Department of Academic Advancement Fifth Grade Science Curriculum Guide Fifth Grade Pacing Guide
|
|
|
- Meredith Richardson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cells & Relationships in the Ecosystem 3 weeks Department of Academic Advancement Fifth Grade Pacing Guide First Nine Weeks Second Nine Weeks Units Topics Units Topics 1. Cell Structures of Animal & Plant Cells Planets & Stars 2. Nutrition Among Organisms 5 weeks 3. Symbiotic 4. Commensalism 5. Parasitic 1. Physical Characteristics of the Planets 2. Distance 3. Exploration 4. Recognition of the Stars 5. Identification of the Stars Photosynthesis 2 weeks 1. Photosynthesis 2. Plant Energy Geological Features 2 weeks 1. Events 2. Features Reproduction, Traits, & Heredity 2 weeks 1. Transfer of Genetic 2. Inherited vs. Environmental Atmospheric Conditions 2 weeks 1. Major Landforms 2. Bodies of Water Animal Adaptations 2 weeks 1. Physical Characteristics of Animals 2. Organisms & Environments Past & Present Matter 2 weeks Third Nine Weeks Fourth Nine Weeks Units Topics Units Topics 1. Exploration of Types of Matter Building Bridges 1. Create/Design/Test 9 weeks 2. Original Bridge Design Changes of State 2 weeks Motion & Forces 2 weeks Energy & Heat 2 weeks 1. Classification of Matter 2. Temperature Effect 1. Force 2. Mass 3. Distance Traveled 4. Magnetism 1. Potential Energy 2. Kinetic Energy 3. Heat Transfer 4. Conduction, Convection, & Radiation
2 Guiding Questions: What are the differences between plant and animal cells? How is energy transferred within the relationships of an ecosystem? What is the difference in the relationship of parasitism, commensalism and mutualism of organisms? How do human and natural events change our ecosystems? Life Science 1 st Nine Weeks-Cells and Relationships in the Ecosystem (3 weeks) GLE Use microscopes and identify the basic Macmillian/McGraw-Hill Distinguish between the Organize data into appropriate structures of plant and animal cells. Chapter 1, Lesson 1 p 22 basic structures and tables, graphs, drawings, or Chapter 1, Lesson 2 p 36 functions of plant and animal diagrams Chapter 1, Lesson 4 p 64 cells. GLE Investigate different nutritional relationships among organisms in an ecosystem. GLE Explain how organisms interact through symbiotic, commensally, and parasitic relationships. GLE Establish connections between human activities or natural disasters and their impact on the environment. GLE 0507.T/E.1 Describe how tools, technology, and inventions help to answer questions and solve problems. GLE 0507.Inq.4 Identify and interpret simple patterns of evidence to communicate the finding of multiple investigations. Compare and contrast cell structures and functions by making observations of a variety of cells found in both plants and animals. Analyze the structures and functions of plant and animal cells to develop an argument for identifying a single cell as a living thing. Collect and analyze data on the producer/consumer, predator/prey, and parasite/host relationships within an ecosystem. Create an energy pyramid to explain how energy flows through an ecosystem. Explain the mathematical relationship between the number of organisms and the amount of energy available at each level of the food chain. Create a food web to model the inter-specific relationships within an ecosystem. Analyze basic information about the environment. Collect information from a variety of resources and identify key issues or assumptions to draw conclusions about how human activities have affected the environment. Reading Street: Survival Questions p 86 Young People Helping the Environment p 211 Jane Goodall s 10 ways to help save wild life p 212 Dinosaurs p 317 The mystery of Saint Matthew Island p 658 Next Generation Science Standard Practices 1. Asking questions and defining problems 2. Developing and using models 3. Planning and carrying out investigation 4. Analyzing and Interpreting Data 6. Constructing Explanations and Designing : Design investigations to address a question and consider how data collection methods affect the nature of the data set. Evaluate an expression by substituting non-negative rational number values for letter variables in the expression. Construct and analyze double bar and line graphs. Use exponential notation to represent repeated multiplication. Use patterns, models, and relationships as contexts for writing inequalities and simple equations. : Use common text parts and features to enhance understanding. Determine the main ideas and supporting details from text. Use print and non-print materials along with prior knowledge to provide background for writing and or/ presenting. Demonstrate knowledge of Standard English sentence structure. Create and deliver an oral presentation using visual aids or props. Draw conclusions while reading, viewing, or listening to print and non-print media. Compare and contrast two persons, places, things, or ideas. Organize information from text to technological sources using a graphic organizer.
3 GLE Demonstrate how all living things rely on the process of photosynthesis to obtain energy. Department of Academic Advancement Guiding Question: What processes do plants used to obtain energy? How do animals fit into this process? 1 st Nine Weeks-Photosynthesis (2 weeks) Macmillian/McGraw-Hill Chapter 1, Lesson 3 p. 52 Organize data into appropriate tables, graphs, drawings, or diagrams. Explain the importance of photosynthesis to all living things. Design an investigation to demonstrate how the sun acts as the catalyst in the process of photosynthesis. Reading Street: The Mystery of Saint Mathew Island p 658 Next Generation Science Standard Practices 5.Using and Computational Thinking 6.Constructing Explanations and Designing Use patterns, models, and relationships as contexts for writing inequalities and simple equations. Create a well-developed story or passage summary, as well as personal reflections and imaginative writing samples. Organize information from text or technological sources using a graphic organizer. Draw conclusions while reading, viewing, or listening to print and non-print media.
4 Guiding Question: Where do we get our genes? Which traits are inherited from our parents and which do we have instinctual to survive in our environment? 1 st Nine Weeks-Reproduction, Traits, and Heredity (2 weeks) GLE Collect and analyze data to Macmillian/McGraw-Hill Describe how genetic Organize data into appropriate identify patterns of evidence Chapter 2, Lesson 1 p 84 information is passed from tables, graphs, drawings, or supporting the transfer of Chapter 2, Lesson 2 p 98 parents to offspring during diagrams genetic information from parent reproduction. to offspring. GLE Recognize that some characteristics are inherited while others result from interactions with the environment. GLE 0507.T/E.1 Describe how tools, technology, and inventions help to answer questions and solve problems. GLE 0507.T/E.4 Recognize the connection between scientific advances, new knowledge, and the availability of new tools and technologies. GLE 0507.Inq.4 Identify and interpret simple patterns of evidence to communicate the finding of multiple investigations. Create a model that demonstrates an understanding of inherited traits. Describe how technology has aided in the understanding of genetically transferred diseases. Create a chart to compare and contrast traits as to whether they are inherited or environmental. Determine if a trait is the result of genetics or environmental factors. Recognize how have tools and technologies assisted humans in understanding the effects of environmental influences. Next Generation Science Standard Practices 5.Using and Computational Thinking 6.Constructing Explanations and Designing Construct and analyze double bar and line graphs. Demonstrate knowledge of Standard English sentence structure. Compare and contrast two persons, places, things, or ideas. Use current technology as a research and communication tool for personal interest, research, and clarification.
5 Guiding Questions: What physical characteristics allow an organism to survive in different environments? How do fossils help us to connect the past to the present? 1 st Nine Weeks-Animal Adaptations (2 weeks) GLE 0507.Inq.1 Compare and contrast groups of Macmillian/McGraw-Hill Explore different scientific animals using their physical Chapter 2, Lesson 3 p 108 phenomena by asking characteristics. Chapter 2, Lesson 4 p 122 questions, making logical predictions, planning Create a simple classification investigations, and recording system. data. GLE Investigate physical characteristics associated with different groups of animals. GLE Analyze fossils to demonstrate the connection between organisms and environments that existed in the past and those that currently exist. Organize data into appropriate tables, graphs, drawings, or diagrams. GLE 0507.T/E.1 Describe how tools, technology, and inventions help to answer questions and solve problems. GLE 0507.Inq.4 Identify and interpret simple patterns of evidence to communicate the finding of multiple investigations. Explain how the physical characteristics of an organism determine its preferences for different environments. Compare and contrast fossil evidence illustrating the connections between previously existing organisms and ones that exist today. Describe the various types of fossil evidence. Reading Street Story of the Caterpillar p 145 Chimps p 209 Why Some Animals are Considered Bad or Scary p 226 Dinosaurs p 317 The Dinosaurs of Waterhouse Hawkins p 320 Ant Facts p 437 Exploding Ants p 440 Adapting Lagoon p 454 Next Generation Science Standard Practices 5.Using and Computational Thinking 6.Constructing Explanations and Designing Use patterns, models, and relationships as contexts for writing inequalities and simple equations. Create a well-developed story or passage summary, as well as personal reflections and imaginative writing samples. Organize information from text or technological sources using a graphic organizer. Draw conclusions while reading, viewing, or listening to print and non-print media.
