Pacing This topic focuses on observing, exploring, describing, and comparing weather changes, patterns in the sky, and changing seasons.
|
|
|
- Tobias Richard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kindergarten Science Theme Observations of the Environment Strand Connection Living and nonliving things have specific physical properties that can be used to sort and classify. The physical properties of air and water are presented as they apply to weather. Science Inquiry and Applications: All students must be developing the ability to: Observe and ask questions about the natural environment Plan and conduct simple investigations Employ simple equipment and tools to gather data and extend the senses Use appropriate mathematics with data to construct reasonable explanations Communicate about observations, investigations, and explanations Review and ask questions about the observations and explanations of others Topic Daily and Seasonal Changes Pacing This topic focuses on observing, exploring, describing, and comparing weather changes, patterns in the sky, and changing seasons. Ongoing done throughout year Content Statement 1. Weather changes are long term and short term. Learning Targets: I can observe and measure (nonstandard) wind. I can describe wind as moving air. I can observe and measure (nonstandard) temperature. I can observe and measure (nonstandard) precipitation (rain, sleet, hail, snow). I can use technology to communicate and share weather data. Content Elaborations Kindergarten Concepts Wind, temperature, and precipitation are components of the weather that can be observed and measured for Kindergarten. The measurements collected and tools used can be nonstandard and must be age appropriate. For example, the temperature may be above or below a given point (warmer or colder) or the amount of snow is marked on a dowel rod to check the depth. Weather measurements must be collected on a regular basis throughout the school year and then compared, explained, and discussed each week and each month. At the end of the school year, a comparison can be made and seasons can be identified by the patterns that were measured throughout the year. Consistent review and questioning to deepen understanding are essential. Use technology to compare classroom data to local data, study weather events, communicate and share data with other classrooms, and record classroom data. 1
2 Future Application of Concepts Grades 1-2: The properties of water and air are explored as they relate to the weather observations and measurement from Kindergarten. Grades 3-5: Different states of water are defined in Physical Sciences. Wind and water are recognized as processes that can change the surface of Earth through weathering and erosion. The observed seasons from Kindergarten are related to the sun and the tilt and orbit of Earth in grade 5. Content Vocabulary wind air temperature precipitation gauge thermometer Formative Assessments Weather Journal student draw/selected photos Resources Rain Gauge Snow Gauge Beaufort Scale Thermometer Journey North Outside my window? Epals.com The Wind Blew, by Pat Hutchins Integrations Morning routine Read alouds Writing workshop Writing pen pals/epals Science journaling Math graphing Academic Vocabulary observe measure communicate technology Summative Assessments Not applicable at this grade level Enrichment Strategies Introducing standard measurement for temperature and wind Comparing local weather information to other locations Intervention Strategies Peer models One-on-one help with teacher or volunteer Visual prompts and posters Use of technology as aide Small group instruction 2
3 Kindergarten Science Theme Observations of the Environment Strand Connection Living and nonliving things have specific physical properties that can be used to sort and classify. The physical properties of air and water are presented as they apply to weather. Science Inquiry and Applications: All students must be developing the ability to: Observe and ask questions about the natural environment Plan and conduct simple investigations Employ simple equipment and tools to gather data and extend the senses Use appropriate mathematics with data to construct reasonable explanations Communicate about observations, investigations, and explanations Review and ask questions about the observations and explanations of others Topic Daily and Seasonal Changes Pacing This topic focuses on observing, exploring, describing, and comparing weather changes, patterns in the sky, and changing seasons. Watch the moon over the course of a month. Could be ongoing throughout the year. Content Statement 2. The moon, sun, and stars can be observed at different times of the day and night. Learning Targets: I can describe how the moon looks in the sky over a month s time (shape, position in sky, time of day). I can describe how the sun moves across the sky during the day. I can describe when stars can be seen in the sky. I can observe the differences between stars (bright, dim, colors). Content Elaborations Kindergarten Concepts Changes in the position of the sun in the sky can be measured and recorded at different times during the school day. Observations also can be made virtually. This data can be compared from month to month to monitor changes. Stars, groups of stars, and different phases of the moon can be observed through books or virtually and documented throughout the month. The names of the stars, constellations, or moon phases are not appropriate for Kindergarten; only the changes in appearances and what can actually be observed are included. The moon also can be observed in the daylight, at times. Drawings, photographs, or other graphics can be used to document student observations. Demonstrating (either 3-D or virtual) and testing/experimenting (through kits or models) must be used to explain the changing positions (in the sky) of the sun, stars, and moon. Review, question, and discuss the demonstrations and observations to deepen understanding. 3
4 Future Application of Concepts Grades 1-2: The sun is introduced as a primary source of energy that relates to long- and short-term weather changes. Grades 3-5: The tilt and orbit of the Earth and position of the sun are related to the seasons, the sun is the only star in the solar system, and celestial bodies orbit the sun. Content Vocabulary bright/dim moon stars sun Formative Assessments Journaling using virtual sky Resources Virtual sky website Make moon journal page OSU Planetarium Make your own planetarium Integrations Morning routine Read alouds Writing workshop Writing pen pals/epals Science journaling Learning of seasons Academic Vocabulary appearance describe position observe/observation Summative Assessments Not applicable at this grade level Enrichment Strategies Using technology to observe and look up the moon as it appears in different places and times Learning the names of the phases of the moon Intervention Strategies Peer models One-on-one help with teacher or volunteer Visual prompts and posters Use of technology as aide Small group instruction 4
5 Kindergarten Science Theme Observations of the Environment Strand Connection Living and nonliving things have specific physical properties that can be used to sort and classify. The physical properties of air and water are presented as they apply to weather. Science Inquiry and Applications: All students must be developing the ability to: Observe and ask questions about the natural environment Plan and conduct simple investigations Employ simple equipment and tools to gather data and extend the senses Use appropriate mathematics with data to construct reasonable explanations Communicate about observations, investigations, and explanations Review and ask questions about the observations and explanations of others Topic Physical and Behavioral Traits of Living Things Pacing This topic focuses on observing, exploring, describing, and comparing living things in Ohio. Ongoing Spring months Content Statement 3. Living things are different from nonliving things. Learning Targets: I can identify living things. I can identify nonliving things. I can explain what it means to be alive. I know that living things respond to stimuli. I know living things need food/energy. I know living things grow. Content Elaborations Kindergarten Concepts The emphasis of this content statement is to build a grade-appropriate understanding of what it means to be living, not to distinguish living and nonliving. There are different kinds of living things. The focus is on familiar organisms (e.g., grass, trees, flowers, cats, dogs, horses). Some grade-appropriate characteristics include that living things respond to stimuli, grow, and require energy. Living things respond to stimuli. The responses described must be easy to observe (e.g., fish in an aquarium respond to a stimulus food). Living things grow (e.g., plant seeds or seedlings and watch them grow). Observing plants growing toward a light source can lead to experiments and explorations of what happens when the plant is placed in a different location in the classroom (e.g., on the floor, in a closet, on a desk) or rotated 90 degrees. Some observations also can be done virtually. 5
