Level Q/40 Protecting Our Oceans. Science
|
|
|
- Lynne Eileen Houston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Level Q/40 For students reading at Literacy Level Q/40, including: Grade 4 readers Grade 5 8+ students reading below level English-language learners at TESOL Level 5 Science Skills & Strategies Comprehension Strategies Identify Cause and Effect Summarize Information Use Graphic Features to Interpret Information Use Text Features to Locate Information Metacognitive Strategy Make connections Vocabulary Develop academic content vocabulary Phonics/Word Study Recognize words with -y endings Grammar and Usage Use when adverbs Fluency Read exclamation points Bridges Theme: The Environment Deforestation and Desertification (Level R/40) (Level Q/40) Ecological Disasters (Level R/40) Science Big Idea Readers learn how pollution happens, how pollution affects marine life, and what s being done to stop ocean pollution. B e n c h m a r k E d u c a t i o n C o m p a n y
2 Prepare to Read Build Comprehension Pictures To Think About Hand out books. Read the title aloud. Ask students to tell what they see on the cover. Tell students that keeping our oceans clean is important if we want a healthy Earth. Have students turn to the page titled Pictures To Think About. Tell them they will use information on these pages to help recall and add to what they already know about protecting the oceans. Use the map in the center to point out the world s seas and oceans. On the board, create a chart with two columns labeled What is it? and What do I know about it? Have students make a copy on paper. Ask partners to study each photograph, starting with the top picture on the left-hand page and moving clockwise. Have students complete as much of the chart as they can on their own and then share their ideas with the class. Use the sample chart below to help them fill in any missing information. Invite students to find each photograph in the book and read its caption. Words To Think About Have students turn to the Words To Think About spread. Ask them to study the word map for toxic and think of other characteristics and examples to add. Then read page 7 and ask: What characteristics and examples can you add now? What do you think toxic means? (harmful to fish, wildlife, and plants) Ask students to study the word bench for ecosystem. Explain that this word is made up of two word parts from Greek and Latin. Read the parts out loud for students. Say: Put the word parts together. Dwelling place organized doesn t make sense, but think of a dwelling place as a community. Does organized community make sense? Then read the first paragraph on page 3 and ask: What do you think ecosystem means? (a community of things that live together and interact with their environment) Ask students to study the word pedestal for sewage and think of other answers. Then read page 4 and ask: What information can we add now? What do you think the word sewage means? (human waste) Remind students that good readers use their own knowledge and the text to figure out the meanings of words. Pictures To Think About Photograph What is it? What do I know about it? 1 bird covered in oil cannot live with oil on feathers 2 volunteers people picking up litter to keep beaches clean 3 life under the sea clean, healthy ocean environment 4 junk piled up near water often ends up in the ocean Benchmark Education Company, LLC. All rights reserved. No part of the guide may be reproduced or transmitted in whole or in part in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopy, recording, or any information storage or retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher. ISBN: Benchmark Education Company, LLC
3 Before Reading Preview the Book Turn to the Table of Contents. Point out that each chapter title has the word pollution in it. Ask student partners to discuss what they think they will learn while reading the book. Turn to the Index. Explain that an index lists the topics in alphabetical order and the pages they are found on. Ask students to find the words dead zone in the Index and then again on the correct pages in the book. Set Learning Goals Pair students and ask them to generate a learning-goal statement about the book s topic, such as I want to learn what I can do to help keep oceans clean. Have pairs share their statements with the group. Post the learning-goal statements on the board in the classroom. Build Vocabulary for Comprehension Write the words toxic, ecosystem, and sewage on the board. Remind students that they have already discussed these three important words. Tell them you will now share additional words they will need to know, adding acid rain, bacteria, chemicals, currents, debris, food chain, plankton, and polluted to the list on the board. Read each word and ask students to pronounce it. Model how to sort the words on a threecolumn chart labeled Know, Think I Know, and Do Not Know. Say: I know the word polluted. I will write polluted in the first column. I do not know the word debris. I will write debris in the last column. I have heard of a food chain, but I do not know much about it. I will write food chain in the center column. Ask students to make their own charts and sort the words according to their current understanding of each one. Explain that as they learn more about these words, they can move them to different columns. Know Think I Know Do Not Know polluted food chain debris Introduction Ask students to turn to the Introduction on pages 2 and 3. Explain that an introduction tells what a book is about. Ask students to discuss what they see in the photograph and map and why they think the author put these here. Invite students to read the Introduction silently. Then ask: What is the most surprising or interesting thing you learned about oceans? What would you like to learn more about? Turn to a partner and discuss your answers. After partners confer, invite them to share their thoughts with the group. Text and Graphic Features Use this table to help students see how text and graphic features provide extra information to readers. Chapter Feature Prompts Answers 1 map (pp. 8 9) 1. What vocabulary word goes with this map? 2. What does the map help explain? 1. currents 2. how currents can carry sewage and debris thousands of miles 2 sidebar (p. 15) 3 chart (p. 27) 1. Why do you think the author included this sidebar? 2. How are the sidebar photographs similar? How are they different? 1. What vocabulary word goes with this chart? 2. How are the items on the chart arranged? 1. to introduce the term food chain and describe one food source, plankton 2. Both photos show plankton: the top photo shows plankton from a distance; the bottom photo shows plankton close up. 1. debris 2. from most to least pieces of debris 2011 Benchmark Education Company, LLC 3
4 Chapter 1 4 Before Reading Build Vocabulary for Comprehension Write polluted, debris, chemicals, bacteria, currents, and acid rain on the board. Point out that the author defines polluted with a synonym on page 2 by using a comma and the word or. Ask: What is the synonym for polluted? (dirtied) Say: The author uses the words another word for on page 5 to tell us she is defining the word. Ask students to define debris. Repeat the process with chemicals on page 7, bacteria on page 8, and acid rain on page 13. Say: The author describes currents on page 9. Let s find the clues to its meaning. (ocean, can carry, thousands of miles) Have students define currents. Model Monitor-Reading Strategy: Make Connections Say: One way to make sure I understand what I read is to make connections to the information. I can make connections to my own life, to the world, or to other books I have read. Use a real-life example to demonstrate making connections. Explain that today, students will connect the information in Chapter 1 with their own lives. Read page 4 aloud while students follow along. Say: I ve seen trash that people leave behind in the park, so I can imagine what this beach looks like. This connection helps me understand how trash is a form of pollution. Set Purpose for Reading Ask students to read pages 4 13 silently and write about connections to their own lives in their journals. Tell students they will read to answer the question How does pollution happen? During Reading Observe and Prompt Reading Strategies Watch as students record connections between their lives and the text. Document who is and is not using this monitor-reading strategy. Take note of students who have difficulty. After Reading Discuss the Reading Ask students to share the connections they made as they read pages 4 13, and invite volunteers to explain how making text-to-self connections helped them better understand their reading. Have students answer the question How does pollution happen? To focus on