6 First Nine Weeks Resources Vocabulary: cells, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, cell wall, predator, prey, mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, photosynthesis, heredity, inherited trait, adaptation, relative age Inquiry Skills: predict, record data, observe, infer, communicate, classify, make a model, compare, draw conclusions Plans Cells and Relationships in the Ecosystem Understand the structure of cells and the parts of a animal and plant cell. Grasp the concept of symbiotic, commensalism and parasitic communities as it relates to nature. Photosynthesis Understand the wonder of transfer of energy that is photosynthesis and why it is so important to the survival of the plants. Reproduction, Traits, and Heredity Understand human traits and animal traits as well as reproduction Animal Adaptations Understand how animals and plants adapt to new environments in order to survive. Background for Teachers Cells and Relationships in the Ecosystem Photosynthesis Organisms that have chloroplast use the act of photosynthesis to make food for survival. Reproduction, Traits, and Heredity Animal Adaptations Adaptations are not isolated to animals, plants also adapt. Student Activities Cells and Relationships in the Ecosystem Create a chart/diagram explaining the difference in a animal and plant cell, unicellular organism and multicellular organisms. Photosynthesis Examine existing plants using microscopes or hand lenses, observing the intricate details of the leaves and stems. Draw what it seen and label. Reproduction, Traits, and Heredity Explore activity page 89 Tennessee Science Closer look Macmillan/McGraw-Hill Animal Adaptations Explore activity page 109 Tennessee Science Closer look Macmillan/McGraw-Hill While using a variety of objects like; oven mittens, chop sticks, spoons etc. try and pick up small and large objects and place them in a container or build a structure to represent animals adapting to change.
7 Earth Science Guiding Questions: How are the physical characteristics of each planet different? 2nd Nine Weeks-Planets and Stars (2 weeks) GLE Compare planets based on their known characteristics. Macmillian/McGraw-Hill Chapter 3, Lesson 1 p. 148 Chapter 3, Lesson 2 p. 162 GLE 0507.Inq.1 Explore different scientific phenomena by asking questions, making logical predictions, planning investigations, and recording data. Organize data into appropriate tables, graphs, drawings, or diagrams. GLE 0507.Inq.4 Identify and interpret simple patterns of evidence to communicate the finding of multiple investigations. GLE0507.Inq.6 Compare the results of an investigation with what scientists already accept about this question. GLE 0507.T/E.1 Describe how tools, technology, and inventions help to answer questions and solve problems. Research, analyze compare and contrast the physical characteristics of the planets based on their composition, distance from the sun and apparent motion. Use scientific notation to describe distances between planets in the solar system Create a model of the planets in the solar system scaling the size of the planets, the distance between each planet, and their distance from the sun.. Research how the use of technologies has enabled humans in exploring the solar system and beyond. Develop a logical argument for or against Pluto being a planet. Reading Street: Earth p. 583 Journey to the Center of the Earth p. 586 Crust Mantle Core p. 600 Next Generation Science Standard Practices 5.Using and Computational Thinking 6. Constructing Explanations and Designing Use exponential notation to represent repeated multiplication of whole numbers. Communicate answers in correct verbal and numerical form including use of mixed numbers or fractions and use of units. Recognize the differences in representing categorical and numerical data. Compare and contrast two persons, places, things, or ideas. Present research in a simple written report. Organize information from text or technological sources using a graphic organizer.
8 Guiding Question: How are the physical characteristics of each planet different? 2nd Nine Weeks- Planets and Stars (3 weeks) GLE Compare planets based on their known characteristics. Macmillian/McGraw-Hill Chapter 3, Lesson 3 p. 172 GLE 0507.Inq.1 Explore different scientific phenomena by asking questions, making logical predictions, planning investigations, and recording data. Organize data into appropriate tables, graphs, drawings, or diagrams. GLE 0507.Inq.4 Identify and interpret simple patterns of evidence to communicate the finding of multiple investigations. GLE0507.Inq.6 Compare the results of an investigation with what scientists already accept about this question. GLE 0507.T/E.1 Describe how tools, technology, and inventions help to answer questions and solve problems. Research, analyze compare and contrast the physical characteristics of the planets based on their composition, distance from the sun and apparent motion. Use scientific notation to describe distances between planets in the solar system. Create a model of the planets in the solar system scaling the size of the planets, the distance between each planet, and their distance from the sun. Research how the use of technologies has enabled humans in exploring the solar system and beyond. Develop a logical argument for or against Pluto being a planet. Next Generation Science Standard Practices 5.Using and Computational Thinking 6. Constructing Explanations and Designing Use exponential notation to represent repeated multiplication of whole numbers. Communicate answers in correct verbal and numerical form including use of mixed numbers or fractions and use of units. Recognize the differences in representing categorical and numerical data. Compare and contrast two persons, places, things, or ideas. Present research in a simple written report. Organize information from text or technological sources using a graphic organizer.
9 Guiding Question: What type of plate movements can create volcanoes, earthquakes, and faulting? How do these forces change/create earth s geological features? 2nd Nine Weeks-Geological Features (2 weeks) GLE Research, collect and analyze Macmillian/McGraw-Hill Compare geological events Organize data into appropriate data on the earth s geological Chapter 4, Lesson 1 p. 190 responsible for the earth s tables, graphs, drawings, or features and develop a rational Chapter 4, Lesson 2 p. 208 major geological features. diagrams for surrounding landforms. Chapter 4, Lesson 3 p. 218 GLE 0507.Inq.4 Identify and interpret simple patterns of evidence to communicate the finding of multiple investigations. GLE0507.Inq.6 Compare the results of an investigation with what scientists already accept about this question. GLE 0507.T/E.1 Describe how tools, technology, and inventions help to answer questions and solve problems. GLE 0507.T/E.3 Identify appropriate materials, tools, and machines that can extend or enhance the ability to solve a specified problem. Create a model and use it to explain how a geological event resulted in that landform. Classify geologic features based on how quickly they were formed. Explore the technologies that have improved the ability of humans to understand earth s geological events. Use data to create a map depicting the locations of major geological events such as earthquakes and volcanoes and draw conclusions about the reason for such events. Describe internal forces such as volcanoes, earthquakes, faulting, and plate movements that are responsible for the earth s geological features. Use technology to monitor major geological events, their strengths and impact. Reading Street: Journey to the Center of the Earth p. 586 Next Generation Science Standard Practices 1. Asking questions and defining problems 2. Developing and using models 3. Planning and carrying out investigation 4. Analyzing and Interpreting Data 6. Constructing Explanations and Designing Understand, select and use units of appropriate size and type to measure angles, lengths/distances, area, surface area and volume. Understand the usefulness of approximations. Explore numbers less and 0 by extending the number line through familiar applications (e.g. temperatures below zero, owing money, measuring elevation below sea level. Compose and respond in writing to original questions and/or problems from all content areas. Organize information from text or technological sources using a graphic organizer. Gather and record information on a research topic using three different sources, at least one of which must be a print source.
10 Guiding Question: How do the oceans and mountains affect weather as well as climate? What affect will land breezes and sea breezes have on weather/climate? What is happening with weather as it moves over the mountain? 2nd Nine Weeks-Atmospheric Conditions (2 weeks) GLE Analyze and predict how Organize data into appropriate Create a graph or chart to compare the climates of coastal and inland Macmillian/McGraw-Hill Chapter 4, Lesson 4 p. 230 major landforms and bodies tables, graphs, drawings, or areas at similar latitudes to of water affect atmospheric diagrams determine the ocean s impact on weather and climate. conditions. GLE 0507.Inq.4 Identify and interpret simple patterns of evidence to communicate the finding of multiple investigations. GLE0507.Inq.6 Compare the results of an investigation with what scientists already accept about this question. GLE 0507.T/E.1 Describe how tools, technology, and inventions help to answer questions and solve problems. GLE 0507.T/E.3 Identify appropriate materials, tools, and machines that can extend or enhance the ability to solve a specified problem GLE 0507.T/E.4 Recognize the connection between scientific advances, new knowledge, and the availability of new tools and technologies. Use land maps to compare and contrast weather and climate to explain the effect of mountain ranges. Create a graph of temperature and precipitation data for inland and coastal regions Use local environmental information to analyze if weather and climate are affected by landforms and bodies of water. Research the tools and technologies that are used to collect and analyze data on weather and climates. Create a model to explain the affect that landforms have on weather and climate. Demonstrate the effect of uneven heating and cooling on the weather and climate of a region. Next Generation Science Standard Practices 1. Asking questions and defining problems 2. Developing and using models 3. Planning and carrying out investigation 4. Analyzing and Interpreting Data 6. Constructing Explanations and Designing Construct and analyze double bar and line graphs determining the length of vertical or horizontal segments in the first quadrant of a coordinate system using fractions and decimals. Design investigations to address a question and consider how data collection methods affect the nature of the data set. Recognize the differences in representing categorical and numerical data. Demonstrate knowledge of Standard English sentence structure. Compare and contrast two persons, places, things, or ideas. Use current technology as a research and communication tool for personal interest, research, and clarification.
11 Second Nine Weeks Resources Vocabulary: revolution, rotation, star, nebula, white dwarf, supernova, constellation, star chart, core, mantle, crust, geological features, volcano, earthquake, plate tectonics, magma, hydrosphere Inquiry Skills: predict, record data, observe, infer, communicate, classify, make a model, compare, draw conclusions Plans Planets and Stars Compare planets understand their characteristics and their relation to earth. Understand how stars are created, characterization of stars and the life span of a star. Geological Features Write about and create a diagram of the earth s surface and layers. Atmospheric Conditions Analyze different atmosphere around the world, compare and contrast with charts and diagrams. Background for Teachers Planets and Stars According to most recent research Pluto is not a planet. Atmospheric Conditions Each part of the world and the United States has different atmospheres whether they are cold, hot, raining, year long. Student Activities Planets and Stars Calculate the age of the students on the various planets based on the number of earth days it takes to revolve around the sun. Calculate the weight of students on each planet. Geological Features Construct a functional paper on the earth s surface and layers explaining past events, present and future possibilities. Atmospheric Conditions Create a chart with explanations of the type of atmosphere a region has and what inhabitants may be found there.