6 Animals need food; plants make their own food. Read grade-appropriate, nonfiction books to students or by students (e.g., picture books) that accurately describe the characteristics of living things found in Ohio. Technology also can be used to find photographs and stories or take photographs of living things in Ohio. When studying living things, ethical treatment of animals and safety must be employed. Respect for and proper treatment of living things must be modeled. For example, shaking a container, rapping on insect bottles, unclean cages or aquariums, leaving living things in the hot sun, or exposure to extreme temperatures (hot or cold) must be avoided. The National Science Teachers Association (NSTA) has a position paper to provide guidance in the ethical use and treatment of animals in the classroom at Future Application of Concepts Grades 1-2: This content builds to understanding that living things use the environment to acquire what they need in order to survive. Grades 3-5: Food webs and food chains are used to illustrate energy transfer within an ecosystem. Grades 6-8: The characteristics of life are detailed via Modern Cell Theory and reproduction. Content Vocabulary alive living nonliving stimuli grow energy Formative Assessments Picture sort living vs. nonliving things (pocket chart, Smart Board, etc.) Resources Seeds, soil, planting materials, etc. Light source Academic Vocabulary identify respond explain Summative Assessments Not applicable at this grade level Enrichment Strategies Exposing plants to different variables and allowing students to make predictions as to what may or may not happen (i.e., changing where it is growing, changing the food source, etc.). 6
7 Photographs of living things Class pet Integrations Measuring and graphing plant growth Read alouds Science journaling (writing/drawing observations) Sorting living and nonliving things Intervention Strategies Peer models One-on-one help with teacher or volunteer Visual prompts and posters Use of technology as aide Small group instruction 7
8 Kindergarten Science Theme Observations of the Environment Strand Connection Living and nonliving things have specific physical properties that can be used to sort and classify. The physical properties of air and water are presented as they apply to weather. Science Inquiry and Applications: All students must be developing the ability to: Observe and ask questions about the natural environment Plan and conduct simple investigations Employ simple equipment and tools to gather data and extend the senses Use appropriate mathematics with data to construct reasonable explanations Communicate about observations, investigations, and explanations Review and ask questions about the observations and explanations of others Topic Physical and Behavioral Traits of Living Things Pacing This topic focuses on observing, exploring, describing, and comparing living things in Ohio. 2 weeks Content Statement 4. Living things have physical traits and behaviors which influence their survival. Learning Targets: I can recognize the physical characteristics of living things that help them survive. I can describe how parts of plants and animals are used for different things. Content Elaborations Kindergarten Concepts At this grade level, providing exposure through personal observation and stories to a large variety of living things is required. The focus is not on naming the parts of living thing but associating through interaction and observation that living things are made of parts, and because of those parts living things can do specific things. The scientific explanations of how those parts function will come later. Identify and discuss examples such as birds have wings for flying and beaks for eating. Dogs have eyes for seeing, teeth for chewing, and legs for moving. Trees have leaves and trunks. Concrete experiences are necessary to deepen knowledge of the traits and behaviors of living things. Technology can be used to compare data on the number of honeybees observed in the schoolyard with other schools. Additional inquiry investigations include conducting observations of pond water (e.g., using a hand lens, focusing on macroscopic organisms), raising a classroom pet, planting seeds and watching them grow, and noting differences between different types of plants or bird watching. 8
9 Note: To ensure the health of students, check for allergies prior to raising a classroom pet. Future Application of Concepts Grades 1-2: The physical environment is identified as the source for what organisms need to survive. Grades 3-5: Plants and animals have certain physical or behavioral characteristics that improve their chances of surviving in particular environments. Grades 6-8: Changes in environmental conditions can affect how beneficial a trait will be for survival and reproductive success of an individual or an entire species. Content Vocabulary physical characteristics survive Formative Assessments Compare and contrast a variety of living things Resources Hand lens Integrations Discussion of fiction vs. nonfiction in regard to characteristics plants and animals possess in books and in real life Sorting animals by characteristics Academic Vocabulary parts recognize describe compare contrast Summative Assessments Not applicable at this grade level Enrichment Strategies Make a Venn Diagram that compares and contrasts physical traits of living things. Design and write about your own animal including its environment and physical traits. Intervention Strategies Peer models One-on-one help with teacher or volunteer Visual prompts and posters Use of technology as aide Small group instruction 9
10 Kindergarten Science Theme Observations of the Environment Strand Connection Living and nonliving things have specific physical properties that can be used to sort and classify. The physical properties of air and water are presented as they apply to weather. Science Inquiry and Applications: All students must be developing the ability to: Observe and ask questions about the natural environment Plan and conduct simple investigations Employ simple equipment and tools to gather data and extend the senses Use appropriate mathematics with data to construct reasonable explanations Communicate about observations, investigations, and explanations Review and ask questions about the observations and explanations of others Topic Properties of Everyday Objects and Materials Pacing This topic focuses on the production of sound and on observing, exploring, describing, and comparing the properties of objects and materials with which the student is familiar. 2 weeks Content Statement 5. Objects and materials can be sorted and described by their properties. Learning Targets: I can use my senses to describe properties of objects. I can identify materials (clay, cloth, paper, metal, glass). I can sort objects by materials or other properties (color, size, texture). Content Elaborations Kindergarten Concepts In Kindergarten, the concept that objects are made of specific materials (e.g., clay, cloth, paper, metal, class) is reinforced. Objects have certain properties (e.g., color, shape, size, temperature, odor, texture, flexibility) that can be described, compared, and sorted. Temperature observations must be limited to descriptors such as hot, warm, and cold. Observations of weight must be limited to describing objects as heavy or light. Comparisons must be used to sort and describe objects (e.g., Is the wooden block heavier or lighter than the plastic block?). Standard and nonstandard measuring tools can give additional information about the environment and can be used to make comparisons of objects and events. Magnifiers can be used to see detail that cannot be seen with the unaided eye. Familiar objects from home, the classroom, or the natural environment must be explored and investigated. 10 Note: Using the sense of taste should be prohibited in the classroom. Discussions of taste can be limited to experiences outside the classroom. Comparisons of objects are a precursor to measurement.