text and graphic features for Chapter 1, use the map prompt from the chart on page 3 of this guide. Read and discuss the checkpoint on page 13. Use the Bridges: Com pre hension Question Card for textdependent questions that refer to this section. Review Vocabulary Ask students to restate the synonym given for polluted; the direct definitions given for debris, chemicals, bacteria, and acid rain; and the description given for currents. Ask students to locate the words on their vocabulary charts and decide if they want to move any to another column. Summarize Information Explain that a summary gives the key ideas from a book. Say: To help myself remember what I read, I often summarize the information in a chapter. Summarizing means pulling out the most important ideas and details and reducing a long piece of text to something short and to the point. Have students review Chapter 1. As a group, decide on the key ideas and have one or two students write the information on chart paper or the board. (Our oceans are badly polluted. People let debris and sewage get into the water. Currents then spread the pollution all over the world. Oil spills and acid rain also pollute the oceans.) Keep the key ideas posted. Say: After we select the key ideas from the rest of the book, we will write a summary together Benchmark Education Company, LLC
5 Chapter 2 Before Reading Build Vocabulary for Comprehension Write the words food chain and plankton on the board. Guide students to see that food chain is directly defined on page 15. Say: The word called is a clue that the author is defining food chain. Ask students to define food chain using the text. Repeat the process with plankton on page 15. Guide Monitor-Reading Strategy: Make Connections Remind students that when they make connections to what they read, they better understand and remember the information. Say: Today we will make another type of connection. We will connect what we read in the text with what we already know about the world. As you read page 14 aloud, stop to model a text-to-world connection. At the end of the page, ask: What connections can you make between the plants and animals in the ocean ecosystem and what you already know about plants and animals? Set Purpose for Reading Ask students to read Chapter 2 and to make and record connections between what they are reading and what they know about the world. Tell students they will read to answer the question How does pollution affect marine life? After Reading Discuss the Reading Ask students to share some of their text-toworld connections with the class. Ask: How did connecting your reading to what you know about the world help you understand how pollution affects plants and animals? Discuss students responses. Have students answer the question How does pollution affect marine life? To focus on text and graphic features for Chapter 2, use the sidebar prompt from the chart on page 3 of this guide. Use the Bridges: Com prehension Question Card for textdependent questions that refer to this section. Review Vocabulary Ask students to restate the direct definitions given for food chain and plankton. Ask students to decide if they want to move either of the words to another column on their vocabulary charts. Summarize Information As a group, decide on the key ideas from Chapter 2 and add them to the Chapter 1 summary. (Ocean pollution affects all living things. Pollution kills plants. Pollution can blind or burn fish. Birds with oil on their feathers cannot fly. Sea animals may swallow debris and die. Marine biologists study the ocean and its animals. They try to find ways to protect the ocean s ecosystems.) During Reading Observe and Prompt Reading Strategies As students read, observe them carefully. For students who struggle with making connections, model it again. Then read the first paragraph on page 16 aloud. Encourage students to make connections between the text and what they already know about oil spills Benchmark Education Company, LLC 5
6 Chapter 3 and Conclusion Before Reading Build Vocabulary for Comprehension Although no glossary words appear in Chapter 3 or the Conclusion, use this opportunity to introduce additional content words. Write the words cooperate and recycle on the board. Have students turn to page 26 and find cooperate. Say: The author does not directly define cooperate, but we can figure out the meaning using clues in the paragraphs. Guide students to see that people cooperate when they all clean up the coasts, so cooperate must mean work together. Repeat the process with recycle on page 30, noting the clues in the previous sentence and defining recycle as to process materials to use again. Apply Monitor-Reading Strategy: Make Connections Remind students that they have connected the information in the book to their own lives and to what they know about the world. Say: Now we will make connections to other texts we have read. Read page 24 aloud as students follow along. Say: This reminds me of an article I read about recycling. The author said communities that recycle have less litter. Then ask students to share other texts they have read about trash, recycling, or pollution. Say: Making connections helps you better understand what you read. Encourage students to make text-to-text connections as they finish reading the book. Set Purpose for Reading Ask students to read Chapter 3 and the Conclusion, making connections to other texts they have read. Tell students they will read to answer the question How can we stop ocean pollution? During Reading Observe and Prompt Reading Strategies As students read, watch them record connections between this text and other texts they have read. Ask yourself Who is still struggling with this strategy? How can I help them? and provide support as needed. After Reading Discuss the Reading Ask students to share text-to-text connections with the group. Ask: How did making connections to other texts you have read help you understand the efforts to stop pollution? Discuss students responses. Have students answer the question How can we stop ocean pollution? To focus on text and graphic features for Chapter 3, use the chart prompt from the chart on page 3 of this guide. Read and discuss the checkpoint on page 29. Use the Bridges: Com prehension Question Card for textdependent questions that refer to this section. Review Vocabulary Ask students to restate the descriptions given for cooperate and recycle, and invite them to add the words to a column on their vocabulary charts. Summarize Information Have students turn to Chapter 3. Ask: What are the key ideas from Chapter 3? (People and governments are working to prevent ocean pollution. People clean up beaches, throw garbage away safely, and recycle paper, aluminum, and glass. Governments create laws to make the air and water cleaner.) Tell students they will write a summary of the book later on in the lesson Benchmark Education Company, LLC
7 After Reading Build Comprehension Identify Cause and Effect Model Say: A cause is what makes something happen, and an effect is what happens. Sometimes authors provide clue words, such as because or as a result. Other times we must recognize causes and effects on our own. I notice on page 4 the author asks, What causes pollution? The clue word causes tells me the author is talking about a cause-andeffect relationship. She gives the cause in the next sentence. People being careless about throwing out trash is the cause. The effect is pollution of beaches and oceans. Draw a chart on the board with three columns labeled Page, Cause, and Effect and ask students to create similar charts on paper. Record information for the cause and effect from pp. 4 5 while students do the same. Guide Help students locate the cause-andeffect relationship in the second paragraph on page 11, making sure they note the clue word cause. Record their responses on your chart as students do the same. Have students reread page 14. Say: The author says sometimes pollution harms one plant or animal, and the whole ecosystem changes. What is the cause? What is the effect? Record students responses in the appropriate columns while they do the same. Apply Reread the chart and then explain that student partners will find causes and effects on pages 16 and 19. Remind them to look for clue words, such as how. Ask students if they have any questions before they begin. Monitor their work and intervene if they have difficulty. If students find cause-and-effect relationships different from those in the sample, be sure they are supported by the text. Review the completed graphic organizer. Shared Writing Summarize the Book Say: We have selected key ideas from each chapter. Now we will work together to write a summary of the entire book. Review the key ideas recorded on chart paper, and then ask: How can we summarize the book in our own words? Ask one or two students to serve as scribes as the class forms summary sentences. Sample Summary for The world s oceans are polluted. Debris, sewage, and toxic waste escape from the land into the water. Oil spills and acid rain damage ocean plants and animals. Pollution harms the oceans ecosystems. Chemicals can kill fish and make plants grow too fast. Oil covers birds so they cannot fly. Animals die from eating debris. Fortunately, scientists, governments, and citizens are learning to solve the problems. New laws and better practices can clean up our oceans. Identify Cause and Effect Page Cause Effect 5 People were careless about throwing out their trash. The beaches and oceans were polluted. 11 An oil tanker hits rocks, which make a hole in its tanks. Oil flows from the tanks into the ocean. 14 Pollution harms one plant or animal. The whole ecosystem changes. 16 Algae use up all the oxygen in the ocean. Fish do not have enough oxygen to breathe. 19 Oil coats birds feathers. Birds cannot fly Benchmark Education Company, LLC 7