12 Guiding Questions: How can matter be described? How are the physical and chemical properties of matter different? Physical Science 3rd Nine Weeks-Matter Changes (2 weeks) GLE GLE 0507.Inq.2 Compare and contrast simple Macmillian/McGraw-Hill Observe and measure the Select and use appropriate tools chemical properties of common Chapter 5 Lesson 1 p. 254 simple chemical properties and simple equipment to conduct substances. Chapter 5 Lesson 2 p. 270 of common substances. an investigation. Chapter 5 Lesson 3 p. 292 Organize data into appropriate tables, graphs, drawings, or diagrams. GLE 0507.Inq.4 Identify and interpret simple patterns of evidence to communicate the finding of multiple investigations. GLE0507.Inq.6 Compare the results of an investigation with what scientists already accept about this question. GLE 0507.T/E.3 Identify appropriate materials, tools, and machines that can extend or enhance the ability to solve a specified problem. Organize data about the chemical properties of matter and determine how they impact its use. Compare the quantities of a solid material necessary to produce a saturated solution. Compare the crystals from a variety of salts such as alum, citric acid, Epsom salts. Design a means of separating an unknown mixture. Next Generation Science Standard Practices 5.Using and Computational Thinking 6. Constructing Explanations and Designing Collect and organize data using observations, surveys, and experiments. Compare and interpret different representations of the same data. Write for a variety of purposes and to a variety of audiences. Distinguish fact from opinion and cause from effect. Use common text parts and features to enhance understanding. Predict outcomes and adjust as additional information is acquired.
13 Guiding Question: What factors influence how matter moves? 3rd Nine Weeks-Changes of State (2 weeks) GLE Observe and measure the Design an investigation to classify various substances based on their Macmillian/McGraw-Hill Chapter 5 Lesson 3 p. 282 simple chemical properties rate of freezing, melting or of common substances. evaporating. GLE Design and conduct an experiment to demonstrate how various types of matter freeze, melt, or evaporate. GLE Investigate factors that affect the rate at which materials freeze, melt or evaporate. GLE 0507.Inq.1 Explore different scientific phenomena by asking questions, making logical predictions, planning investigations, and recording data. GLE 0507.Inq.2 Select and use appropriate tools and simple equipment to conduct an investigation. Organize data into appropriate tables, graphs, drawings, or diagrams. GLE 0507.Inq.6 Compare the results of an investigation with what scientists already accept about this question. GLE 0507.T/E.3 Identify appropriate materials, tools, and machines that can extend or enhance the ability to solve a specified problem. Graph the data and use it to explain the results of the investigation. Explain how people could get different data if they are working with similar matter. Investigate the effect of temperature on the concentration and saturation of a solid in a mixture. Compare and contrast various substances by the factors that affect the rate of freezing, melting, or evaporation by creating a graphic organizer. Create a presentation that demonstrates an understanding of how temperature affects condensation and evaporation rates. Investigate how new technologies have been developed to make use of the variance in rates of freezing, melting, or evaporating. Next Generation Science Standard Practices 5.Using and Computational Thinking 6. Constructing Explanations and Designing Recognize and use measures of weight and temperature. Construct and analyze double bar and line graphs. Design investigations to address a question and consider how data collection methods affect the nature of the data set. Create and deliver an oral presentation using visual aids or props. Organize information from text or technological sources using a graphic organizer. Compare and contrast two persons, places, things or ideas. Construct and complete analogies. Use media to enhance reports and oral presentations.
14 Guiding Questions: How can matter be described? What causes matter to move? Can the shape of an object affect how gravity pulls on it? 3rd Nine Weeks-Motion and Forces (3 weeks) GLE GLE 0507.Inq.1 Explore different Observe and describe how motion Macmillian/McGraw-Hill Design an experiment, scientific phenomena by asking can be changed. Conduct an Chapter 6, Lesson 1 p. 308 questions, making logical predictions, collect data and draw investigation that provides data on Chapter 6, Lesson 2 p. 322 planning investigations, and recording conclusions about the the effects of different variables on data. the distance an object travels. Use relationships among mass, a two coordinate graph display to force, and distance traveled. GLE 0507.Inq.2 Select and use show the relationship between appropriate tools and simple equipment to conduct an investigation. variables in an investigation. GLE Recognize that the earth attracts objects without touching them GLE Investigate how the shape of an object influences the way that it falls toward the earth. GLE Provide examples of how forces can actata distance. Organize data into appropriate tables, graphs, drawings, or diagrams. GLE 0507.Inq.4 Identify and interpret simple patterns of evidence to communicate the finding of multiple investigations. GLE 0507.Inq.5 Recognize that people may interpret the same results in different ways. GLE 0507.T/E.1 Describe how tools, technology, and inventions help to answer questions and solve problems. GLE 0507.T/E.2 Recognize that new tools, technology, and inventions. GLE 0507.T/E.3 Identify appropriate materials, tools, and machines that can extend or enhance the ability to solve a specified problem. GLE 0507.T/E.4 Recognize the connection between scientific advances, new knowledge, and the availability of new tools and technologies. Develop a system to demonstrate how the relationship between mass, force, and distance traveled works within that system. Create a chart and provide examples of when forces act at a distance. Design an investigation, collect and analyze data using shape as a variable to determine if shape affects the way an object falls to earth. Using what is learned from the investigation; design a container to safely transport an object while falling. Use the appropriate technology to describe how the shape of an object influences the way it falls to Earth. Explain how scientific advancements have allowed scientist to observe and measure unseen forces. Next Generation Science Standard Practices 5.Using and Computational Thinking 6. Constructing Explanations and Designing Use variables appropriately to represent numbers whose values are not yet known. Represent data using ordered pairs in the first quadrant of the coordinate system Make, record, display and interpret data and graphs that include whole numbers, decimals, and fractions. Make conjectures about geometric properties and develop logical arguments to justify conclusions. Design investigations to address a question and consider how data collection methods affect the nature of the data set. Organize information from text or technological sources using a graphic organizer. Predict outcomes and adjust as additional information is acquired. Build vocabulary by reading from a wide variety of texts and literary genres. Write for a variety of purposes and to a variety of audiences. Use current technology as a research and communication tool for personal interest, research, and clarification.
15 Guiding Questions: How is energy defined? What is the difference in potential and kinetic energy? How does energy travel through solids, liquids, and gases? Physical Science 3rd Nine Weeks-Energy and Heat (2 weeks) GLE GLE 0507.Inq.1 Explore different Conduct an experiment that Macmillian/McGraw-Hill Design an experiment to scientific phenomena by asking includes controlled and Chapter 6, Lesson 3 p. 336 illustrate the difference questions, making logical manipulated variables using a Chapter 6, Lesson 4 p. 346 between potential and kinetic energy. predictions, planning investigations, and recording data. pendulum. GLE Conduct experiments on the transfer of heat energy through conduction, convection, and radiation. Organize data into appropriate tables, graphs, drawings, or diagrams. GLE 0507.T/E.4 Recognize the connection between scientific advances, new knowledge, and the availability of new tools and technologies. GLE 0507.Inq.2 Select and use appropriate tools and simple equipment to conduct an investigation. GLE 0507.T/E.3 Identify appropriate materials, tools, and machines that can extend or enhance the ability to solve a specified problem. Design a toy that demonstrates kinetic and potential energy. Create a graphic organizer to compare and contrast potential and kinetic energy to use in writing a paragraph. Given a diagram of something in motion, explain where it has potential or kinetic energy. Differentiate among conduction, convection and radiation as type so heat transfer. Provide examples for each kind of energy transfer and explain the reason for the choice. Summarize how heat moves from one place to another, citing examples. Identify and explain how some machines use conduction, convection or radiation to solve problems. Next Generation Science Standard Practices 5.Using and Computational Thinking 6. Constructing Explanations and Designing Develop strategies for choosing correct tools of measurement. Evaluate how different measures of central tendency describe data. Represent data using ordered pairs in the first quadrant of the coordinate system. Create and deliver an oral presentation using visual aids or props. Create a well-developed story or passage summary, as well as person reflections and imaginative writing samples.