11 Future Application of Concepts Grades 1-2: Changes in objects are investigated, including temperature changes, solid-liquid phase changes, and possible changes in amount of liquid water in open and/or closed containers. Grades 3-5: Matter is defined and gases (air) are introduced. Measurements of weight and liquid volume are made. The mass* and kind of material remains the same when an object is reshaped or broken into pieces. The properties of solids, liquids, and gases (air) and phase changes are explored. *While mass is the scientifically correct term to use in this context, the NAEP 2009 Science Framework (page 27) recommends using the more familiar term weight in the elementary grades with the distinction between mass and weight being introduced at the middle school level. In Ohio, students will not be assessed on the differences between mass and weight until Grade 6. Content Vocabulary properties materials senses objects clay cloth paper metal glass color size texture heavy light hot warm cold Formative Assessments Picture sort Academic Vocabulary identify sort compare Summative Assessments Not applicable at this grade level 11
12 Feely box Journal response Resources Balance Magnifiers Integrations Sorting objects Writing workshop Using your 5 senses 3 Little Pigs compare and contrast materials in different versions of the story Enrichment Strategies Building and testing structures made of various materials and describing which materials work best for the situation/structure Intervention Strategies Peer models One-on-one help with teacher or volunteer Visual prompts and posters Use of technology as aide Small group instruction 12
13 Kindergarten Science Theme Observations of the Environment Strand Connection Living and nonliving things have specific physical properties that can be used to sort and classify. The physical properties of air and water are presented as they apply to weather. Science Inquiry and Applications: All students must be developing the ability to: Observe and ask questions about the natural environment Plan and conduct simple investigations Employ simple equipment and tools to gather data and extend the senses Use appropriate mathematics with data to construct reasonable explanations Communicate about observations, investigations, and explanations Review and ask questions about the observations and explanations of others Topic Properties of Everyday Objects and Materials Pacing This topic focuses on the production of sound and on observing, exploring, describing, and comparing the properties of objects and materials with which the student is familiar. 2 weeks Content Statement 6. Some objects and materials can be made to vibrate to produce sound. Learning Targets: I can describe ways sound can be made. I can observe and explore how different sounds can be made with the same object. I can experiment with vibrations and sounds. I can recognize that sound is caused by vibrating objects. I can describe the effect vibrations have on pitch (fast = high; slow = low). I can create and compare ways to make loud and soft sounds. Content Elaborations Kindergarten Concepts Sound can be made in many ways. Objects like cymbals, the tabletop, or drums can be tapped to produce sound. Objects like a rubber band or a guitar string can be plucked to produce sound. Objects like a bottle or a trumpet can be blown into to produce sound. A wide variety of sounds can be made with the same object (e.g., a plastic bottle could be tapped or blown into). The connection between sound energy and the vibration of an object must be made. Vibrations can be made visible when water splashes from a cymbal or triangle placed in water or rice vibrates on the top of a banging drum. The concepts of pitch (low vs. high notes) and loudness are introduced. The pitch of sound can be changed by changing how fast an object vibrates. Objects that vibrate slowly produce low pitches; objects that vibrate quickly produce high pitches. Sound must be experienced, investigated, and explored through observations and experimentation. Standard, virtual, and student-constructed instruments must be used to explore sound. 13
14 Note: Wave descriptions of sound and the propagation of sound energy are not appropriate at this grade. Future Application of Concepts Grades 1-2: Exploring sound provides an experiential basis for the concepts of motion and energy. A variety of motions is explored. Forces are needed to change the motion of objects. Grades 3-5: Energy is introduced as something that can make things move or cause change. The concept of a medium for sound is introduced and disturbances in liquid and solid media are observed. Grades 6-8: The wave nature of sound is introduced. Content Vocabulary sound vibrate pitch object fast slow high low loud soft Formative Assessments Nonverbal cues to communicate pitch and loudness Identifying objects in containers based on their sounds Resources Standard instruments (cymbals, bells, drums, guitar) Virtual instruments Student-constructed instruments Thump, Thump, Tat-a-Tat-Tat, by Gene Baer Sounds All Around (Let s-read-and-find-out Science I) Sound: Loud, Soft, High, and Low, by Natalie Rosinsky All About Sound (Rookie Reader) Academic Vocabulary describe observe experiment recognize create compare effect Summative Assessments Not applicable at this grade level Enrichment Strategies Compare and contrast objects or instruments by loudness and pitch 14
15 Integrations Music 5 senses Intervention Strategies Peer models One-on-one help with teacher or volunteer Visual prompts and posters Use of technology as aide Small group instruction 15
Maryland Science Voluntary State Curriculum Grades K-6
 A Correlation of 2006 to the Maryland Science Voluntary State Curriculum Grades K-6 O/S-60 Introduction This document demonstrates how Scott Foresman Science meets the Maryland Science Voluntary State
A Correlation of 2006 to the Maryland Science Voluntary State Curriculum Grades K-6 O/S-60 Introduction This document demonstrates how Scott Foresman Science meets the Maryland Science Voluntary State
5.1 Sound & Light Unit Overview
 5.1 Sound & Light Unit Overview Enduring Understanding: Sound and light are forms of energy that travel and interact with objects in various ways. Essential Question: How is sound energy transmitted, absorbed,
5.1 Sound & Light Unit Overview Enduring Understanding: Sound and light are forms of energy that travel and interact with objects in various ways. Essential Question: How is sound energy transmitted, absorbed,
Physical Features of Humans
 Grade 1 Science, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Physical Features of Humans Overview Number of instructional days: 11 (1 day = 20 30 minutes) Content to be learned Observe, identify, and record the external features
Grade 1 Science, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Physical Features of Humans Overview Number of instructional days: 11 (1 day = 20 30 minutes) Content to be learned Observe, identify, and record the external features
been each get other TASK #1 Fry Words TASK #2 Fry Words Write the following words in ABC order: Write the following words in ABC order:
 TASK #1 Fry Words 1-100 been each called down about first TASK #2 Fry Words 1-100 get other long people number into TASK #3 Fry Words 1-100 could part more find now her TASK #4 Fry Words 1-100 for write
TASK #1 Fry Words 1-100 been each called down about first TASK #2 Fry Words 1-100 get other long people number into TASK #3 Fry Words 1-100 could part more find now her TASK #4 Fry Words 1-100 for write
Unit: Human Impact Differentiated (Tiered) Task How Does Human Activity Impact Soil Erosion?
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
INSTRUCTIONAL FOCUS DOCUMENT Grade 5/Science
 Exemplar Lesson 01: Comparing Weather and Climate Exemplar Lesson 02: Sun, Ocean, and the Water Cycle State Resources: Connecting to Unifying Concepts through Earth Science Change Over Time RATIONALE:
Exemplar Lesson 01: Comparing Weather and Climate Exemplar Lesson 02: Sun, Ocean, and the Water Cycle State Resources: Connecting to Unifying Concepts through Earth Science Change Over Time RATIONALE:
PROJECT LEARNING TREE 4 th grade Language Arts Correlation to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
 PROJECT LEARNING TREE 4 th grade Language Arts Correlation/TEKS Language Arts Students are expected to: Activity 4.3A summarize and explain the lesson or message of a work of fiction as its theme 18, 89
PROJECT LEARNING TREE 4 th grade Language Arts Correlation/TEKS Language Arts Students are expected to: Activity 4.3A summarize and explain the lesson or message of a work of fiction as its theme 18, 89
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15
 Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments Plants Are Producers... 17 Producing a Producer... 19 The Part Plants Play...
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments Plants Are Producers... 17 Producing a Producer... 19 The Part Plants Play...