8 Intervention Support for Struggling Readers and ELLs Phonics/Word Study -y Ending Ask students to locate the word partly on page 3. Write partly on the board and circle y. Say: The y at the end of partly stands for the long e sound. Slowly draw your finger under the word as you say it, emphasizing the final sound. Ask students to do the same in their books. Ask students to skim the book for other words in which final y sounds like a long e, such as family, carry, estuary, plenty, many, energy, tiny, biology, chemistry, fifty, very, and every. Write the words on the board as students locate them. Model selecting a word to use in an oral sentence about oceans, such as Big fish eat tiny fish. Then invite student partners to do the same. See SpiralUp Phonics Skill Bag #25 from BEC for more in-depth instruction. Fluency Read Exclamation Points Say: Sometimes authors show that something is amazing or exciting by using an exclamation point. Our voices sound different when we are excited or amazed. We speak a bit faster and our voices move to a higher pitch. Ask students to turn to page 9. Read the page in a flat voice. Then read the page again, saying the exclamation more quickly and in a higher pitch. Say: Reading more quickly and using a higher pitch expresses the author s amazement at this interesting fact. Have students read the paragraph aloud as modeled. Invite students to locate a sentence with an exclamation point on page 12 and take turns reading it, speaking faster and using a higher pitch. Grammar and Usage When Adverbs Say: Authors often use describing words when they write. Adverbs are words that describe where, how, or when. Today we will use adverbs that describe when. Ask students to turn to page 5. Say: The author writes Sometimes tires and used needles become debris. The word sometimes is an adverb. Sometimes tells us when tires and used needles become debris. Invite students to read the third paragraph of page 15 with you. Ask: Which word is an adverb? (often) Why is often an adverb? (Often describes when food chains are connected.) What could you describe with the adverb often? Ask students to locate the when adverb in the sidebar on page 19. (today) Invite partners to make up their own sentences using today. Then ask them to think of another adverb that could replace today in the sentence, such as now or presently Benchmark Education Company, LLC
A Pumpkin Grows. Written by Linda D. Bullock and illustrated by Debby Fisher
 GUIDED READING REPORT A Pumpkin Grows Written by Linda D. Bullock and illustrated by Debby Fisher KEY IDEA This nonfiction text traces the stages a pumpkin goes through as it grows from a seed to become
GUIDED READING REPORT A Pumpkin Grows Written by Linda D. Bullock and illustrated by Debby Fisher KEY IDEA This nonfiction text traces the stages a pumpkin goes through as it grows from a seed to become
Biome I Can Statements
 Biome I Can Statements I can recognize the meanings of abbreviations. I can use dictionaries, thesauruses, glossaries, textual features (footnotes, sidebars, etc.) and technology to define and pronounce
Biome I Can Statements I can recognize the meanings of abbreviations. I can use dictionaries, thesauruses, glossaries, textual features (footnotes, sidebars, etc.) and technology to define and pronounce
Chapter 9 Banked gap-filling
 Chapter 9 Banked gap-filling This testing technique is known as banked gap-filling, because you have to choose the appropriate word from a bank of alternatives. In a banked gap-filling task, similarly
Chapter 9 Banked gap-filling This testing technique is known as banked gap-filling, because you have to choose the appropriate word from a bank of alternatives. In a banked gap-filling task, similarly
been each get other TASK #1 Fry Words TASK #2 Fry Words Write the following words in ABC order: Write the following words in ABC order:
 TASK #1 Fry Words 1-100 been each called down about first TASK #2 Fry Words 1-100 get other long people number into TASK #3 Fry Words 1-100 could part more find now her TASK #4 Fry Words 1-100 for write
TASK #1 Fry Words 1-100 been each called down about first TASK #2 Fry Words 1-100 get other long people number into TASK #3 Fry Words 1-100 could part more find now her TASK #4 Fry Words 1-100 for write
Tap vs. Bottled Water
 Tap vs. Bottled Water CSU Expository Reading and Writing Modules Tap vs. Bottled Water Student Version 1 CSU Expository Reading and Writing Modules Tap vs. Bottled Water Student Version 2 Name: Block:
Tap vs. Bottled Water CSU Expository Reading and Writing Modules Tap vs. Bottled Water Student Version 1 CSU Expository Reading and Writing Modules Tap vs. Bottled Water Student Version 2 Name: Block:
Grade 8: Module 4: Unit 1: Lesson 11 Evaluating an Argument: The Joy of Hunting
 Grade 8: Module 4: Unit 1: Lesson 11 Evaluating an Argument: The Joy of Hunting This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party
Grade 8: Module 4: Unit 1: Lesson 11 Evaluating an Argument: The Joy of Hunting This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party
Fountas-Pinnell Level P Informational Text
 LESSON 7 TEACHER S GUIDE Now Showing in Your Living Room by Lisa Cocca Fountas-Pinnell Level P Informational Text Selection Summary This selection spans the history of television in the United States,
LESSON 7 TEACHER S GUIDE Now Showing in Your Living Room by Lisa Cocca Fountas-Pinnell Level P Informational Text Selection Summary This selection spans the history of television in the United States,
Grade 5: Module 2A: Unit 1: Lesson 6 Analyzing an Interview with a Rainforest Scientist Part 1
 Grade 5: Module 2A: Unit 1: Lesson 6 Analyzing an Interview with a Rainforest Scientist Part 1 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Grade 5: Module 2A: Unit 1: Lesson 6 Analyzing an Interview with a Rainforest Scientist Part 1 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Trophies Grade 5
 Unit 6/Week 2 Title: The Golden Lion Tamarin Comes Home Suggested Time: 5 days (45 minutes per day) Common Core ELA Standards: RI.5.1, RI.5.3, RL.5.4, RI.5.8; RF.5.3, RF.5.4; W.5.2, W.5.4, W.5.9; SL.5.1,
Unit 6/Week 2 Title: The Golden Lion Tamarin Comes Home Suggested Time: 5 days (45 minutes per day) Common Core ELA Standards: RI.5.1, RI.5.3, RL.5.4, RI.5.8; RF.5.3, RF.5.4; W.5.2, W.5.4, W.5.9; SL.5.1,
Universal Design for Learning Lesson Plan
 Universal Design for Learning Lesson Plan Teacher(s): Alexandra Romano Date: April 9 th, 2014 Subject: English Language Arts NYS Common Core Standard: RL.5 Reading Standards for Literature Cluster Key
Universal Design for Learning Lesson Plan Teacher(s): Alexandra Romano Date: April 9 th, 2014 Subject: English Language Arts NYS Common Core Standard: RL.5 Reading Standards for Literature Cluster Key
Stakeholder Debate: Wind Energy
 Activity ENGAGE For Educator Stakeholder Debate: Wind Energy How do stakeholder interests determine which specific resources a community will use? For the complete activity with media resources, visit:
Activity ENGAGE For Educator Stakeholder Debate: Wind Energy How do stakeholder interests determine which specific resources a community will use? For the complete activity with media resources, visit:
Table of Contents. Introduction Choral Reading How to Use This Book...5. Cloze Activities Correlation to TESOL Standards...
 Table of Contents Introduction.... 4 How to Use This Book.....................5 Correlation to TESOL Standards... 6 ESL Terms.... 8 Levels of English Language Proficiency... 9 The Four Language Domains.............
Table of Contents Introduction.... 4 How to Use This Book.....................5 Correlation to TESOL Standards... 6 ESL Terms.... 8 Levels of English Language Proficiency... 9 The Four Language Domains.............
