There are many
 Schmidt 1 Eric Schmidt Prof. Suzanne Flynn Linguistic Study of Bilingualism December 13, 2013 A Minimalist Approach to Code-Switching In the field of linguistics, the topic of bilingualism is a broad one.
Schmidt 1 Eric Schmidt Prof. Suzanne Flynn Linguistic Study of Bilingualism December 13, 2013 A Minimalist Approach to Code-Switching In the field of linguistics, the topic of bilingualism is a broad one.
Key concepts for the insider-researcher
 02-Costley-3998-CH-01:Costley -3998- CH 01 07/01/2010 11:09 AM Page 1 1 Key concepts for the insider-researcher Key points A most important aspect of work based research is the researcher s situatedness
02-Costley-3998-CH-01:Costley -3998- CH 01 07/01/2010 11:09 AM Page 1 1 Key concepts for the insider-researcher Key points A most important aspect of work based research is the researcher s situatedness
DOROTHY ECONOMOU CURRICULUM VITAE
 DOROTHY ECONOMOU CURRICULUM VITAE 115/71 Victoria St Pott s Pt, Sydney NSW 2011 AUSTRALIA TEL: 0418403629 dorothyeconomou@gmail.com NATIONALITY: Australian LANGUAGES: English/Greek (bilingual) ACADEMIC
DOROTHY ECONOMOU CURRICULUM VITAE 115/71 Victoria St Pott s Pt, Sydney NSW 2011 AUSTRALIA TEL: 0418403629 dorothyeconomou@gmail.com NATIONALITY: Australian LANGUAGES: English/Greek (bilingual) ACADEMIC
Applying Second Language Acquisition Research to English Language Teaching in Taiwan
 International Journal on Studies in English Language and Literature (IJSELL) Volume 1, Issue 2 (July 2013), PP 1-12 ISSN 2347-3126 (Print) & ISSN 2347-3134 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Applying Second
International Journal on Studies in English Language and Literature (IJSELL) Volume 1, Issue 2 (July 2013), PP 1-12 ISSN 2347-3126 (Print) & ISSN 2347-3134 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Applying Second
International Conference on Education and Educational Psychology (ICEEPSY 2012)
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 69 ( 2012 ) 984 989 International Conference on Education and Educational Psychology (ICEEPSY 2012) Second language research
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 69 ( 2012 ) 984 989 International Conference on Education and Educational Psychology (ICEEPSY 2012) Second language research