Grade 3 Science Life Unit (3.L.2)
 Grade 3 Science Life Unit (3.L.2) Decision 1: What will students learn in this unit? Standards Addressed: Science 3.L.2 Understand how plants survive in their environments. Ask and answer questions to
Grade 3 Science Life Unit (3.L.2) Decision 1: What will students learn in this unit? Standards Addressed: Science 3.L.2 Understand how plants survive in their environments. Ask and answer questions to
SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE
 FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York Le REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION LIVING ENVIRONMENT Wednesday, June 19, 2002 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Directions
FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York Le REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION LIVING ENVIRONMENT Wednesday, June 19, 2002 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Directions
Creating Coherent Inquiry Projects to Support Student Cognition and Collaboration in Physics
 Creating Coherent Inquiry Projects to Support Student Cognition and Collaboration in Physics 6 Douglas B. Clark, Arizona State University S. Raj Chaudhury, Christopher Newport University As a physics teacher,
Creating Coherent Inquiry Projects to Support Student Cognition and Collaboration in Physics 6 Douglas B. Clark, Arizona State University S. Raj Chaudhury, Christopher Newport University As a physics teacher,
The Ontario Curriculum
 The Ontario Curriculum GRADE 1 checklist format compiled by: The Canadian Homeschooler using the current Ontario Curriculum Content Introduction... Page 3 Mathematics... Page 4 Language Arts... Page 9
The Ontario Curriculum GRADE 1 checklist format compiled by: The Canadian Homeschooler using the current Ontario Curriculum Content Introduction... Page 3 Mathematics... Page 4 Language Arts... Page 9
SOCIAL STUDIES GRADE 1. Clear Learning Targets Office of Teaching and Learning Curriculum Division FAMILIES NOW AND LONG AGO, NEAR AND FAR
 SOCIAL STUDIES FAMILIES NOW AND LONG AGO, NEAR AND FAR GRADE 1 Clear Learning Targets 2015-2016 Aligned with Ohio s Learning Standards for Social Studies Office of Teaching and Learning Curriculum Division
SOCIAL STUDIES FAMILIES NOW AND LONG AGO, NEAR AND FAR GRADE 1 Clear Learning Targets 2015-2016 Aligned with Ohio s Learning Standards for Social Studies Office of Teaching and Learning Curriculum Division
A Pumpkin Grows. Written by Linda D. Bullock and illustrated by Debby Fisher
 GUIDED READING REPORT A Pumpkin Grows Written by Linda D. Bullock and illustrated by Debby Fisher KEY IDEA This nonfiction text traces the stages a pumpkin goes through as it grows from a seed to become
GUIDED READING REPORT A Pumpkin Grows Written by Linda D. Bullock and illustrated by Debby Fisher KEY IDEA This nonfiction text traces the stages a pumpkin goes through as it grows from a seed to become
For information only, correct responses are listed in the chart below. Question Number. Correct Response
 THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK 4GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST JUNE 207 WRITTEN TEST FOR TEACHERS ONLY SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Note: All schools (public, nonpublic, and charter) administering
THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK 4GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST JUNE 207 WRITTEN TEST FOR TEACHERS ONLY SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Note: All schools (public, nonpublic, and charter) administering
Rendezvous with Comet Halley Next Generation of Science Standards
 Next Generation of Science Standards 5th Grade 6 th Grade 7 th Grade 8 th Grade 5-PS1-3 Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties. MS-PS1-4 Develop a model that
Next Generation of Science Standards 5th Grade 6 th Grade 7 th Grade 8 th Grade 5-PS1-3 Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties. MS-PS1-4 Develop a model that
Cognitive Development Facilitator s Guide
 Cognitive Development Facilitator s Guide Competency-Based Learning Objectives Description of Target Audience Training Methodologies/ Strategies Utilized Sequence of Training By the end of this module,
Cognitive Development Facilitator s Guide Competency-Based Learning Objectives Description of Target Audience Training Methodologies/ Strategies Utilized Sequence of Training By the end of this module,
All Systems Go! Using a Systems Approach in Elementary Science
 All Systems Go! CAST November Tracey Ramirez Professional Learning Facilitator The Charles A. Dana Center What we do and how we do it The Dana Center collaborates with others locally and nationally to
All Systems Go! CAST November Tracey Ramirez Professional Learning Facilitator The Charles A. Dana Center What we do and how we do it The Dana Center collaborates with others locally and nationally to
Unit 1: Scientific Investigation-Asking Questions
 Unit 1: Scientific Investigation-Asking Questions Standards: OKC 3 Process Standard 3: Experimental design - Understanding experimental designs requires that students recognize the components of a valid
Unit 1: Scientific Investigation-Asking Questions Standards: OKC 3 Process Standard 3: Experimental design - Understanding experimental designs requires that students recognize the components of a valid
Planting Seeds, Part 1: Can You Design a Fair Test?
 Planting Seeds, Part 1: Can You Design a Fair Test? In this investigation, your team will choose 2 or 3 seeds in order to design an investigation to learn something more about them. First, you will need
Planting Seeds, Part 1: Can You Design a Fair Test? In this investigation, your team will choose 2 or 3 seeds in order to design an investigation to learn something more about them. First, you will need
Literacy THE KEYS TO SUCCESS. Tips for Elementary School Parents (grades K-2)
 Literacy THE KEYS TO SUCCESS Tips for Elementary School Parents (grades K-2) Randi Weingarten president Lorretta Johnson secretary-treasurer Mary Cathryn Ricker executive vice president OUR MISSION The
Literacy THE KEYS TO SUCCESS Tips for Elementary School Parents (grades K-2) Randi Weingarten president Lorretta Johnson secretary-treasurer Mary Cathryn Ricker executive vice president OUR MISSION The
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15
 Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments School Supplies... 17 A Place to Call Home... 21 Paste Up Habitats... 37
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments School Supplies... 17 A Place to Call Home... 21 Paste Up Habitats... 37
Abc Of Science 8th Grade
 Abc Of 8th Grade Free PDF ebook Download: Abc Of 8th Grade Download or Read Online ebook abc of science 8th grade in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database In addition, some courses such as 7th grade
Abc Of 8th Grade Free PDF ebook Download: Abc Of 8th Grade Download or Read Online ebook abc of science 8th grade in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database In addition, some courses such as 7th grade
SESSION 2: HELPING HAND
 SESSION 2: HELPING HAND Ready for the next challenge? Build a device with a long handle that can grab something hanging high! This week you ll also check out your Partner Club s Paper Structure designs.
SESSION 2: HELPING HAND Ready for the next challenge? Build a device with a long handle that can grab something hanging high! This week you ll also check out your Partner Club s Paper Structure designs.
2.B.4 Balancing Crane. The Engineering Design Process in the classroom. Summary
 2.B.4 Balancing Crane The Engineering Design Process in the classroom Grade Level 2 Sessions 1 40 minutes 2 30 minutes Seasonality None Instructional Mode(s) Whole class, groups of 4 5 students, individual
2.B.4 Balancing Crane The Engineering Design Process in the classroom Grade Level 2 Sessions 1 40 minutes 2 30 minutes Seasonality None Instructional Mode(s) Whole class, groups of 4 5 students, individual
Kindergarten SAMPLE MATERIAL INSIDE
 Kindergarten SAMPLE MATERIAL INSIDE About Nelson Science Developed by an experienced team of BC educators, Nelson Science is a comprehensive series built from the ground up to fully align with the new
Kindergarten SAMPLE MATERIAL INSIDE About Nelson Science Developed by an experienced team of BC educators, Nelson Science is a comprehensive series built from the ground up to fully align with the new
Teaching NGSS in Elementary School Third Grade
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Teaching NGSS in Elementary School Third Grade Presented by: Ted Willard, Carla Zembal-Saul, Mary Starr, and Kathy Renfrew December 17, 2014 6:30 p.m. ET / 5:30
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Teaching NGSS in Elementary School Third Grade Presented by: Ted Willard, Carla Zembal-Saul, Mary Starr, and Kathy Renfrew December 17, 2014 6:30 p.m. ET / 5:30
1. READING ENGAGEMENT 2. ORAL READING FLUENCY
 Teacher Observation Guide Animals Can Help Level 28, Page 1 Name/Date Teacher/Grade Scores: Reading Engagement /8 Oral Reading Fluency /16 Comprehension /28 Independent Range: 6 7 11 14 19 25 Book Selection
Teacher Observation Guide Animals Can Help Level 28, Page 1 Name/Date Teacher/Grade Scores: Reading Engagement /8 Oral Reading Fluency /16 Comprehension /28 Independent Range: 6 7 11 14 19 25 Book Selection
Science Grade 03 Unit 04 Exemplar Lesson 02: Exploring Energy
 Grade 03 Unit 04 Exemplar Lesson 02: Exploring Energy This lesson is one approach to teaching the State Standards associated with this unit. Districts are encouraged to customize this lesson by supplementing