Common Core Exemplar for English Language Arts and Social Studies: GRADE 1
 The Common Core State Standards and the Social Studies: Preparing Young Students for College, Career, and Citizenship Common Core Exemplar for English Language Arts and Social Studies: Why We Need Rules
The Common Core State Standards and the Social Studies: Preparing Young Students for College, Career, and Citizenship Common Core Exemplar for English Language Arts and Social Studies: Why We Need Rules
Characteristics of the Text Genre Informational Text Text Structure
 LESSON 4 TEACHER S GUIDE by Taiyo Kobayashi Fountas-Pinnell Level C Informational Text Selection Summary The narrator presents key locations in his town and why each is important to the community: a store,
LESSON 4 TEACHER S GUIDE by Taiyo Kobayashi Fountas-Pinnell Level C Informational Text Selection Summary The narrator presents key locations in his town and why each is important to the community: a store,
SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE
 FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York Le REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION LIVING ENVIRONMENT Wednesday, June 19, 2002 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Directions
FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York Le REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION LIVING ENVIRONMENT Wednesday, June 19, 2002 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Directions
Grade 8: Module 4: Unit 1: Lesson 8 Reading for Gist and Answering Text-Dependent Questions: Local Sustainable Food Chain
 Grade 8: Module 4: Unit 1: Lesson 8 Reading for Gist and Answering Text-Dependent Questions: This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt
Grade 8: Module 4: Unit 1: Lesson 8 Reading for Gist and Answering Text-Dependent Questions: This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt
First Grade Curriculum Highlights: In alignment with the Common Core Standards
 First Grade Curriculum Highlights: In alignment with the Common Core Standards ENGLISH LANGUAGE ARTS Foundational Skills Print Concepts Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features
First Grade Curriculum Highlights: In alignment with the Common Core Standards ENGLISH LANGUAGE ARTS Foundational Skills Print Concepts Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features
21st CENTURY SKILLS IN 21-MINUTE LESSONS. Using Technology, Information, and Media
 21st CENTURY SKILLS IN 21-MINUTE LESSONS Using Technology, Information, and Media T Copyright 2011 by Saddleback Educational Publishing. All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced in any
21st CENTURY SKILLS IN 21-MINUTE LESSONS Using Technology, Information, and Media T Copyright 2011 by Saddleback Educational Publishing. All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced in any
Characteristics of the Text Genre Informational Text Text Structure
 LESSON 4 TEACHER S GUIDE by Jacob Walker Fountas-Pinnell Level A Informational Text Selection Summary A fire fighter shows the clothes worn when fighting fires. Number of Words: 25 Characteristics of the
LESSON 4 TEACHER S GUIDE by Jacob Walker Fountas-Pinnell Level A Informational Text Selection Summary A fire fighter shows the clothes worn when fighting fires. Number of Words: 25 Characteristics of the
Conversation Task: The Environment Concerns Us All
 At a glance Level: ISE II Conversation Task: The Environment Concerns Us All Focus: Conversation task Aims: To develop students active vocabulary when discussing the environment, to expand their knowledge
At a glance Level: ISE II Conversation Task: The Environment Concerns Us All Focus: Conversation task Aims: To develop students active vocabulary when discussing the environment, to expand their knowledge
GRADE 2 SUPPLEMENT. Set D4 Measurement: Capacity. Includes. Skills & Concepts. Activity 1: Predict & Fill D4.1
 GRADE 2 SUPPLEMENT Set D4 Measurement: Capacity Includes Activity 1: Predict & Fill D4.1 Skills & Concepts H use non-standard units to measure to determine capacity H compare and order containers according
GRADE 2 SUPPLEMENT Set D4 Measurement: Capacity Includes Activity 1: Predict & Fill D4.1 Skills & Concepts H use non-standard units to measure to determine capacity H compare and order containers according
Grade 6: Module 2A: Unit 2: Lesson 8 Mid-Unit 3 Assessment: Analyzing Structure and Theme in Stanza 4 of If
 Grade 6: Module 2A: Unit 2: Lesson 8 Mid-Unit 3 Assessment: Analyzing Structure and This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party
Grade 6: Module 2A: Unit 2: Lesson 8 Mid-Unit 3 Assessment: Analyzing Structure and This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party
TEACHING Simple Tools Set II
 TEACHING GUIDE TEACHING Simple Tools Set II Kindergarten Reading Level ISBN-10: 0-8225-6880-2 Green ISBN-13: 978-0-8225-6880-3 2 TEACHING SIMPLE TOOLS SET II Standards Science Mathematics Language Arts
TEACHING GUIDE TEACHING Simple Tools Set II Kindergarten Reading Level ISBN-10: 0-8225-6880-2 Green ISBN-13: 978-0-8225-6880-3 2 TEACHING SIMPLE TOOLS SET II Standards Science Mathematics Language Arts
P a g e 1. Grade 4. Grant funded by: MS Exemplar Unit English Language Arts Grade 4 Edition 1
 P a g e 1 Grade 4 Grant funded by: P a g e 2 Lesson 1: Understanding Themes Focus Standard(s): RL.4.2 Additional Standard(s): RL.4.1 Estimated Time: 1-2 days Resources and Materials: Handout 1.1: Details,
P a g e 1 Grade 4 Grant funded by: P a g e 2 Lesson 1: Understanding Themes Focus Standard(s): RL.4.2 Additional Standard(s): RL.4.1 Estimated Time: 1-2 days Resources and Materials: Handout 1.1: Details,
SESSION 2: HELPING HAND
 SESSION 2: HELPING HAND Ready for the next challenge? Build a device with a long handle that can grab something hanging high! This week you ll also check out your Partner Club s Paper Structure designs.
SESSION 2: HELPING HAND Ready for the next challenge? Build a device with a long handle that can grab something hanging high! This week you ll also check out your Partner Club s Paper Structure designs.