16 Third Nine Weeks Resources Vocabulary: physical property, chemical property, atom, element, molecule, proton, electron, condensation, evaporation, mass, weight, volume, density, buoyancy, conductor, physical property, position, motion frame of reference, speed, velocity, acceleration, momentum, gravity, friction, balanced force, action force, reaction force, unbalanced, potential energy, kinetic energy, conduction, convection, and radiation, law of conservation of energy Inquiry Skills: predict, record data, observe, infer, classify, compare, draw conclusions Plans Matter Changes Observe and measure the simple chemical properties of common substances. Changes of State Design and conduct an experiment to demonstrate how various types of matter freeze, melt, or evaporate Motion and Forces Design an experiment, collect data and draw conclusions about the relationships among mass, force, and distance traveled. Energy and Heat Design an experiment to illustrate the difference between potential and kinetic energy. Conduct experiments on the transfer of heat energy through conduction, convection, and radiation. Student Activities Matter Changes Compare the crystals from a variety of salts such as alum, citric acid, and Epsom salt Changes of State Design an investigation to classify various substances based on their rate of freezing, melting, or evaporating. Motion and Forces Write and evaluate the expressions related to speed of tsunami, jet stream, tornado, jet plane etc. Find out the cost of operating a passenger plane based on the number of passengers and the time of a flight. Energy and Heat Design a toy that demonstrates kinetic and potential energy. Provide examples of each kind of transfer and explain the reason for the choice.
17 Technology and Engineering Science Department of Academic Advancement Guiding Question: What tools, skills, knowledge, and dispositions are needed to construct a bridge? 4 th Nine Weeks-Building Bridges (9 weeks) GLE 0507.T/E.1 Describe how tools, technology, and inventions help to answer questions and solve problems. Create a structured bridge that can be tested in theory and relativity. Macmillian/McGraw-Hill Chapter 6, Lesson 1 p. 308 Chapter 6, Lesson 2 p. 322 GLE 0507.T/E.2 Recognize that new tools, technology, and inventions GLE 0507.T/E.3 Identify appropriate materials, tools, and machines that can extend or enhance the ability to solve a specified problem. GLE 0507.T/E.4 Recognize the connection between scientific advances, new knowledge, and the availability of new tools and technologies. GLE 0507.T/E.5 Apply a creative design strategy to solve a particular problem generated by societal needs. GLE 0507.Inq.1 Explore different scientific phenomena by asking questions, making logical predictions, planning investigations, and recording data. GLE 0507.Inq.2 Select and use appropriate tools and simple equipment to conduct an investigation. Organize data into appropriate tables, graphs, drawings, or diagrams. GLE 0507.Inq.4 Identify and interpret simple patterns of evidence to communicate the finding of multiple investigations. GLE 0507.Inq.5 Recognize that people may interpret the same results in different ways Analyze and communicate findings from multiple investigations of similar phenomena to reach a conclusion. Apply a creative design strategy to solve a particular problem generated by societal the needs and wants. Use a two coordinate graph display to show the relationship between variables in an investigation. Analyze data to develop a conclusion and extend a graph to make predictions. Compare results of an investigation with others and interpret the results. Describe technologies or inventions that could be used to determine these relationships. Develop a system to demonstrate how the relationship between mass, force, and distance traveled works within that system. Create a chart and provide examples of when forces act at a distance. Next Generation Science Standard Practices 5.Using and Computational Thinking 6. Constructing Explanations and Designing Use variables appropriately to represent numbers whose values are not yet known. Make, record, display and interpret data and graphs that include whole numbers, decimals, and fractions. Make conjectures about geometric properties and develop logical arguments to justify conclusions. Design investigations to address a question and consider how data collection methods affect the nature of the data set. Organize information from text or technological sources using a graphic organizer. Predict outcomes and adjust as additional information is acquired. Build vocabulary by reading from a wide variety of texts and literary genres. Write for a variety of purposes and to a variety of audiences. Use current technology as a research and communication tool for personal interest, research, and clarification.
18 Vocabulary: motion, speed, distance, force Department of Academic Advancement Fourth Nine Weeks Resources Inquiry Skills: record data, observe, infer, draw conclusions Plans Design and create structures that will withstand simulated forces of strong wind or earthquakes. Background for Teachers Student Activities Lego blocks, popsicle sticks, spaghetti, and the like are good inexpensive items to create and design structures for this activity. Write and evaluate the expressions related to speed of tsunami, jet stream, tornado, jet plane etc. Find out the cost of operating a passenger plane based on the number of passengers and the time of a flight.
INSTRUCTIONAL FOCUS DOCUMENT Grade 5/Science
 Exemplar Lesson 01: Comparing Weather and Climate Exemplar Lesson 02: Sun, Ocean, and the Water Cycle State Resources: Connecting to Unifying Concepts through Earth Science Change Over Time RATIONALE:
Exemplar Lesson 01: Comparing Weather and Climate Exemplar Lesson 02: Sun, Ocean, and the Water Cycle State Resources: Connecting to Unifying Concepts through Earth Science Change Over Time RATIONALE:
Rendezvous with Comet Halley Next Generation of Science Standards
 Next Generation of Science Standards 5th Grade 6 th Grade 7 th Grade 8 th Grade 5-PS1-3 Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties. MS-PS1-4 Develop a model that
Next Generation of Science Standards 5th Grade 6 th Grade 7 th Grade 8 th Grade 5-PS1-3 Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties. MS-PS1-4 Develop a model that
This Performance Standards include four major components. They are
 Environmental Physics Standards The Georgia Performance Standards are designed to provide students with the knowledge and skills for proficiency in science. The Project 2061 s Benchmarks for Science Literacy
Environmental Physics Standards The Georgia Performance Standards are designed to provide students with the knowledge and skills for proficiency in science. The Project 2061 s Benchmarks for Science Literacy
Fourth Grade. Reporting Student Progress. Libertyville School District 70. Fourth Grade
 Fourth Grade Libertyville School District 70 Reporting Student Progress Fourth Grade A Message to Parents/Guardians: Libertyville Elementary District 70 teachers of students in kindergarten-5 utilize a
Fourth Grade Libertyville School District 70 Reporting Student Progress Fourth Grade A Message to Parents/Guardians: Libertyville Elementary District 70 teachers of students in kindergarten-5 utilize a
GUIDE CURRICULUM. Science 10
 Science 10 Arts Education Business Education English Language Arts Entrepreneurship Family Studies Health Education International Baccalaureate Languages Mathematics Personal Development and Career Education
Science 10 Arts Education Business Education English Language Arts Entrepreneurship Family Studies Health Education International Baccalaureate Languages Mathematics Personal Development and Career Education
How to Read the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS)
 How to Read the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) are distinct from prior science standards in three essential ways. 1) Performance. Prior standards
How to Read the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) are distinct from prior science standards in three essential ways. 1) Performance. Prior standards
Abc Of Science 8th Grade
 Abc Of 8th Grade Free PDF ebook Download: Abc Of 8th Grade Download or Read Online ebook abc of science 8th grade in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database In addition, some courses such as 7th grade
Abc Of 8th Grade Free PDF ebook Download: Abc Of 8th Grade Download or Read Online ebook abc of science 8th grade in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database In addition, some courses such as 7th grade
AGS THE GREAT REVIEW GAME FOR PRE-ALGEBRA (CD) CORRELATED TO CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS
 AGS THE GREAT REVIEW GAME FOR PRE-ALGEBRA (CD) CORRELATED TO CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS 1 CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS: Chapter 1 ALGEBRA AND WHOLE NUMBERS Algebra and Functions 1.4 Students use algebraic
AGS THE GREAT REVIEW GAME FOR PRE-ALGEBRA (CD) CORRELATED TO CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS 1 CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS: Chapter 1 ALGEBRA AND WHOLE NUMBERS Algebra and Functions 1.4 Students use algebraic
Physical Features of Humans
 Grade 1 Science, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Physical Features of Humans Overview Number of instructional days: 11 (1 day = 20 30 minutes) Content to be learned Observe, identify, and record the external features
Grade 1 Science, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Physical Features of Humans Overview Number of instructional days: 11 (1 day = 20 30 minutes) Content to be learned Observe, identify, and record the external features
Maryland Science Voluntary State Curriculum Grades K-6
 A Correlation of 2006 to the Maryland Science Voluntary State Curriculum Grades K-6 O/S-60 Introduction This document demonstrates how Scott Foresman Science meets the Maryland Science Voluntary State
A Correlation of 2006 to the Maryland Science Voluntary State Curriculum Grades K-6 O/S-60 Introduction This document demonstrates how Scott Foresman Science meets the Maryland Science Voluntary State
Biome I Can Statements
 Biome I Can Statements I can recognize the meanings of abbreviations. I can use dictionaries, thesauruses, glossaries, textual features (footnotes, sidebars, etc.) and technology to define and pronounce
Biome I Can Statements I can recognize the meanings of abbreviations. I can use dictionaries, thesauruses, glossaries, textual features (footnotes, sidebars, etc.) and technology to define and pronounce
Grade 6: Correlated to AGS Basic Math Skills
 Grade 6: Correlated to AGS Basic Math Skills Grade 6: Standard 1 Number Sense Students compare and order positive and negative integers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. They find multiples and
Grade 6: Correlated to AGS Basic Math Skills Grade 6: Standard 1 Number Sense Students compare and order positive and negative integers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. They find multiples and
Unit: Human Impact Differentiated (Tiered) Task How Does Human Activity Impact Soil Erosion?