Grade 03 Unit 04 Exemplar Lesson 02: Exploring Energy This lesson is one approach to teaching the State Standards associated with this unit. Districts are encouraged to customize this lesson by supplementing
This Performance Standards include four major components. They are
 Environmental Physics Standards The Georgia Performance Standards are designed to provide students with the knowledge and skills for proficiency in science. The Project 2061 s Benchmarks for Science Literacy
Environmental Physics Standards The Georgia Performance Standards are designed to provide students with the knowledge and skills for proficiency in science. The Project 2061 s Benchmarks for Science Literacy
Teaching Literacy Through Videos
 Teaching Literacy Through Videos Elizabeth Stavis Reading Intervention Specialist RR Teacher Santa Clara Unified Jenny Maehara Elementary Literacy Specialist RR Teacher Santa Clara Unified February 9,
Teaching Literacy Through Videos Elizabeth Stavis Reading Intervention Specialist RR Teacher Santa Clara Unified Jenny Maehara Elementary Literacy Specialist RR Teacher Santa Clara Unified February 9,
Lesson 1 Taking chances with the Sun
 P2 Radiation and life Lesson 1 Taking chances with the Sun consider health benefits as well as risks that sunlight presents introduce two ideas: balancing risks and benefits, reducing risks revisit the
P2 Radiation and life Lesson 1 Taking chances with the Sun consider health benefits as well as risks that sunlight presents introduce two ideas: balancing risks and benefits, reducing risks revisit the
Biome I Can Statements
 Biome I Can Statements I can recognize the meanings of abbreviations. I can use dictionaries, thesauruses, glossaries, textual features (footnotes, sidebars, etc.) and technology to define and pronounce
Biome I Can Statements I can recognize the meanings of abbreviations. I can use dictionaries, thesauruses, glossaries, textual features (footnotes, sidebars, etc.) and technology to define and pronounce
Lesson Plan Title Aquatic Ecology
 Lesson Plan Title Aquatic Ecology Name (last, first): Larson, Don Scientific Theme(s): C-2: develop an understanding of the structure, function, behavior, development, life cycles, and diversity of living
Lesson Plan Title Aquatic Ecology Name (last, first): Larson, Don Scientific Theme(s): C-2: develop an understanding of the structure, function, behavior, development, life cycles, and diversity of living
Chapter 9 Banked gap-filling
 Chapter 9 Banked gap-filling This testing technique is known as banked gap-filling, because you have to choose the appropriate word from a bank of alternatives. In a banked gap-filling task, similarly
Chapter 9 Banked gap-filling This testing technique is known as banked gap-filling, because you have to choose the appropriate word from a bank of alternatives. In a banked gap-filling task, similarly
Measuring physical factors in the environment
 B2 3.1a Student practical sheet Measuring physical factors in the environment Do environmental conditions affect the distriution of plants? Aim To find out whether environmental conditions affect the distriution
B2 3.1a Student practical sheet Measuring physical factors in the environment Do environmental conditions affect the distriution of plants? Aim To find out whether environmental conditions affect the distriution
Airplane Rescue: Social Studies. LEGO, the LEGO logo, and WEDO are trademarks of the LEGO Group The LEGO Group.
 Airplane Rescue: Social Studies LEGO, the LEGO logo, and WEDO are trademarks of the LEGO Group. 2010 The LEGO Group. Lesson Overview The students will discuss ways that people use land and their physical
Airplane Rescue: Social Studies LEGO, the LEGO logo, and WEDO are trademarks of the LEGO Group. 2010 The LEGO Group. Lesson Overview The students will discuss ways that people use land and their physical
Unpacking a Standard: Making Dinner with Student Differences in Mind
 Unpacking a Standard: Making Dinner with Student Differences in Mind Analyze how particular elements of a story or drama interact (e.g., how setting shapes the characters or plot). Grade 7 Reading Standards
Unpacking a Standard: Making Dinner with Student Differences in Mind Analyze how particular elements of a story or drama interact (e.g., how setting shapes the characters or plot). Grade 7 Reading Standards
ELPAC. Practice Test. Kindergarten. English Language Proficiency Assessments for California
 ELPAC English Language Proficiency Assessments for California Practice Test Kindergarten Copyright 2017 by the California Department of Education (CDE). All rights reserved. Copying and distributing these
ELPAC English Language Proficiency Assessments for California Practice Test Kindergarten Copyright 2017 by the California Department of Education (CDE). All rights reserved. Copying and distributing these
Growing Gifted Readers. with Lisa Pagano & Marie Deegan Charlotte-Mecklenburg Schools
 Growing Gifted Readers with Lisa Pagano & Marie Deegan Charlotte-Mecklenburg Schools Who Are We Learning with Today? Marie Deegan Lisa Pagano Our Time Together Key Components of Reading Instruction Gifted
Growing Gifted Readers with Lisa Pagano & Marie Deegan Charlotte-Mecklenburg Schools Who Are We Learning with Today? Marie Deegan Lisa Pagano Our Time Together Key Components of Reading Instruction Gifted
Fourth Grade. Reporting Student Progress. Libertyville School District 70. Fourth Grade
 Fourth Grade Libertyville School District 70 Reporting Student Progress Fourth Grade A Message to Parents/Guardians: Libertyville Elementary District 70 teachers of students in kindergarten-5 utilize a
Fourth Grade Libertyville School District 70 Reporting Student Progress Fourth Grade A Message to Parents/Guardians: Libertyville Elementary District 70 teachers of students in kindergarten-5 utilize a
MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm
 MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm Why participate in the Science Fair? Science fair projects give students
MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm Why participate in the Science Fair? Science fair projects give students
Standard 1: Number and Computation
 Standard 1: Number and Computation Standard 1: Number and Computation The student uses numerical and computational concepts and procedures in a variety of situations. Benchmark 1: Number Sense The student
Standard 1: Number and Computation Standard 1: Number and Computation The student uses numerical and computational concepts and procedures in a variety of situations. Benchmark 1: Number Sense The student
What is this species called? Generation Bar Graph
 Name: Date: What is this species called? Color Count Blue Green Yellow Generation Bar Graph 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Blue Green Yellow Name: Date: What is this species called? Color Count Blue Green
Name: Date: What is this species called? Color Count Blue Green Yellow Generation Bar Graph 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Blue Green Yellow Name: Date: What is this species called? Color Count Blue Green
Michigan GLCE Kindergarten Grade Level Content Expectations
 Michigan GLCE Kindergarten Grade Level Content Expectations A Guide for Parents, Teachers and Students St. Robert Bellarmine School St. Robert Bellarmine School Dear Parents, Teachers and Students: The
Michigan GLCE Kindergarten Grade Level Content Expectations A Guide for Parents, Teachers and Students St. Robert Bellarmine School St. Robert Bellarmine School Dear Parents, Teachers and Students: The
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Trophies Grade 5
 Unit 6/Week 2 Title: The Golden Lion Tamarin Comes Home Suggested Time: 5 days (45 minutes per day) Common Core ELA Standards: RI.5.1, RI.5.3, RL.5.4, RI.5.8; RF.5.3, RF.5.4; W.5.2, W.5.4, W.5.9; SL.5.1,
Unit 6/Week 2 Title: The Golden Lion Tamarin Comes Home Suggested Time: 5 days (45 minutes per day) Common Core ELA Standards: RI.5.1, RI.5.3, RL.5.4, RI.5.8; RF.5.3, RF.5.4; W.5.2, W.5.4, W.5.9; SL.5.1,
The Day of a 4th Grade Student
 ATTACHMENT 1 The Day of a 4th Grade Student At 7:00 a.m., Keisha arrives to school greeted at her car door by a parent/community volunteer. Keisha then enters the library where she is instructed to take
ATTACHMENT 1 The Day of a 4th Grade Student At 7:00 a.m., Keisha arrives to school greeted at her car door by a parent/community volunteer. Keisha then enters the library where she is instructed to take
Content Language Objectives (CLOs) August 2012, H. Butts & G. De Anda
 Content Language Objectives (CLOs) Outcomes Identify the evolution of the CLO Identify the components of the CLO Understand how the CLO helps provide all students the opportunity to access the rigor of
Content Language Objectives (CLOs) Outcomes Identify the evolution of the CLO Identify the components of the CLO Understand how the CLO helps provide all students the opportunity to access the rigor of
Name of Course: French 1 Middle School. Grade Level(s): 7 and 8 (half each) Unit 1
 Name of Course: French 1 Middle School Grade Level(s): 7 and 8 (half each) Unit 1 Estimated Instructional Time: 15 classes PA Academic Standards: Communication: Communicate in Languages Other Than English
Name of Course: French 1 Middle School Grade Level(s): 7 and 8 (half each) Unit 1 Estimated Instructional Time: 15 classes PA Academic Standards: Communication: Communicate in Languages Other Than English
Table of Contents. Introduction Choral Reading How to Use This Book...5. Cloze Activities Correlation to TESOL Standards...