Grade 4: Module 2A: Unit 2: Lesson 4 Word Choice: Using Academic Vocabulary to Apply for a Colonial Trade Job
 Grade 4: Module 2A: Unit 2: Lesson 4 Using Academic Vocabulary to Apply for a Colonial Trade Job This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Grade 4: Module 2A: Unit 2: Lesson 4 Using Academic Vocabulary to Apply for a Colonial Trade Job This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Teaching Literacy Through Videos
 Teaching Literacy Through Videos Elizabeth Stavis Reading Intervention Specialist RR Teacher Santa Clara Unified Jenny Maehara Elementary Literacy Specialist RR Teacher Santa Clara Unified February 9,
Teaching Literacy Through Videos Elizabeth Stavis Reading Intervention Specialist RR Teacher Santa Clara Unified Jenny Maehara Elementary Literacy Specialist RR Teacher Santa Clara Unified February 9,
About this unit. Lesson one
 Unit 30 Abuja Carnival About this unit This unit revises language and phonics done throughout the year. The theme of the unit is Abuja carnival. Pupils describe a happy carnival picture and read a story
Unit 30 Abuja Carnival About this unit This unit revises language and phonics done throughout the year. The theme of the unit is Abuja carnival. Pupils describe a happy carnival picture and read a story
Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium:
 Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium: ELA Practice Test Scoring Guide Grade 5 04/25/2014 G5_PracticeTest_ScoringGuide_ELA.docx 0 1 5 1 1 2 RI-1 The student will identify text evidence to support a given
Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium: ELA Practice Test Scoring Guide Grade 5 04/25/2014 G5_PracticeTest_ScoringGuide_ELA.docx 0 1 5 1 1 2 RI-1 The student will identify text evidence to support a given
Fountas-Pinnell Level M Realistic Fiction
 LESSON 17 TEACHER S GUIDE by Vidas Barzdukas Fountas-Pinnell Level M Realistic Fiction Selection Summary Miguel lives in the Dominican Republic and loves baseball. His hero is Pedro Sanchez, a major league
LESSON 17 TEACHER S GUIDE by Vidas Barzdukas Fountas-Pinnell Level M Realistic Fiction Selection Summary Miguel lives in the Dominican Republic and loves baseball. His hero is Pedro Sanchez, a major league
Test Blueprint. Grade 3 Reading English Standards of Learning
 Test Blueprint Grade 3 Reading 2010 English Standards of Learning This revised test blueprint will be effective beginning with the spring 2017 test administration. Notice to Reader In accordance with the
Test Blueprint Grade 3 Reading 2010 English Standards of Learning This revised test blueprint will be effective beginning with the spring 2017 test administration. Notice to Reader In accordance with the
Grade 4. Common Core Adoption Process. (Unpacked Standards)
 Grade 4 Common Core Adoption Process (Unpacked Standards) Grade 4 Reading: Literature RL.4.1 Refer to details and examples in a text when explaining what the text says explicitly and when drawing inferences
Grade 4 Common Core Adoption Process (Unpacked Standards) Grade 4 Reading: Literature RL.4.1 Refer to details and examples in a text when explaining what the text says explicitly and when drawing inferences
Let's Learn English Lesson Plan
 Let's Learn English Lesson Plan Introduction: Let's Learn English lesson plans are based on the CALLA approach. See the end of each lesson for more information and resources on teaching with the CALLA
Let's Learn English Lesson Plan Introduction: Let's Learn English lesson plans are based on the CALLA approach. See the end of each lesson for more information and resources on teaching with the CALLA
Multiple Intelligence Teaching Strategy Response Groups
 Multiple Intelligence Teaching Strategy Response Groups Steps at a Glance 1 2 3 4 5 Create and move students into Response Groups. Give students resources that inspire critical thinking. Ask provocative
Multiple Intelligence Teaching Strategy Response Groups Steps at a Glance 1 2 3 4 5 Create and move students into Response Groups. Give students resources that inspire critical thinking. Ask provocative
Summarize The Main Ideas In Nonfiction Text
 Summarize The Main Ideas In Free PDF ebook Download: Summarize The Main Ideas In Download or Read Online ebook summarize the main ideas in nonfiction text in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database
Summarize The Main Ideas In Free PDF ebook Download: Summarize The Main Ideas In Download or Read Online ebook summarize the main ideas in nonfiction text in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database
Richardson, J., The Next Step in Guided Writing, Ohio Literacy Conference, 2010
 1 Procedures and Expectations for Guided Writing Procedures Context: Students write a brief response to the story they read during guided reading. At emergent levels, use dictated sentences that include
1 Procedures and Expectations for Guided Writing Procedures Context: Students write a brief response to the story they read during guided reading. At emergent levels, use dictated sentences that include
National Literacy and Numeracy Framework for years 3/4
 1. Oracy National Literacy and Numeracy Framework for years 3/4 Speaking Listening Collaboration and discussion Year 3 - Explain information and ideas using relevant vocabulary - Organise what they say
1. Oracy National Literacy and Numeracy Framework for years 3/4 Speaking Listening Collaboration and discussion Year 3 - Explain information and ideas using relevant vocabulary - Organise what they say
Effective Instruction for Struggling Readers
 Section II Effective Instruction for Struggling Readers Chapter 5 Components of Effective Instruction After conducting assessments, Ms. Lopez should be aware of her students needs in the following areas:
Section II Effective Instruction for Struggling Readers Chapter 5 Components of Effective Instruction After conducting assessments, Ms. Lopez should be aware of her students needs in the following areas:
Unit: Human Impact Differentiated (Tiered) Task How Does Human Activity Impact Soil Erosion?
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
READTHEORY TEACHING STUDENTS TO READ AND THINK CRITICALLY
 READTHEORY TEACHING STUDENTS TO READ AND THINK CRITICALLY "Bullet Trains" Reading Comprehension Assessment ReadTheory.org For exciting updates, offers, and other helpful information, follow us on Facebook
READTHEORY TEACHING STUDENTS TO READ AND THINK CRITICALLY "Bullet Trains" Reading Comprehension Assessment ReadTheory.org For exciting updates, offers, and other helpful information, follow us on Facebook
Welcome to the Purdue OWL. Where do I begin? General Strategies. Personalizing Proofreading
 Welcome to the Purdue OWL This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue (http://owl.english.purdue.edu/). When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice at bottom. Where do I begin?
Welcome to the Purdue OWL This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue (http://owl.english.purdue.edu/). When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice at bottom. Where do I begin?
1. Locate and describe major physical features and analyze how they influenced cultures/civilizations studied.
 Unit Plan 8th Grade Geography Ciara Timothy SOST 450- Professor Johnson 2.22.2012 Contents: 1. Student Handout 2. Day to Day Outline 3. MN Graduation Standards and Benchmarks 4. Differentiated for Content,
Unit Plan 8th Grade Geography Ciara Timothy SOST 450- Professor Johnson 2.22.2012 Contents: 1. Student Handout 2. Day to Day Outline 3. MN Graduation Standards and Benchmarks 4. Differentiated for Content,
CLASSIFICATION OF PROGRAM Critical Elements Analysis 1. High Priority Items Phonemic Awareness Instruction
 CLASSIFICATION OF PROGRAM Critical Elements Analysis 1 Program Name: Macmillan/McGraw Hill Reading 2003 Date of Publication: 2003 Publisher: Macmillan/McGraw Hill Reviewer Code: 1. X The program meets
CLASSIFICATION OF PROGRAM Critical Elements Analysis 1 Program Name: Macmillan/McGraw Hill Reading 2003 Date of Publication: 2003 Publisher: Macmillan/McGraw Hill Reviewer Code: 1. X The program meets
Characteristics of the Text Genre Realistic fi ction Text Structure