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
LOUISIANA HIGH SCHOOL RALLY ASSOCIATION
 LOUISIANA HIGH SCHOOL RALLY ASSOCIATION Literary Events 2014-15 General Information There are 44 literary events in which District and State Rally qualifiers compete. District and State Rally tests are
LOUISIANA HIGH SCHOOL RALLY ASSOCIATION Literary Events 2014-15 General Information There are 44 literary events in which District and State Rally qualifiers compete. District and State Rally tests are
Dublin City Schools Mathematics Graded Course of Study GRADE 4
 I. Content Standard: Number, Number Sense and Operations Standard Students demonstrate number sense, including an understanding of number systems and reasonable estimates using paper and pencil, technology-supported
I. Content Standard: Number, Number Sense and Operations Standard Students demonstrate number sense, including an understanding of number systems and reasonable estimates using paper and pencil, technology-supported
Biology and Microbiology
 November 14, 2006 California State University (CSU) Statewide Pattern The Lower-Division Transfer Pattern (LDTP) consists of the CSU statewide pattern of coursework outlined below, plus campus-specific
November 14, 2006 California State University (CSU) Statewide Pattern The Lower-Division Transfer Pattern (LDTP) consists of the CSU statewide pattern of coursework outlined below, plus campus-specific
Text: envisionmath by Scott Foresman Addison Wesley. Course Description
 Ms. Burr 4B Mrs. Hession 4A Math Syllabus 4A & 4B Text: envisionmath by Scott Foresman Addison Wesley In fourth grade we will learn and develop in the acquisition of different mathematical operations while
Ms. Burr 4B Mrs. Hession 4A Math Syllabus 4A & 4B Text: envisionmath by Scott Foresman Addison Wesley In fourth grade we will learn and develop in the acquisition of different mathematical operations while
SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE
 FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York Le REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION LIVING ENVIRONMENT Wednesday, June 19, 2002 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Directions
FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York Le REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION LIVING ENVIRONMENT Wednesday, June 19, 2002 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Directions
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15
 Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments Plants Are Producers... 17 Producing a Producer... 19 The Part Plants Play...
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments Plants Are Producers... 17 Producing a Producer... 19 The Part Plants Play...
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL
 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL PART ONE: SHORT-ANSWER
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL PART ONE: SHORT-ANSWER
Teaching NGSS in Elementary School Third Grade
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Teaching NGSS in Elementary School Third Grade Presented by: Ted Willard, Carla Zembal-Saul, Mary Starr, and Kathy Renfrew December 17, 2014 6:30 p.m. ET / 5:30
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Teaching NGSS in Elementary School Third Grade Presented by: Ted Willard, Carla Zembal-Saul, Mary Starr, and Kathy Renfrew December 17, 2014 6:30 p.m. ET / 5:30
Mathematics subject curriculum
 Mathematics subject curriculum Dette er ei omsetjing av den fastsette læreplanteksten. Læreplanen er fastsett på Nynorsk Established as a Regulation by the Ministry of Education and Research on 24 June
Mathematics subject curriculum Dette er ei omsetjing av den fastsette læreplanteksten. Læreplanen er fastsett på Nynorsk Established as a Regulation by the Ministry of Education and Research on 24 June
Lesson 1 Taking chances with the Sun
 P2 Radiation and life Lesson 1 Taking chances with the Sun consider health benefits as well as risks that sunlight presents introduce two ideas: balancing risks and benefits, reducing risks revisit the
P2 Radiation and life Lesson 1 Taking chances with the Sun consider health benefits as well as risks that sunlight presents introduce two ideas: balancing risks and benefits, reducing risks revisit the
People: Past and Present
 People: Past and Present Field Trip Grade Level: 1 Process Skills: Observation Connections Enduring understanding: There are similarities and differences across cultures. Alignment to Utah Core Curriculum
People: Past and Present Field Trip Grade Level: 1 Process Skills: Observation Connections Enduring understanding: There are similarities and differences across cultures. Alignment to Utah Core Curriculum
Gifted/Challenge Program Descriptions Summer 2016
 Gifted/Challenge Program Descriptions Summer 2016 (Please note: Select courses that have your child s current grade for the 2015/2016 school year, please do NOT select courses for any other grade level.)
Gifted/Challenge Program Descriptions Summer 2016 (Please note: Select courses that have your child s current grade for the 2015/2016 school year, please do NOT select courses for any other grade level.)
Introductory Astronomy. Physics 134K. Fall 2016
 Introductory Astronomy Physics 134K Fall 2016 Dates / contact hours: 7 week course; 300 contact minutes per week Academic Credit: 1 Areas of Knowledge: NS Modes of Inquiry: QS Course format: Lecture/Discussion.
Introductory Astronomy Physics 134K Fall 2016 Dates / contact hours: 7 week course; 300 contact minutes per week Academic Credit: 1 Areas of Knowledge: NS Modes of Inquiry: QS Course format: Lecture/Discussion.
Characteristics of Functions
 Characteristics of Functions Unit: 01 Lesson: 01 Suggested Duration: 10 days Lesson Synopsis Students will collect and organize data using various representations. They will identify the characteristics
Characteristics of Functions Unit: 01 Lesson: 01 Suggested Duration: 10 days Lesson Synopsis Students will collect and organize data using various representations. They will identify the characteristics
The Ontario Curriculum
 The Ontario Curriculum GRADE 1 checklist format compiled by: The Canadian Homeschooler using the current Ontario Curriculum Content Introduction... Page 3 Mathematics... Page 4 Language Arts... Page 9
The Ontario Curriculum GRADE 1 checklist format compiled by: The Canadian Homeschooler using the current Ontario Curriculum Content Introduction... Page 3 Mathematics... Page 4 Language Arts... Page 9
Language Acquisition Chart
 Language Acquisition Chart This chart was designed to help teachers better understand the process of second language acquisition. Please use this chart as a resource for learning more about the way people
Language Acquisition Chart This chart was designed to help teachers better understand the process of second language acquisition. Please use this chart as a resource for learning more about the way people
Teaching a Laboratory Section
 Chapter 3 Teaching a Laboratory Section Page I. Cooperative Problem Solving Labs in Operation 57 II. Grading the Labs 75 III. Overview of Teaching a Lab Session 79 IV. Outline for Teaching a Lab Session
Chapter 3 Teaching a Laboratory Section Page I. Cooperative Problem Solving Labs in Operation 57 II. Grading the Labs 75 III. Overview of Teaching a Lab Session 79 IV. Outline for Teaching a Lab Session
PROJECT LEARNING TREE 4 th grade Language Arts Correlation to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
 PROJECT LEARNING TREE 4 th grade Language Arts Correlation/TEKS Language Arts Students are expected to: Activity 4.3A summarize and explain the lesson or message of a work of fiction as its theme 18, 89
PROJECT LEARNING TREE 4 th grade Language Arts Correlation/TEKS Language Arts Students are expected to: Activity 4.3A summarize and explain the lesson or message of a work of fiction as its theme 18, 89
Scientific Inquiry Test Questions
 Test Questions Free PDF ebook Download: Test Questions Download or Read Online ebook scientific inquiry test questions in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Understandings about scientific inquiry
Test Questions Free PDF ebook Download: Test Questions Download or Read Online ebook scientific inquiry test questions in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Understandings about scientific inquiry
5.1 Sound & Light Unit Overview
 5.1 Sound & Light Unit Overview Enduring Understanding: Sound and light are forms of energy that travel and interact with objects in various ways. Essential Question: How is sound energy transmitted, absorbed,
5.1 Sound & Light Unit Overview Enduring Understanding: Sound and light are forms of energy that travel and interact with objects in various ways. Essential Question: How is sound energy transmitted, absorbed,
Extending Place Value with Whole Numbers to 1,000,000
 Grade 4 Mathematics, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Extending Place Value with Whole Numbers to 1,000,000 Overview Number of Instructional Days: 10 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to Be Learned Recognize that a digit
Grade 4 Mathematics, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Extending Place Value with Whole Numbers to 1,000,000 Overview Number of Instructional Days: 10 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to Be Learned Recognize that a digit
All Systems Go! Using a Systems Approach in Elementary Science
 All Systems Go! CAST November Tracey Ramirez Professional Learning Facilitator The Charles A. Dana Center What we do and how we do it The Dana Center collaborates with others locally and nationally to
All Systems Go! CAST November Tracey Ramirez Professional Learning Facilitator The Charles A. Dana Center What we do and how we do it The Dana Center collaborates with others locally and nationally to
TABE 9&10. Revised 8/2013- with reference to College and Career Readiness Standards
 TABE 9&10 Revised 8/2013- with reference to College and Career Readiness Standards LEVEL E Test 1: Reading Name Class E01- INTERPRET GRAPHIC INFORMATION Signs Maps Graphs Consumer Materials Forms Dictionary
TABE 9&10 Revised 8/2013- with reference to College and Career Readiness Standards LEVEL E Test 1: Reading Name Class E01- INTERPRET GRAPHIC INFORMATION Signs Maps Graphs Consumer Materials Forms Dictionary
Missouri Mathematics Grade-Level Expectations
 A Correlation of to the Grades K - 6 G/M-223 Introduction This document demonstrates the high degree of success students will achieve when using Scott Foresman Addison Wesley Mathematics in meeting the
A Correlation of to the Grades K - 6 G/M-223 Introduction This document demonstrates the high degree of success students will achieve when using Scott Foresman Addison Wesley Mathematics in meeting the
For information only, correct responses are listed in the chart below. Question Number. Correct Response
 THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK 4GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST JUNE 207 WRITTEN TEST FOR TEACHERS ONLY SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Note: All schools (public, nonpublic, and charter) administering
THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK 4GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST JUNE 207 WRITTEN TEST FOR TEACHERS ONLY SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Note: All schools (public, nonpublic, and charter) administering
Instructional Approach(s): The teacher should introduce the essential question and the standard that aligns to the essential question
 1 Instructional Approach(s): The teacher should introduce the essential question and the standard that aligns to the essential question 2 Instructional Approach(s): The teacher should conduct the Concept
1 Instructional Approach(s): The teacher should introduce the essential question and the standard that aligns to the essential question 2 Instructional Approach(s): The teacher should conduct the Concept
Innovative Teaching in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math
 Innovative Teaching in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math Take-Aways- What is S.T.E.M. education and why STEM skills are so important in ECE now and in our future; Current research about quality
Innovative Teaching in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math Take-Aways- What is S.T.E.M. education and why STEM skills are so important in ECE now and in our future; Current research about quality
Sugar And Salt Solutions Phet Simulation Packet
 Sugar And Salt Solutions Phet Simulation Packet Free PDF ebook Download: Sugar And Salt Solutions Phet Simulation Packet Download or Read Online ebook sugar and salt solutions phet simulation packet in
Sugar And Salt Solutions Phet Simulation Packet Free PDF ebook Download: Sugar And Salt Solutions Phet Simulation Packet Download or Read Online ebook sugar and salt solutions phet simulation packet in
Finding a Classroom Volunteer
 Finding a Classroom Volunteer 1 Teacher Looking for Volunteer Support Page My Requirements as a Teacher...1 Classroom Instruction Monitoring Volunteers Flexibility of Visits Volunteer Updates Looking for
Finding a Classroom Volunteer 1 Teacher Looking for Volunteer Support Page My Requirements as a Teacher...1 Classroom Instruction Monitoring Volunteers Flexibility of Visits Volunteer Updates Looking for
What can I learn from worms?