 Table of Contents Introduction.... 4 How to Use This Book.....................5 Correlation to TESOL Standards... 6 ESL Terms.... 8 Levels of English Language Proficiency... 9 The Four Language Domains.............
Table of Contents Introduction.... 4 How to Use This Book.....................5 Correlation to TESOL Standards... 6 ESL Terms.... 8 Levels of English Language Proficiency... 9 The Four Language Domains.............
TEACHING Simple Tools Set II
 TEACHING GUIDE TEACHING Simple Tools Set II Kindergarten Reading Level ISBN-10: 0-8225-6880-2 Green ISBN-13: 978-0-8225-6880-3 2 TEACHING SIMPLE TOOLS SET II Standards Science Mathematics Language Arts
TEACHING GUIDE TEACHING Simple Tools Set II Kindergarten Reading Level ISBN-10: 0-8225-6880-2 Green ISBN-13: 978-0-8225-6880-3 2 TEACHING SIMPLE TOOLS SET II Standards Science Mathematics Language Arts
Evolution in Paradise
 Evolution in Paradise Engaging science lessons for middle and high school brought to you by BirdSleuth K-12 and the most extravagant birds in the world! The Evolution in Paradise lesson series is part
Evolution in Paradise Engaging science lessons for middle and high school brought to you by BirdSleuth K-12 and the most extravagant birds in the world! The Evolution in Paradise lesson series is part
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Activityengage Educator Version FO O D W EB FU N How do tiger sharks
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Activityengage Educator Version FO O D W EB FU N How do tiger sharks
THE HEAD START CHILD OUTCOMES FRAMEWORK
 THE HEAD START CHILD OUTCOMES FRAMEWORK Released in 2000, the Head Start Child Outcomes Framework is intended to guide Head Start programs in their curriculum planning and ongoing assessment of the progress
THE HEAD START CHILD OUTCOMES FRAMEWORK Released in 2000, the Head Start Child Outcomes Framework is intended to guide Head Start programs in their curriculum planning and ongoing assessment of the progress
Curriculum Scope and Sequence
 Curriculum Scope and Sequence First Baptist Academy Mathematics: Number and Counting Concepts Understand that numbers are used to denote quantity: two birds Count to 10 by rote Count to 10 in Spanish Begin
Curriculum Scope and Sequence First Baptist Academy Mathematics: Number and Counting Concepts Understand that numbers are used to denote quantity: two birds Count to 10 by rote Count to 10 in Spanish Begin
Targeted Alaska Reading Performance Standards for the High School Graduation Qualifying Exam
 DIGITAL TIME CAPSULE Overview: In this activity students explore the University of Alaska Fairbanks Oral History Program s Climate Change Jukebox to make observations about climate change based on interviews
DIGITAL TIME CAPSULE Overview: In this activity students explore the University of Alaska Fairbanks Oral History Program s Climate Change Jukebox to make observations about climate change based on interviews
This document has been produced by:
 year 6 This document has been produced by: The All Wales ESDGC Officer Group to support schools introducing the National Literacy and Numeracy Framework through ESDGC activities. With support from: Developing
year 6 This document has been produced by: The All Wales ESDGC Officer Group to support schools introducing the National Literacy and Numeracy Framework through ESDGC activities. With support from: Developing
Introductory Astronomy. Physics 134K. Fall 2016
 Introductory Astronomy Physics 134K Fall 2016 Dates / contact hours: 7 week course; 300 contact minutes per week Academic Credit: 1 Areas of Knowledge: NS Modes of Inquiry: QS Course format: Lecture/Discussion.
Introductory Astronomy Physics 134K Fall 2016 Dates / contact hours: 7 week course; 300 contact minutes per week Academic Credit: 1 Areas of Knowledge: NS Modes of Inquiry: QS Course format: Lecture/Discussion.
Picture It, Dads! Facilitator Activities For. The Mitten
 Picture It, Dads! Facilitator Activities For The Mitten Picture It Dads! The Mitten Goals for Dads: 1. To practice effective read-aloud techniques. 2. To develop strategies to help retell the story. 3.
Picture It, Dads! Facilitator Activities For The Mitten Picture It Dads! The Mitten Goals for Dads: 1. To practice effective read-aloud techniques. 2. To develop strategies to help retell the story. 3.
Special Educational Needs Assessment for Learning. Phil Dexter, British Council, Teacher Development Adviser
 Special Educational Needs Assessment for Learning Phil Dexter, British Council, Teacher Development Adviser Working towards achievement for all Inclusive practices Quality teaching & learning SEN Interventions
Special Educational Needs Assessment for Learning Phil Dexter, British Council, Teacher Development Adviser Working towards achievement for all Inclusive practices Quality teaching & learning SEN Interventions
Prewriting: Drafting: Revising: Editing: Publishing:
 Prewriting: children begin to plan writing. Drafting: children put their ideas into writing and drawing. Revising: children reread the draft and decide how to rework and improve it. Editing: children polish
Prewriting: children begin to plan writing. Drafting: children put their ideas into writing and drawing. Revising: children reread the draft and decide how to rework and improve it. Editing: children polish
Elementary Supplemental (purchase only) Instructional Materials -- Draft
 Health 2014-15 Elementary Supplemental (purchase only) Instructional Materials -- Draft Instructional Materials Title NF (Not Funded) ISBN-13 Grade Price Copyright Health and Physical Education, Elementary
Health 2014-15 Elementary Supplemental (purchase only) Instructional Materials -- Draft Instructional Materials Title NF (Not Funded) ISBN-13 Grade Price Copyright Health and Physical Education, Elementary
Physical Versus Virtual Manipulatives Mathematics
 Physical Versus Free PDF ebook Download: Physical Versus Download or Read Online ebook physical versus virtual manipulatives mathematics in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Engineering Haptic
Physical Versus Free PDF ebook Download: Physical Versus Download or Read Online ebook physical versus virtual manipulatives mathematics in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Engineering Haptic
RI.2.4 Determine the meaning of words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 2 topic or subject area.