 LESSON 14 TEACHER S GUIDE by Oscar Hagen Fountas-Pinnell Level A Realistic Fiction Selection Summary A boy and his mom visit a pond and see and count a bird, fish, turtles, and frogs. Number of Words:
LESSON 14 TEACHER S GUIDE by Oscar Hagen Fountas-Pinnell Level A Realistic Fiction Selection Summary A boy and his mom visit a pond and see and count a bird, fish, turtles, and frogs. Number of Words:
Language Acquisition Chart
 Language Acquisition Chart This chart was designed to help teachers better understand the process of second language acquisition. Please use this chart as a resource for learning more about the way people
Language Acquisition Chart This chart was designed to help teachers better understand the process of second language acquisition. Please use this chart as a resource for learning more about the way people
Evolution in Paradise
 Evolution in Paradise Engaging science lessons for middle and high school brought to you by BirdSleuth K-12 and the most extravagant birds in the world! The Evolution in Paradise lesson series is part
Evolution in Paradise Engaging science lessons for middle and high school brought to you by BirdSleuth K-12 and the most extravagant birds in the world! The Evolution in Paradise lesson series is part
9.2.2 Lesson 5. Introduction. Standards D R A F T
 9.2.2 Lesson 5 Introduction In this lesson, students will begin their exploration of Oedipus s confrontation with the blind prophet Teiresias in Oedipus the King. Students will read from Teiresias, you
9.2.2 Lesson 5 Introduction In this lesson, students will begin their exploration of Oedipus s confrontation with the blind prophet Teiresias in Oedipus the King. Students will read from Teiresias, you
PART C: ENERGIZERS & TEAM-BUILDING ACTIVITIES TO SUPPORT YOUTH-ADULT PARTNERSHIPS
 PART C: ENERGIZERS & TEAM-BUILDING ACTIVITIES TO SUPPORT YOUTH-ADULT PARTNERSHIPS The following energizers and team-building activities can help strengthen the core team and help the participants get to
PART C: ENERGIZERS & TEAM-BUILDING ACTIVITIES TO SUPPORT YOUTH-ADULT PARTNERSHIPS The following energizers and team-building activities can help strengthen the core team and help the participants get to
Writing Unit of Study Kindergarten- Looking Closely: Observing, Labeling and Listing Like Scientists Unit #3 KDG Label & List Unit #3 10/15/12 Draft
 KDG Label & List 10/15/12 Draft Table of Contents Background Section Abstract.3 Unit Section Resources and Materials Needed..5 Why a Script?...7 Assessing Writers 8 Overview of Sessions Teaching and Learning
KDG Label & List 10/15/12 Draft Table of Contents Background Section Abstract.3 Unit Section Resources and Materials Needed..5 Why a Script?...7 Assessing Writers 8 Overview of Sessions Teaching and Learning
Learning Lesson Study Course
 Learning Lesson Study Course Developed originally in Japan and adapted by Developmental Studies Center for use in schools across the United States, lesson study is a model of professional development in
Learning Lesson Study Course Developed originally in Japan and adapted by Developmental Studies Center for use in schools across the United States, lesson study is a model of professional development in
Building Vocabulary Knowledge by Teaching Paraphrasing with the Use of Synonyms Improves Comprehension for Year Six ESL Students
 Building Vocabulary Knowledge by Teaching Paraphrasing with the Use of Synonyms Improves Comprehension for Year Six ESL Students Procedure The teaching procedure used in this study was based on John Munro
Building Vocabulary Knowledge by Teaching Paraphrasing with the Use of Synonyms Improves Comprehension for Year Six ESL Students Procedure The teaching procedure used in this study was based on John Munro
Grade 6: Module 4: Unit 3: Overview
 Grade 6: Module 4: Unit 3: Overview This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content is indicated by the footer: (name
Grade 6: Module 4: Unit 3: Overview This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content is indicated by the footer: (name
Grade 6: Module 4: Unit 1: Lesson 3 Tracing a Speaker s Argument: John Stossel DDT Video
 Grade 6: Module 4: Unit 1: Lesson 3 Tracing a Speaker s Argument: John Stossel DDT Video This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt
Grade 6: Module 4: Unit 1: Lesson 3 Tracing a Speaker s Argument: John Stossel DDT Video This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt
Mercer County Schools
 Mercer County Schools PRIORITIZED CURRICULUM Reading/English Language Arts Content Maps Fourth Grade Mercer County Schools PRIORITIZED CURRICULUM The Mercer County Schools Prioritized Curriculum is composed
Mercer County Schools PRIORITIZED CURRICULUM Reading/English Language Arts Content Maps Fourth Grade Mercer County Schools PRIORITIZED CURRICULUM The Mercer County Schools Prioritized Curriculum is composed
Curriculum Scavenger Hunt
 Curriculum Training Guide for The Power of the Wind Purpose: To identify the setup and key components in The Power of the Wind Curriculum Guide. Time: 40 minutes Materials: Trainer Resource: Curriculum
Curriculum Training Guide for The Power of the Wind Purpose: To identify the setup and key components in The Power of the Wind Curriculum Guide. Time: 40 minutes Materials: Trainer Resource: Curriculum
Ocean Exploration: Diving Deep into Ocean Science. Developed by: Sierra Tobiason, Lynn Fujii and Noe Taum
 Ocean Exploration: Diving Deep into Ocean Science Grade Level: Sixth Grade Developed by: Sierra Tobiason, Lynn Fujii and Noe Taum Purpose: This curriculum is designed to communicate: I. Methods scientist
Ocean Exploration: Diving Deep into Ocean Science Grade Level: Sixth Grade Developed by: Sierra Tobiason, Lynn Fujii and Noe Taum Purpose: This curriculum is designed to communicate: I. Methods scientist
How to Use Text Features Poster
 How to Use Text Features Poster Congratulations on your purchase of this Really Good Stuff How to Use Text Features Poster, an excellent visual aide for students learning to identify and use informational
How to Use Text Features Poster Congratulations on your purchase of this Really Good Stuff How to Use Text Features Poster, an excellent visual aide for students learning to identify and use informational
Florida Reading Endorsement Alignment Matrix Competency 1
 Florida Reading Endorsement Alignment Matrix Competency 1 Reading Endorsement Guiding Principle: Teachers will understand and teach reading as an ongoing strategic process resulting in students comprehending
Florida Reading Endorsement Alignment Matrix Competency 1 Reading Endorsement Guiding Principle: Teachers will understand and teach reading as an ongoing strategic process resulting in students comprehending
Lesson Plan Title Aquatic Ecology
 Lesson Plan Title Aquatic Ecology Name (last, first): Larson, Don Scientific Theme(s): C-2: develop an understanding of the structure, function, behavior, development, life cycles, and diversity of living
Lesson Plan Title Aquatic Ecology Name (last, first): Larson, Don Scientific Theme(s): C-2: develop an understanding of the structure, function, behavior, development, life cycles, and diversity of living
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL
 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL PART ONE: SHORT-ANSWER
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL PART ONE: SHORT-ANSWER
PREP S SPEAKER LISTENER TECHNIQUE COACHING MANUAL
 1 PREP S SPEAKER LISTENER TECHNIQUE COACHING MANUAL IMPORTANCE OF THE SPEAKER LISTENER TECHNIQUE The Speaker Listener Technique (SLT) is a structured communication strategy that promotes clarity, understanding,
1 PREP S SPEAKER LISTENER TECHNIQUE COACHING MANUAL IMPORTANCE OF THE SPEAKER LISTENER TECHNIQUE The Speaker Listener Technique (SLT) is a structured communication strategy that promotes clarity, understanding,
Children Make a Difference
 Children Make a Difference KidsPost Reprint: Different Ways to Make a Difference KidsPost Reprint: New book encourages kids to change the world e-replica Activity: Know the News Create a News Alert Monitor