 What can I learn from worms? Stem cells, regeneration, and models Lesson 7: What does planarian regeneration tell us about human regeneration? I. Overview In this lesson, students use the information that
What can I learn from worms? Stem cells, regeneration, and models Lesson 7: What does planarian regeneration tell us about human regeneration? I. Overview In this lesson, students use the information that
MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm
 MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm Why participate in the Science Fair? Science fair projects give students
MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm Why participate in the Science Fair? Science fair projects give students
Stakeholder Debate: Wind Energy
 Activity ENGAGE For Educator Stakeholder Debate: Wind Energy How do stakeholder interests determine which specific resources a community will use? For the complete activity with media resources, visit:
Activity ENGAGE For Educator Stakeholder Debate: Wind Energy How do stakeholder interests determine which specific resources a community will use? For the complete activity with media resources, visit:
Honors Mathematics. Introduction and Definition of Honors Mathematics
 Honors Mathematics Introduction and Definition of Honors Mathematics Honors Mathematics courses are intended to be more challenging than standard courses and provide multiple opportunities for students
Honors Mathematics Introduction and Definition of Honors Mathematics Honors Mathematics courses are intended to be more challenging than standard courses and provide multiple opportunities for students
4th Grade Science Test Ecosystems
 4th Grade Science Free PDF ebook Download: 4th Grade Science Download or Read Online ebook 4th grade science test ecosystems in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database 4th Grade--LIFE SCIENCE. Unit
4th Grade Science Free PDF ebook Download: 4th Grade Science Download or Read Online ebook 4th grade science test ecosystems in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database 4th Grade--LIFE SCIENCE. Unit
Syllabus Fall 2014 Earth Science 130: Introduction to Oceanography
 Syllabus Fall 2014 Earth Science 130: Introduction to Oceanography Background Information Welcome Aboard! These guidelines establish specific requirements, grading criteria, descriptions of assignments
Syllabus Fall 2014 Earth Science 130: Introduction to Oceanography Background Information Welcome Aboard! These guidelines establish specific requirements, grading criteria, descriptions of assignments
Graphic Organizer For Movie Notes
 For Movie Notes Free PDF ebook Download: For Movie Notes Download or Read Online ebook graphic organizer for movie notes in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database. Use this graphic organizer to take
For Movie Notes Free PDF ebook Download: For Movie Notes Download or Read Online ebook graphic organizer for movie notes in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database. Use this graphic organizer to take
Pre-AP Geometry Course Syllabus Page 1
 Pre-AP Geometry Course Syllabus 2015-2016 Welcome to my Pre-AP Geometry class. I hope you find this course to be a positive experience and I am certain that you will learn a great deal during the next
Pre-AP Geometry Course Syllabus 2015-2016 Welcome to my Pre-AP Geometry class. I hope you find this course to be a positive experience and I am certain that you will learn a great deal during the next
Page 1 of 11. Curriculum Map: Grade 4 Math Course: Math 4 Sub-topic: General. Grade(s): None specified
 Curriculum Map: Grade 4 Math Course: Math 4 Sub-topic: General Grade(s): None specified Unit: Creating a Community of Mathematical Thinkers Timeline: Week 1 The purpose of the Establishing a Community
Curriculum Map: Grade 4 Math Course: Math 4 Sub-topic: General Grade(s): None specified Unit: Creating a Community of Mathematical Thinkers Timeline: Week 1 The purpose of the Establishing a Community
been each get other TASK #1 Fry Words TASK #2 Fry Words Write the following words in ABC order: Write the following words in ABC order:
 TASK #1 Fry Words 1-100 been each called down about first TASK #2 Fry Words 1-100 get other long people number into TASK #3 Fry Words 1-100 could part more find now her TASK #4 Fry Words 1-100 for write
TASK #1 Fry Words 1-100 been each called down about first TASK #2 Fry Words 1-100 get other long people number into TASK #3 Fry Words 1-100 could part more find now her TASK #4 Fry Words 1-100 for write
PHYSICS 40S - COURSE OUTLINE AND REQUIREMENTS Welcome to Physics 40S for !! Mr. Bryan Doiron
 PHYSICS 40S - COURSE OUTLINE AND REQUIREMENTS Welcome to Physics 40S for 2016-2017!! Mr. Bryan Doiron The course covers the following topics (time permitting): Unit 1 Kinematics: Special Equations, Relative
PHYSICS 40S - COURSE OUTLINE AND REQUIREMENTS Welcome to Physics 40S for 2016-2017!! Mr. Bryan Doiron The course covers the following topics (time permitting): Unit 1 Kinematics: Special Equations, Relative
Math-U-See Correlation with the Common Core State Standards for Mathematical Content for Third Grade
 Math-U-See Correlation with the Common Core State Standards for Mathematical Content for Third Grade The third grade standards primarily address multiplication and division, which are covered in Math-U-See
Math-U-See Correlation with the Common Core State Standards for Mathematical Content for Third Grade The third grade standards primarily address multiplication and division, which are covered in Math-U-See
Course outline. Code: ENS281 Title: Introduction to Sustainable Energy Systems
 Course outline Code: ENS281 Title: Introduction to Sustainable Energy Systems Faculty of: Science, Health, Education and Engineering Teaching Session: Semester 1 Year: 2017 Course Coordinator: Dr Damon
Course outline Code: ENS281 Title: Introduction to Sustainable Energy Systems Faculty of: Science, Health, Education and Engineering Teaching Session: Semester 1 Year: 2017 Course Coordinator: Dr Damon
Scott Foresman Science Grade 4
 Science Grade 4 Free PDF ebook Download: Science Grade 4 Download or Read Online ebook scott foresman science grade 4 in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database GRADE TEXTBOOK REQUIRED. -Addison Wesley
Science Grade 4 Free PDF ebook Download: Science Grade 4 Download or Read Online ebook scott foresman science grade 4 in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database GRADE TEXTBOOK REQUIRED. -Addison Wesley
Anatomy & Physiology II
 Curricular Guide for Anatomy/Physiology Ii Anatomy & Physiology II This is an advanced placement course in human anatomy and physiology with emphasis on the structure and function of the human body. Major
Curricular Guide for Anatomy/Physiology Ii Anatomy & Physiology II This is an advanced placement course in human anatomy and physiology with emphasis on the structure and function of the human body. Major
Probability and Statistics Curriculum Pacing Guide
 Unit 1 Terms PS.SPMJ.3 PS.SPMJ.5 Plan and conduct a survey to answer a statistical question. Recognize how the plan addresses sampling technique, randomization, measurement of experimental error and methods
Unit 1 Terms PS.SPMJ.3 PS.SPMJ.5 Plan and conduct a survey to answer a statistical question. Recognize how the plan addresses sampling technique, randomization, measurement of experimental error and methods
Program Alignment Worksheet High School
 Program Alignment Worksheet High School Publisher Name Pearson Program Title Prentice Hall Biology (Miler/Levine) 2010; Event Based Science 2005 Computer Based? Requires Internet? Target Grades 9 12 Steps
Program Alignment Worksheet High School Publisher Name Pearson Program Title Prentice Hall Biology (Miler/Levine) 2010; Event Based Science 2005 Computer Based? Requires Internet? Target Grades 9 12 Steps
Friction Stops Motion
 activity Friction Stops Motion BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade Quarter Activity SC.C... The student understands that the motion of an object can be described and measured. SC.H...
activity Friction Stops Motion BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade Quarter Activity SC.C... The student understands that the motion of an object can be described and measured. SC.H...