 Reading Mini-Lesson Plans Week: March 11-15 Standards: RL.2.10 By the end of the year, read and comprehend literature, including stories and poetry, in the grades 2-3 text complexity band proficiently,
Reading Mini-Lesson Plans Week: March 11-15 Standards: RL.2.10 By the end of the year, read and comprehend literature, including stories and poetry, in the grades 2-3 text complexity band proficiently,
Going to School: Measuring Schooling Behaviors in GloFish
 Name Period Date Going to School: Measuring Schooling Behaviors in GloFish Objective The learner will collect data to determine if schooling behaviors are exhibited in GloFish fluorescent fish. The learner
Name Period Date Going to School: Measuring Schooling Behaviors in GloFish Objective The learner will collect data to determine if schooling behaviors are exhibited in GloFish fluorescent fish. The learner
Common Core State Standards
 Common Core State Standards Common Core State Standards 7.NS.3 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. Mathematical Practices 1, 3, and 4 are aspects
Common Core State Standards Common Core State Standards 7.NS.3 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. Mathematical Practices 1, 3, and 4 are aspects
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SOCIAL STUDIES SYLLABUS FOR BASIC EDUCATION STANDARD III-VI
 THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SOCIAL STUDIES SYLLABUS FOR BASIC EDUCATION STANDARD III-VI THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SOCIAL STUDIES SYLLABUS FOR BASIC EDUCATION STANDARD III-VI THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND
Ocean Exploration: Diving Deep into Ocean Science. Developed by: Sierra Tobiason, Lynn Fujii and Noe Taum
 Ocean Exploration: Diving Deep into Ocean Science Grade Level: Sixth Grade Developed by: Sierra Tobiason, Lynn Fujii and Noe Taum Purpose: This curriculum is designed to communicate: I. Methods scientist
Ocean Exploration: Diving Deep into Ocean Science Grade Level: Sixth Grade Developed by: Sierra Tobiason, Lynn Fujii and Noe Taum Purpose: This curriculum is designed to communicate: I. Methods scientist
2 months: Social and Emotional Begins to smile at people Can briefly calm self (may bring hands to mouth and suck on hand) Tries to look at parent
 2 months: Begins to smile at people Can briefly calm self (may bring hands to mouth and suck on hand) Tries to look at parent Coos, makes gurgling sounds Turns head toward sounds Pays attention to faces
2 months: Begins to smile at people Can briefly calm self (may bring hands to mouth and suck on hand) Tries to look at parent Coos, makes gurgling sounds Turns head toward sounds Pays attention to faces
Function Number 1 Work as part of a team. Thorough knowledge of theoretical procedures and ability to integrate knowledge and performance into
 Function Essential Functions EMT PARAMEDIC 1 Work as part of a team. Thorough knowledge of theoretical procedures and ability to integrate knowledge and performance into practical situations is critical.
Function Essential Functions EMT PARAMEDIC 1 Work as part of a team. Thorough knowledge of theoretical procedures and ability to integrate knowledge and performance into practical situations is critical.
Dear Teacher: Welcome to Reading Rods! Reading Rods offer many outstanding features! Read on to discover how to put Reading Rods to work today!
 Dear Teacher: Welcome to Reading Rods! Your Sentence Building Reading Rod Set contains 156 interlocking plastic Rods printed with words representing different parts of speech and punctuation marks. Students
Dear Teacher: Welcome to Reading Rods! Your Sentence Building Reading Rod Set contains 156 interlocking plastic Rods printed with words representing different parts of speech and punctuation marks. Students
Large Kindergarten Centers Icons
 Large Kindergarten Centers Icons To view and print each center icon, with CCSD objectives, please click on the corresponding thumbnail icon below. ABC / Word Study Read the Room Big Book Write the Room
Large Kindergarten Centers Icons To view and print each center icon, with CCSD objectives, please click on the corresponding thumbnail icon below. ABC / Word Study Read the Room Big Book Write the Room
Innovative Teaching in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math
 Innovative Teaching in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math Take-Aways- What is S.T.E.M. education and why STEM skills are so important in ECE now and in our future; Current research about quality
Innovative Teaching in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math Take-Aways- What is S.T.E.M. education and why STEM skills are so important in ECE now and in our future; Current research about quality
About this unit. Lesson one
 Unit 30 Abuja Carnival About this unit This unit revises language and phonics done throughout the year. The theme of the unit is Abuja carnival. Pupils describe a happy carnival picture and read a story
Unit 30 Abuja Carnival About this unit This unit revises language and phonics done throughout the year. The theme of the unit is Abuja carnival. Pupils describe a happy carnival picture and read a story
Activities. Standards-Based Skill-Builders with Seasonal Themes. Written by Brenda Kaufmann. Sample file. Illustrated by Janet Armbrust
 Spring Math Activities Standards-Based Skill-Builders with Seasonal Themes Written by Brenda Kaufmann Illustrated by Janet Armbrust Teaching & Learning Company 1204 Buchanan St., P.O. Box 10 Carthage,
Spring Math Activities Standards-Based Skill-Builders with Seasonal Themes Written by Brenda Kaufmann Illustrated by Janet Armbrust Teaching & Learning Company 1204 Buchanan St., P.O. Box 10 Carthage,
1. Listen carefully as your teacher assigns you two or more rows of the Biome Jigsaw Chart (page S2) to fill in.
 Biome Bags - Student Guide In this activity, you will explore ecology and biodiversity will be to work cooperatively to: in seven terrestrial biomes. Your task 1. Research and share information to complete
Biome Bags - Student Guide In this activity, you will explore ecology and biodiversity will be to work cooperatively to: in seven terrestrial biomes. Your task 1. Research and share information to complete
TEKS Resource System. Effective Planning from the IFD & Assessment. Presented by: Kristin Arterbury, ESC Region 12
 TEKS Resource System Effective Planning from the IFD & Assessments Presented by: Kristin Arterbury, ESC Region 12 karterbury@esc12.net, 254-297-1115 Assessment Curriculum Instruction planwithifd.wikispaces.com
TEKS Resource System Effective Planning from the IFD & Assessments Presented by: Kristin Arterbury, ESC Region 12 karterbury@esc12.net, 254-297-1115 Assessment Curriculum Instruction planwithifd.wikispaces.com
English Comprehension Question For Grade 7
 English Question For Grade 7 Free PDF ebook Download: English Question For Grade 7 Download or Read Online ebook english comprehension question for grade 7 in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database
English Question For Grade 7 Free PDF ebook Download: English Question For Grade 7 Download or Read Online ebook english comprehension question for grade 7 in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database
Kindergarten Curriculum Guide
 Our Mission as a Friends School A handbook of the curriculum will always be a work in progress, a phrase that describes many aspects of schools with dynamic vision. We invite your comments so that we can
Our Mission as a Friends School A handbook of the curriculum will always be a work in progress, a phrase that describes many aspects of schools with dynamic vision. We invite your comments so that we can
How to Read the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS)
 How to Read the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) are distinct from prior science standards in three essential ways. 1) Performance. Prior standards
How to Read the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) are distinct from prior science standards in three essential ways. 1) Performance. Prior standards
Table of Contents. This descriptive guide will assist you in integrating the DVD science and education content into your instructional program.