Children Make a Difference KidsPost Reprint: Different Ways to Make a Difference KidsPost Reprint: New book encourages kids to change the world e-replica Activity: Know the News Create a News Alert Monitor
Can Money Buy Happiness? EPISODE # 605
 Can Money Buy Happiness? EPISODE # 605 LESSON LEVEL Grades 6-8 KEY TOPICS Community Entrepreneurship Social responsibility LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Recognize a need in your community. 2. Learn how to come
Can Money Buy Happiness? EPISODE # 605 LESSON LEVEL Grades 6-8 KEY TOPICS Community Entrepreneurship Social responsibility LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Recognize a need in your community. 2. Learn how to come
Grade 6: Module 3B: Unit 2: Overview
 Grade 6: Module 3B: Unit 2: Overview This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content is indicated by the footer: (name
Grade 6: Module 3B: Unit 2: Overview This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content is indicated by the footer: (name
Welcome to ACT Brain Boot Camp
 Welcome to ACT Brain Boot Camp 9:30 am - 9:45 am Basics (in every room) 9:45 am - 10:15 am Breakout Session #1 ACT Math: Adame ACT Science: Moreno ACT Reading: Campbell ACT English: Lee 10:20 am - 10:50
Welcome to ACT Brain Boot Camp 9:30 am - 9:45 am Basics (in every room) 9:45 am - 10:15 am Breakout Session #1 ACT Math: Adame ACT Science: Moreno ACT Reading: Campbell ACT English: Lee 10:20 am - 10:50
Using SAM Central With iread
 Using SAM Central With iread January 1, 2016 For use with iread version 1.2 or later, SAM Central, and Student Achievement Manager version 2.4 or later PDF0868 (PDF) Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing
Using SAM Central With iread January 1, 2016 For use with iread version 1.2 or later, SAM Central, and Student Achievement Manager version 2.4 or later PDF0868 (PDF) Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing
Grade 3 Science Life Unit (3.L.2)
 Grade 3 Science Life Unit (3.L.2) Decision 1: What will students learn in this unit? Standards Addressed: Science 3.L.2 Understand how plants survive in their environments. Ask and answer questions to
Grade 3 Science Life Unit (3.L.2) Decision 1: What will students learn in this unit? Standards Addressed: Science 3.L.2 Understand how plants survive in their environments. Ask and answer questions to
Grade 3: Module 1: Unit 3: Lesson 5 Jigsaw Groups and Planning for Paragraph Writing about Waiting for the Biblioburro
 Grade 3: Module 1: Unit 3: Lesson 5 Jigsaw Groups and Planning for Paragraph Writing about Waiting for the Biblioburro This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Grade 3: Module 1: Unit 3: Lesson 5 Jigsaw Groups and Planning for Paragraph Writing about Waiting for the Biblioburro This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Discover how you can build students reading skills with SRA Leveled Readers!
 Discover how you can build students reading skills with SRA Leveled Readers! Your comprehensive Leveled Reading Library for Grades 1 8 Including titles for science, social studies, and intervention Interest
Discover how you can build students reading skills with SRA Leveled Readers! Your comprehensive Leveled Reading Library for Grades 1 8 Including titles for science, social studies, and intervention Interest
MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm
 MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm Why participate in the Science Fair? Science fair projects give students
MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm Why participate in the Science Fair? Science fair projects give students
Grade 6: Module 4: Unit 1: Overview
 Grade 6: Module 4: Unit 1: Overview This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content is indicated by the footer: (name
Grade 6: Module 4: Unit 1: Overview This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content is indicated by the footer: (name
Creation. Shepherd Guides. Creation 129. Tear here for easy use!
 Shepherd Guides Creation Creation 129 SHEPHERD GUIDE Creation (Genesis 1 2) Lower Elementary Welcome to the story of Creation! As the caring leader of your small group of kids, you are an important part
Shepherd Guides Creation Creation 129 SHEPHERD GUIDE Creation (Genesis 1 2) Lower Elementary Welcome to the story of Creation! As the caring leader of your small group of kids, you are an important part
Igneous Rock Formation
 Igneous Rock Formation *adapted from TOPS Learning Systems 1) Lay down a row of saturated salt water drops along the diameter of an aluminum pie tin. 2) Rest the tin on a jar so a candle fits under the
Igneous Rock Formation *adapted from TOPS Learning Systems 1) Lay down a row of saturated salt water drops along the diameter of an aluminum pie tin. 2) Rest the tin on a jar so a candle fits under the
ELA/ELD Standards Correlation Matrix for ELD Materials Grade 1 Reading
 ELA/ELD Correlation Matrix for ELD Materials Grade 1 Reading The English Language Arts (ELA) required for the one hour of English-Language Development (ELD) Materials are listed in Appendix 9-A, Matrix
ELA/ELD Correlation Matrix for ELD Materials Grade 1 Reading The English Language Arts (ELA) required for the one hour of English-Language Development (ELD) Materials are listed in Appendix 9-A, Matrix
Grade 5: Module 3A: Overview
 Grade 5: Module 3A: Overview This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content is indicated by the footer: (name of copyright
Grade 5: Module 3A: Overview This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content is indicated by the footer: (name of copyright
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 5: HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS
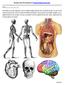 SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 5: HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS NAME: This booklet is an in-class assignment; you must complete all pages during the class work periods provided. You must use full sentences for all sections
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 5: HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS NAME: This booklet is an in-class assignment; you must complete all pages during the class work periods provided. You must use full sentences for all sections
Primary English Curriculum Framework
 Primary English Curriculum Framework Primary English Curriculum Framework This curriculum framework document is based on the primary National Curriculum and the National Literacy Strategy that have been
Primary English Curriculum Framework Primary English Curriculum Framework This curriculum framework document is based on the primary National Curriculum and the National Literacy Strategy that have been
Operations and Algebraic Thinking Number and Operations in Base Ten
 Operations and Algebraic Thinking Number and Operations in Base Ten Teaching Tips: First Grade Using Best Instructional Practices with Educational Media to Enhance Learning pbskids.org/lab Boston University
Operations and Algebraic Thinking Number and Operations in Base Ten Teaching Tips: First Grade Using Best Instructional Practices with Educational Media to Enhance Learning pbskids.org/lab Boston University
Food Chain Cut And Paste Activities
 Cut And Paste Activities Free PDF ebook Download: Cut And Paste Activities Download or Read Online ebook food chain cut and paste activities in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database CO #3: Organise
Cut And Paste Activities Free PDF ebook Download: Cut And Paste Activities Download or Read Online ebook food chain cut and paste activities in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database CO #3: Organise
1. READING ENGAGEMENT 2. ORAL READING FLUENCY
 Teacher Observation Guide Animals Can Help Level 28, Page 1 Name/Date Teacher/Grade Scores: Reading Engagement /8 Oral Reading Fluency /16 Comprehension /28 Independent Range: 6 7 11 14 19 25 Book Selection
Teacher Observation Guide Animals Can Help Level 28, Page 1 Name/Date Teacher/Grade Scores: Reading Engagement /8 Oral Reading Fluency /16 Comprehension /28 Independent Range: 6 7 11 14 19 25 Book Selection
Grade 4: Module 2A: Unit 1: Lesson 3 Inferring: Who was John Allen?