EGRHS Course Fair. Science & Math AP & IB Courses
 EGRHS Course Fair Science & Math AP & IB Courses Science Courses: AP Physics IB Physics SL IB Physics HL AP Biology IB Biology HL AP Physics Course Description Course Description AP Physics C (Mechanics)
EGRHS Course Fair Science & Math AP & IB Courses Science Courses: AP Physics IB Physics SL IB Physics HL AP Biology IB Biology HL AP Physics Course Description Course Description AP Physics C (Mechanics)
1. Locate and describe major physical features and analyze how they influenced cultures/civilizations studied.
 Unit Plan 8th Grade Geography Ciara Timothy SOST 450- Professor Johnson 2.22.2012 Contents: 1. Student Handout 2. Day to Day Outline 3. MN Graduation Standards and Benchmarks 4. Differentiated for Content,
Unit Plan 8th Grade Geography Ciara Timothy SOST 450- Professor Johnson 2.22.2012 Contents: 1. Student Handout 2. Day to Day Outline 3. MN Graduation Standards and Benchmarks 4. Differentiated for Content,
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15
 Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments School Supplies... 17 A Place to Call Home... 21 Paste Up Habitats... 37
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments School Supplies... 17 A Place to Call Home... 21 Paste Up Habitats... 37
LESSON TITLE: The Road to Writing Perfect Paragraphs: Follow The Old Red Trail
 LESSON TITLE: The Road to Writing Perfect Paragraphs: Follow The Old Red Trail WRITTEN BY: Julie Costello GRADE LEVELS: Sixth grade, but appropriate for 4-8 TIME ALLOTMENT: 1 class period, 45 minutes in
LESSON TITLE: The Road to Writing Perfect Paragraphs: Follow The Old Red Trail WRITTEN BY: Julie Costello GRADE LEVELS: Sixth grade, but appropriate for 4-8 TIME ALLOTMENT: 1 class period, 45 minutes in
Unit 1: Scientific Investigation-Asking Questions
 Unit 1: Scientific Investigation-Asking Questions Standards: OKC 3 Process Standard 3: Experimental design - Understanding experimental designs requires that students recognize the components of a valid
Unit 1: Scientific Investigation-Asking Questions Standards: OKC 3 Process Standard 3: Experimental design - Understanding experimental designs requires that students recognize the components of a valid
Curriculum Design Project with Virtual Manipulatives. Gwenanne Salkind. George Mason University EDCI 856. Dr. Patricia Moyer-Packenham
 Curriculum Design Project with Virtual Manipulatives Gwenanne Salkind George Mason University EDCI 856 Dr. Patricia Moyer-Packenham Spring 2006 Curriculum Design Project with Virtual Manipulatives Table
Curriculum Design Project with Virtual Manipulatives Gwenanne Salkind George Mason University EDCI 856 Dr. Patricia Moyer-Packenham Spring 2006 Curriculum Design Project with Virtual Manipulatives Table
Electromagnetic Spectrum Webquest Answer Key
 Webquest Answer Key Free PDF ebook Download: Webquest Answer Key Download or Read Online ebook electromagnetic spectrum webquest answer key in PDF Format From Best User Guide Database Section:. & Light
Webquest Answer Key Free PDF ebook Download: Webquest Answer Key Download or Read Online ebook electromagnetic spectrum webquest answer key in PDF Format From Best User Guide Database Section:. & Light
2.B.4 Balancing Crane. The Engineering Design Process in the classroom. Summary
 2.B.4 Balancing Crane The Engineering Design Process in the classroom Grade Level 2 Sessions 1 40 minutes 2 30 minutes Seasonality None Instructional Mode(s) Whole class, groups of 4 5 students, individual
2.B.4 Balancing Crane The Engineering Design Process in the classroom Grade Level 2 Sessions 1 40 minutes 2 30 minutes Seasonality None Instructional Mode(s) Whole class, groups of 4 5 students, individual
Ohio s Learning Standards-Clear Learning Targets
 Ohio s Learning Standards-Clear Learning Targets Math Grade 1 Use addition and subtraction within 20 to solve word problems involving situations of 1.OA.1 adding to, taking from, putting together, taking
Ohio s Learning Standards-Clear Learning Targets Math Grade 1 Use addition and subtraction within 20 to solve word problems involving situations of 1.OA.1 adding to, taking from, putting together, taking
CENTENNIAL SCHOOL DISTRICT
 CENTENNIAL SCHOOL DISTRICT MIDDLE SCHOOL PROGRAM OF STUDIES 2017-18 Klinger Middle School Log College Middle School 1 Table of Contents Middle School Program Overview 3 Core Course Descriptions 4 Grade
CENTENNIAL SCHOOL DISTRICT MIDDLE SCHOOL PROGRAM OF STUDIES 2017-18 Klinger Middle School Log College Middle School 1 Table of Contents Middle School Program Overview 3 Core Course Descriptions 4 Grade
Cal s Dinner Card Deals
 Cal s Dinner Card Deals Overview: In this lesson students compare three linear functions in the context of Dinner Card Deals. Students are required to interpret a graph for each Dinner Card Deal to help
Cal s Dinner Card Deals Overview: In this lesson students compare three linear functions in the context of Dinner Card Deals. Students are required to interpret a graph for each Dinner Card Deal to help
Environmental Science Curriculum Guide NMHZHS
 MOUNT VERNON CITY SCHOOL DISTRICT Environmental Science Curriculum Guide NMHZHS THIS HANDBOOK IS FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE CURRICULUM IN MOUNT VERNON. 2015-16 Mount Vernon City
MOUNT VERNON CITY SCHOOL DISTRICT Environmental Science Curriculum Guide NMHZHS THIS HANDBOOK IS FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE CURRICULUM IN MOUNT VERNON. 2015-16 Mount Vernon City
Introducing the New Iowa Assessments Mathematics Levels 12 14
 Introducing the New Iowa Assessments Mathematics Levels 12 14 ITP Assessment Tools Math Interim Assessments: Grades 3 8 Administered online Constructed Response Supplements Reading, Language Arts, Mathematics
Introducing the New Iowa Assessments Mathematics Levels 12 14 ITP Assessment Tools Math Interim Assessments: Grades 3 8 Administered online Constructed Response Supplements Reading, Language Arts, Mathematics
1 Copyright Texas Education Agency, All rights reserved.
 Lesson Plan-Diversity at Work Course Title: Business Information Management II Session Title: Diversity at Work Performance Objective: Upon completion of this lesson, students will understand diversity
Lesson Plan-Diversity at Work Course Title: Business Information Management II Session Title: Diversity at Work Performance Objective: Upon completion of this lesson, students will understand diversity
Chapter 9 Banked gap-filling
 Chapter 9 Banked gap-filling This testing technique is known as banked gap-filling, because you have to choose the appropriate word from a bank of alternatives. In a banked gap-filling task, similarly
Chapter 9 Banked gap-filling This testing technique is known as banked gap-filling, because you have to choose the appropriate word from a bank of alternatives. In a banked gap-filling task, similarly
ENVR 205 Engineering Tools for Environmental Problem Solving Spring 2017
 ENVR 205 Engineering Tools for Environmental Problem Solving Spring 2017 Instructor: Dr. Barbara rpin, Professor Environmental Science and Engineering Gillings School of Global Public Health University
ENVR 205 Engineering Tools for Environmental Problem Solving Spring 2017 Instructor: Dr. Barbara rpin, Professor Environmental Science and Engineering Gillings School of Global Public Health University
Food Chain Cut And Paste Activities
 Cut And Paste Activities Free PDF ebook Download: Cut And Paste Activities Download or Read Online ebook food chain cut and paste activities in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database CO #3: Organise
Cut And Paste Activities Free PDF ebook Download: Cut And Paste Activities Download or Read Online ebook food chain cut and paste activities in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database CO #3: Organise
Seventh Grade Course Catalog
 2017-2018 Seventh Grade Course Catalog Any information parents want to give the school which would be helpful for the student s educational placement needs to be addressed to the grade level counselor.
2017-2018 Seventh Grade Course Catalog Any information parents want to give the school which would be helpful for the student s educational placement needs to be addressed to the grade level counselor.
Build on students informal understanding of sharing and proportionality to develop initial fraction concepts.