 Bill Nye the Science Guy Comets & Meteors 1. Implementation Guide........................................ 2 9 This descriptive guide will assist you in integrating the DVD science and education content
Bill Nye the Science Guy Comets & Meteors 1. Implementation Guide........................................ 2 9 This descriptive guide will assist you in integrating the DVD science and education content
Kindergarten Lessons for Unit 7: On The Move Me on the Map By Joan Sweeney
 Kindergarten Lessons for Unit 7: On The Move Me on the Map By Joan Sweeney Aligned with the Common Core State Standards in Reading, Speaking & Listening, and Language Written & Prepared for: Baltimore
Kindergarten Lessons for Unit 7: On The Move Me on the Map By Joan Sweeney Aligned with the Common Core State Standards in Reading, Speaking & Listening, and Language Written & Prepared for: Baltimore
Kindergarten - Unit One - Connecting Themes
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary for the Kindergarten Social Studies Course. Kindergarten
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary for the Kindergarten Social Studies Course. Kindergarten
Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium:
 Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium: ELA Practice Test Scoring Guide Grade 5 04/25/2014 G5_PracticeTest_ScoringGuide_ELA.docx 0 1 5 1 1 2 RI-1 The student will identify text evidence to support a given
Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium: ELA Practice Test Scoring Guide Grade 5 04/25/2014 G5_PracticeTest_ScoringGuide_ELA.docx 0 1 5 1 1 2 RI-1 The student will identify text evidence to support a given
Characteristics of the Text Genre Informational Text Text Structure
 LESSON 4 TEACHER S GUIDE by Taiyo Kobayashi Fountas-Pinnell Level C Informational Text Selection Summary The narrator presents key locations in his town and why each is important to the community: a store,
LESSON 4 TEACHER S GUIDE by Taiyo Kobayashi Fountas-Pinnell Level C Informational Text Selection Summary The narrator presents key locations in his town and why each is important to the community: a store,
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 5: HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS
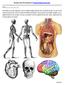 SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 5: HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS NAME: This booklet is an in-class assignment; you must complete all pages during the class work periods provided. You must use full sentences for all sections
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 5: HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS NAME: This booklet is an in-class assignment; you must complete all pages during the class work periods provided. You must use full sentences for all sections
Fisk Street Primary School
 Fisk Street Primary School Literacy at Fisk Street Primary School is made up of the following components: Speaking and Listening Reading Writing Spelling Grammar Handwriting The Australian Curriculum specifies
Fisk Street Primary School Literacy at Fisk Street Primary School is made up of the following components: Speaking and Listening Reading Writing Spelling Grammar Handwriting The Australian Curriculum specifies
Adaptations and Survival: The Story of the Peppered Moth
 Adaptations and Survival: The Story of the Peppered Moth Teacher: Rachel Card Subject Areas: Science/ELA Grade Level: Fourth Unit Title: Animal Adaptations Lesson Title: Adaptations and Survival: The Story
Adaptations and Survival: The Story of the Peppered Moth Teacher: Rachel Card Subject Areas: Science/ELA Grade Level: Fourth Unit Title: Animal Adaptations Lesson Title: Adaptations and Survival: The Story
Sight Word Assessment
 Make, Take & Teach Sight Word Assessment Assessment and Progress Monitoring for the Dolch 220 Sight Words What are sight words? Sight words are words that are used frequently in reading and writing. Because
Make, Take & Teach Sight Word Assessment Assessment and Progress Monitoring for the Dolch 220 Sight Words What are sight words? Sight words are words that are used frequently in reading and writing. Because
MATH Study Skills Workshop
 MATH Study Skills Workshop Become an expert math student through understanding your personal learning style, by incorporating practical memory skills, and by becoming proficient in test taking. 11/30/15
MATH Study Skills Workshop Become an expert math student through understanding your personal learning style, by incorporating practical memory skills, and by becoming proficient in test taking. 11/30/15
WHAT DOES IT REALLY MEAN TO PAY ATTENTION?
 WHAT DOES IT REALLY MEAN TO PAY ATTENTION? WHAT REALLY WORKS CONFERENCE CSUN CENTER FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING MARCH 22, 2013 Kathy Spielman and Dorothee Chadda Special Education Specialists Agenda Students
WHAT DOES IT REALLY MEAN TO PAY ATTENTION? WHAT REALLY WORKS CONFERENCE CSUN CENTER FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING MARCH 22, 2013 Kathy Spielman and Dorothee Chadda Special Education Specialists Agenda Students
We are going to talk about the meaning of the word weary. Then we will learn how it can be used in different sentences.
 Vocabulary Instructional Routine: Make Connections with New Vocabulary Preparation/Materials: several words selected from Hansel and Gretel (e.g.,, glorious, scare) 1 Italicized sentences are what the
Vocabulary Instructional Routine: Make Connections with New Vocabulary Preparation/Materials: several words selected from Hansel and Gretel (e.g.,, glorious, scare) 1 Italicized sentences are what the
4th Grade Science Test Ecosystems
 4th Grade Science Free PDF ebook Download: 4th Grade Science Download or Read Online ebook 4th grade science test ecosystems in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database 4th Grade--LIFE SCIENCE. Unit
4th Grade Science Free PDF ebook Download: 4th Grade Science Download or Read Online ebook 4th grade science test ecosystems in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database 4th Grade--LIFE SCIENCE. Unit
First Grade Curriculum Highlights: In alignment with the Common Core Standards
 First Grade Curriculum Highlights: In alignment with the Common Core Standards ENGLISH LANGUAGE ARTS Foundational Skills Print Concepts Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features
First Grade Curriculum Highlights: In alignment with the Common Core Standards ENGLISH LANGUAGE ARTS Foundational Skills Print Concepts Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features
J j W w. Write. Name. Max Takes the Train. Handwriting Letters Jj, Ww: Words with j, w 321
 Write J j W w Jen Will Directions Have children write a row of each letter and then write the words. Home Activity Ask your child to write each letter and tell you how to make the letter. Handwriting Letters
Write J j W w Jen Will Directions Have children write a row of each letter and then write the words. Home Activity Ask your child to write each letter and tell you how to make the letter. Handwriting Letters
MISSISSIPPI EXTENDED CURRICULUM FRAMEWORKS CORRELATION WITH PROJECT DISCOVERY
 MISSISSIPPI EXTENDED CURRICULUM FRAMEWORKS CORRELATION WITH PROJECT DISCOVERY Middle School Level A U.S. Department of Education Validated and Approved Program Development Team: Ms. Betsy Gentry, Special
MISSISSIPPI EXTENDED CURRICULUM FRAMEWORKS CORRELATION WITH PROJECT DISCOVERY Middle School Level A U.S. Department of Education Validated and Approved Program Development Team: Ms. Betsy Gentry, Special
Characteristics of the Text Genre Realistic fi ction Text Structure
 LESSON 14 TEACHER S GUIDE by Oscar Hagen Fountas-Pinnell Level A Realistic Fiction Selection Summary A boy and his mom visit a pond and see and count a bird, fish, turtles, and frogs. Number of Words:
LESSON 14 TEACHER S GUIDE by Oscar Hagen Fountas-Pinnell Level A Realistic Fiction Selection Summary A boy and his mom visit a pond and see and count a bird, fish, turtles, and frogs. Number of Words:
LA1 - High School English Language Development 1 Curriculum Essentials Document
 LA1 - High School English Language Development 1 Curriculum Essentials Document Boulder Valley School District Department of Curriculum and Instruction April 2012 Access for All Colorado English Language
LA1 - High School English Language Development 1 Curriculum Essentials Document Boulder Valley School District Department of Curriculum and Instruction April 2012 Access for All Colorado English Language
Food Chain Cut And Paste Activities
 Cut And Paste Activities Free PDF ebook Download: Cut And Paste Activities Download or Read Online ebook food chain cut and paste activities in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database CO #3: Organise
Cut And Paste Activities Free PDF ebook Download: Cut And Paste Activities Download or Read Online ebook food chain cut and paste activities in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database CO #3: Organise
GUIDE CURRICULUM. Science 10
 Science 10 Arts Education Business Education English Language Arts Entrepreneurship Family Studies Health Education International Baccalaureate Languages Mathematics Personal Development and Career Education
Science 10 Arts Education Business Education English Language Arts Entrepreneurship Family Studies Health Education International Baccalaureate Languages Mathematics Personal Development and Career Education