 Grade 4: Module 2A: Unit 1: Lesson 3 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content is indicated by the footer: (name
Grade 4: Module 2A: Unit 1: Lesson 3 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content is indicated by the footer: (name
Longman English Interactive
 Longman English Interactive Level 3 Orientation Quick Start 2 Microphone for Speaking Activities 2 Course Navigation 3 Course Home Page 3 Course Overview 4 Course Outline 5 Navigating the Course Page 6
Longman English Interactive Level 3 Orientation Quick Start 2 Microphone for Speaking Activities 2 Course Navigation 3 Course Home Page 3 Course Overview 4 Course Outline 5 Navigating the Course Page 6
Coral Reef Fish Survey Simulation
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and Activitydevelop the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Coral Reef Fish Survey Simulation How do scientists
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and Activitydevelop the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Coral Reef Fish Survey Simulation How do scientists
The Beginning Literacy Framework
 The Beginning Literacy Framework Helping Educators: identify, create and modify text for beginning readers meet literacy goals of students with multiple disabilities in their earliest stages of literacy
The Beginning Literacy Framework Helping Educators: identify, create and modify text for beginning readers meet literacy goals of students with multiple disabilities in their earliest stages of literacy
2018 ELO Handbook Year 7
 2018 ELO Handbook Year 7 CARE COURTESY COOPERATION CHALLENGE COMMITMENT Dear Parents/Guardians In preparation for the 2018 school year we are beginning the selection process for the Enhanced Learning Opportunities
2018 ELO Handbook Year 7 CARE COURTESY COOPERATION CHALLENGE COMMITMENT Dear Parents/Guardians In preparation for the 2018 school year we are beginning the selection process for the Enhanced Learning Opportunities
Sight Word Assessment
 Make, Take & Teach Sight Word Assessment Assessment and Progress Monitoring for the Dolch 220 Sight Words What are sight words? Sight words are words that are used frequently in reading and writing. Because
Make, Take & Teach Sight Word Assessment Assessment and Progress Monitoring for the Dolch 220 Sight Words What are sight words? Sight words are words that are used frequently in reading and writing. Because
Prewriting: Drafting: Revising: Editing: Publishing:
 Prewriting: children begin to plan writing. Drafting: children put their ideas into writing and drawing. Revising: children reread the draft and decide how to rework and improve it. Editing: children polish
Prewriting: children begin to plan writing. Drafting: children put their ideas into writing and drawing. Revising: children reread the draft and decide how to rework and improve it. Editing: children polish
Unit 14 Dangerous animals
 Unit 14 Dangerous About this unit In this unit, the pupils will look at some wild living in Africa at how to keep safe from them, at the sounds they make and at their natural habitats. The unit links with
Unit 14 Dangerous About this unit In this unit, the pupils will look at some wild living in Africa at how to keep safe from them, at the sounds they make and at their natural habitats. The unit links with
Comprehension Recognize plot features of fairy tales, folk tales, fables, and myths.
 4 th Grade Language Arts Scope and Sequence 1 st Nine Weeks Instructional Units Reading Unit 1 & 2 Language Arts Unit 1& 2 Assessments Placement Test Running Records DIBELS Reading Unit 1 Language Arts
4 th Grade Language Arts Scope and Sequence 1 st Nine Weeks Instructional Units Reading Unit 1 & 2 Language Arts Unit 1& 2 Assessments Placement Test Running Records DIBELS Reading Unit 1 Language Arts
Fearless Change -- Patterns for Introducing New Ideas
 Ask for Help Since the task of introducing a new idea into an organization is a big job, look for people and resources to help your efforts. The job of introducing a new idea into an organization is too
Ask for Help Since the task of introducing a new idea into an organization is a big job, look for people and resources to help your efforts. The job of introducing a new idea into an organization is too
5 Day Schedule Paragraph Lesson 2: How-to-Paragraphs
 5 Day Schedule Paragraph Lesson 2: How-to-Paragraphs Day 1: Section 2 Mind Bender (teacher checks), Assignment Segment 1 Section 3 Add to Checklist (instruction) Section 4 Adjectives (instruction and practice)
5 Day Schedule Paragraph Lesson 2: How-to-Paragraphs Day 1: Section 2 Mind Bender (teacher checks), Assignment Segment 1 Section 3 Add to Checklist (instruction) Section 4 Adjectives (instruction and practice)
Syllabus Fall 2014 Earth Science 130: Introduction to Oceanography
 Syllabus Fall 2014 Earth Science 130: Introduction to Oceanography Background Information Welcome Aboard! These guidelines establish specific requirements, grading criteria, descriptions of assignments
Syllabus Fall 2014 Earth Science 130: Introduction to Oceanography Background Information Welcome Aboard! These guidelines establish specific requirements, grading criteria, descriptions of assignments
Summarizing A Nonfiction
 A Nonfiction Free PDF ebook Download: A Nonfiction Download or Read Online ebook summarizing a nonfiction in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Texts (written or spoken). a Process. Ideas in
A Nonfiction Free PDF ebook Download: A Nonfiction Download or Read Online ebook summarizing a nonfiction in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Texts (written or spoken). a Process. Ideas in
Houghton Mifflin Online Assessment System Walkthrough Guide
 Houghton Mifflin Online Assessment System Walkthrough Guide Page 1 Copyright 2007 by Houghton Mifflin Company. All Rights Reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form
Houghton Mifflin Online Assessment System Walkthrough Guide Page 1 Copyright 2007 by Houghton Mifflin Company. All Rights Reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form
Grade Band: High School Unit 1 Unit Target: Government Unit Topic: The Constitution and Me. What Is the Constitution? The United States Government
 The Constitution and Me This unit is based on a Social Studies Government topic. Students are introduced to the basic components of the U.S. Constitution, including the way the U.S. government was started
The Constitution and Me This unit is based on a Social Studies Government topic. Students are introduced to the basic components of the U.S. Constitution, including the way the U.S. government was started
Kindergarten SAMPLE MATERIAL INSIDE
 Kindergarten SAMPLE MATERIAL INSIDE About Nelson Science Developed by an experienced team of BC educators, Nelson Science is a comprehensive series built from the ground up to fully align with the new
Kindergarten SAMPLE MATERIAL INSIDE About Nelson Science Developed by an experienced team of BC educators, Nelson Science is a comprehensive series built from the ground up to fully align with the new
Organizing Comprehensive Literacy Assessment: How to Get Started
 Organizing Comprehensive Assessment: How to Get Started September 9 & 16, 2009 Questions to Consider How do you design individualized, comprehensive instruction? How can you determine where to begin instruction?
Organizing Comprehensive Assessment: How to Get Started September 9 & 16, 2009 Questions to Consider How do you design individualized, comprehensive instruction? How can you determine where to begin instruction?
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SOCIAL STUDIES SYLLABUS FOR BASIC EDUCATION STANDARD III-VI
 THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SOCIAL STUDIES SYLLABUS FOR BASIC EDUCATION STANDARD III-VI THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SOCIAL STUDIES SYLLABUS FOR BASIC EDUCATION STANDARD III-VI THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND
Digital Technology Merit Badge Workbook
 Merit Badge Workbook This workbook can help you but you still need to read the merit badge pamphlet. This Workbook can help you organize your thoughts as you prepare to meet with your merit badge counselor.
Merit Badge Workbook This workbook can help you but you still need to read the merit badge pamphlet. This Workbook can help you organize your thoughts as you prepare to meet with your merit badge counselor.
ALL-IN-ONE MEETING GUIDE THE ECONOMICS OF WELL-BEING
 ALL-IN-ONE MEETING GUIDE THE ECONOMICS OF WELL-BEING LeanIn.0rg, 2016 1 Overview Do we limit our thinking and focus only on short-term goals when we make trade-offs between career and family? This final
ALL-IN-ONE MEETING GUIDE THE ECONOMICS OF WELL-BEING LeanIn.0rg, 2016 1 Overview Do we limit our thinking and focus only on short-term goals when we make trade-offs between career and family? This final