 Recommendation 1 Build on students informal understanding of sharing and proportionality to develop initial fraction concepts. Students come to kindergarten with a rudimentary understanding of basic fraction
Recommendation 1 Build on students informal understanding of sharing and proportionality to develop initial fraction concepts. Students come to kindergarten with a rudimentary understanding of basic fraction
TEKS Resource System. Effective Planning from the IFD & Assessment. Presented by: Kristin Arterbury, ESC Region 12
 TEKS Resource System Effective Planning from the IFD & Assessments Presented by: Kristin Arterbury, ESC Region 12 karterbury@esc12.net, 254-297-1115 Assessment Curriculum Instruction planwithifd.wikispaces.com
TEKS Resource System Effective Planning from the IFD & Assessments Presented by: Kristin Arterbury, ESC Region 12 karterbury@esc12.net, 254-297-1115 Assessment Curriculum Instruction planwithifd.wikispaces.com
Standard 1: Number and Computation
 Standard 1: Number and Computation Standard 1: Number and Computation The student uses numerical and computational concepts and procedures in a variety of situations. Benchmark 1: Number Sense The student
Standard 1: Number and Computation Standard 1: Number and Computation The student uses numerical and computational concepts and procedures in a variety of situations. Benchmark 1: Number Sense The student
FIGURE IT OUT! MIDDLE SCHOOL TASKS. Texas Performance Standards Project
 FIGURE IT OUT! MIDDLE SCHOOL TASKS π 3 cot(πx) a + b = c sinθ MATHEMATICS 8 GRADE 8 This guide links the Figure It Out! unit to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for eighth graders. Figure
FIGURE IT OUT! MIDDLE SCHOOL TASKS π 3 cot(πx) a + b = c sinθ MATHEMATICS 8 GRADE 8 This guide links the Figure It Out! unit to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for eighth graders. Figure
Regions Of Georgia For 2nd Grade
 Regions Of Georgia For 2nd Grade Free PDF ebook Download: Regions Of Georgia For 2nd Grade Download or Read Online ebook regions of georgia for 2nd grade in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database
Regions Of Georgia For 2nd Grade Free PDF ebook Download: Regions Of Georgia For 2nd Grade Download or Read Online ebook regions of georgia for 2nd grade in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database
Simulation of Multi-stage Flash (MSF) Desalination Process
 Advances in Materials Physics and Chemistry, 2012, 2, 200-205 doi:10.4236/ampc.2012.24b052 Published Online December 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ampc) Simulation of Multi-stage Flash (MSF) Desalination
Advances in Materials Physics and Chemistry, 2012, 2, 200-205 doi:10.4236/ampc.2012.24b052 Published Online December 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ampc) Simulation of Multi-stage Flash (MSF) Desalination
Teaching Literacy Through Videos
 Teaching Literacy Through Videos Elizabeth Stavis Reading Intervention Specialist RR Teacher Santa Clara Unified Jenny Maehara Elementary Literacy Specialist RR Teacher Santa Clara Unified February 9,
Teaching Literacy Through Videos Elizabeth Stavis Reading Intervention Specialist RR Teacher Santa Clara Unified Jenny Maehara Elementary Literacy Specialist RR Teacher Santa Clara Unified February 9,
Table of Contents. This descriptive guide will assist you in integrating the DVD science and education content into your instructional program.
 Bill Nye the Science Guy Comets & Meteors 1. Implementation Guide........................................ 2 9 This descriptive guide will assist you in integrating the DVD science and education content
Bill Nye the Science Guy Comets & Meteors 1. Implementation Guide........................................ 2 9 This descriptive guide will assist you in integrating the DVD science and education content
INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY GEOL TUESDAY/FRIDAY, 14:10-15:25 HUNTER NORTH 1021
 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY GEOL 18000 TUESDAY/FRIDAY, 14:10-15:25 HUNTER NORTH 1021 CONTACT INFORMATION Instructor: Dr. Haydee Salmun Email address: hsalmun@hunter.cuny.edu (*) Telephone: 212-772-5224
INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY GEOL 18000 TUESDAY/FRIDAY, 14:10-15:25 HUNTER NORTH 1021 CONTACT INFORMATION Instructor: Dr. Haydee Salmun Email address: hsalmun@hunter.cuny.edu (*) Telephone: 212-772-5224
2016/17 Big History: Sample Semester-Long Course Plan Content Pacing Guide
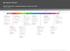 2016/17 Big History: Sample Semester-Long Course Plan Content Pacing Guide August September October November December UNIT 1 UNIT 2 UNIT 3 UNIT 4 UNIT 5 UNIT 6 UNIT 7 UNIT 8 UNIT 9 UNIT 10 What Is Big
2016/17 Big History: Sample Semester-Long Course Plan Content Pacing Guide August September October November December UNIT 1 UNIT 2 UNIT 3 UNIT 4 UNIT 5 UNIT 6 UNIT 7 UNIT 8 UNIT 9 UNIT 10 What Is Big
Numeracy Medium term plan: Summer Term Level 2C/2B Year 2 Level 2A/3C
 Numeracy Medium term plan: Summer Term Level 2C/2B Year 2 Level 2A/3C Using and applying mathematics objectives (Problem solving, Communicating and Reasoning) Select the maths to use in some classroom
Numeracy Medium term plan: Summer Term Level 2C/2B Year 2 Level 2A/3C Using and applying mathematics objectives (Problem solving, Communicating and Reasoning) Select the maths to use in some classroom
Summarizing A Nonfiction
 A Nonfiction Free PDF ebook Download: A Nonfiction Download or Read Online ebook summarizing a nonfiction in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Texts (written or spoken). a Process. Ideas in
A Nonfiction Free PDF ebook Download: A Nonfiction Download or Read Online ebook summarizing a nonfiction in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Texts (written or spoken). a Process. Ideas in
Prentice Hall Outline Map 1914 With Answers
 Outline Map 1914 With Answers Free PDF ebook Download: Outline Map 1914 With Answers Download or Read Online ebook prentice hall outline map 1914 with answers in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database
Outline Map 1914 With Answers Free PDF ebook Download: Outline Map 1914 With Answers Download or Read Online ebook prentice hall outline map 1914 with answers in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database
Lesson Plan Title Aquatic Ecology
 Lesson Plan Title Aquatic Ecology Name (last, first): Larson, Don Scientific Theme(s): C-2: develop an understanding of the structure, function, behavior, development, life cycles, and diversity of living
Lesson Plan Title Aquatic Ecology Name (last, first): Larson, Don Scientific Theme(s): C-2: develop an understanding of the structure, function, behavior, development, life cycles, and diversity of living
Fairfield Methodist School (Secondary) Topics for End of Year Examination Term
 End of Year examination papers will cover all the topics taught in Sec 2 for each subject unless otherwise stated below. Oral Exam for Languages will be conducted by teachers outside of the EOY exam period.
End of Year examination papers will cover all the topics taught in Sec 2 for each subject unless otherwise stated below. Oral Exam for Languages will be conducted by teachers outside of the EOY exam period.
Science Fair Project Handbook
 Science Fair Project Handbook IDENTIFY THE TESTABLE QUESTION OR PROBLEM: a) Begin by observing your surroundings, making inferences and asking testable questions. b) Look for problems in your life or surroundings
Science Fair Project Handbook IDENTIFY THE TESTABLE QUESTION OR PROBLEM: a) Begin by observing your surroundings, making inferences and asking testable questions. b) Look for problems in your life or surroundings
Timeline. Recommendations
 Introduction Advanced Placement Course Credit Alignment Recommendations In 2007, the State of Ohio Legislature passed legislation mandating the Board of Regents to recommend and the Chancellor to adopt
Introduction Advanced Placement Course Credit Alignment Recommendations In 2007, the State of Ohio Legislature passed legislation mandating the Board of Regents to recommend and the Chancellor to adopt
Radius STEM Readiness TM
 Curriculum Guide Radius STEM Readiness TM While today s teens are surrounded by technology, we face a stark and imminent shortage of graduates pursuing careers in Science, Technology, Engineering, and
Curriculum Guide Radius STEM Readiness TM While today s teens are surrounded by technology, we face a stark and imminent shortage of graduates pursuing careers in Science, Technology, Engineering, and
Heredity In Plants For 2nd Grade
 In Plants For 2nd Grade Free PDF ebook Download: In Plants For 2nd Grade Download or Read Online ebook heredity in plants for 2nd grade in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database I Write the letter
In Plants For 2nd Grade Free PDF ebook Download: In Plants For 2nd Grade Download or Read Online ebook heredity in plants for 2nd grade in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database I Write the letter
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SOCIAL STUDIES SYLLABUS FOR BASIC EDUCATION STANDARD III-VI
 THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SOCIAL STUDIES SYLLABUS FOR BASIC EDUCATION STANDARD III-VI THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SOCIAL STUDIES SYLLABUS FOR BASIC EDUCATION STANDARD III-VI THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND
Statistical Analysis of Climate Change, Renewable Energies, and Sustainability An Independent Investigation for Introduction to Statistics
 5/22/2012 Statistical Analysis of Climate Change, Renewable Energies, and Sustainability An Independent Investigation for Introduction to Statistics College of Menominee Nation & University of Wisconsin
5/22/2012 Statistical Analysis of Climate Change, Renewable Energies, and Sustainability An Independent Investigation for Introduction to Statistics College of Menominee Nation & University of Wisconsin
Interactive Whiteboard
 50 Graphic Organizers for the Interactive Whiteboard Whiteboard-ready graphic organizers for reading, writing, math, and more to make learning engaging and interactive by Jennifer Jacobson & Dottie Raymer
50 Graphic Organizers for the Interactive Whiteboard Whiteboard-ready graphic organizers for reading, writing, math, and more to make learning engaging and interactive by Jennifer Jacobson & Dottie Raymer
