Macmillan. Science. Teacher s Book. Pamela Wadsworth
|
|
|
- Felicia Lawson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Macmillan Science Teacher s Book 1 Pamela Wadsworth
2 Contents Introduction 3 Being a scientist 7 Science safety 9 Topic 1 The things around us 12 Topic 2 Plants and their parts 16 Topic 3 The importance of plants 20 Topic 4 Seeds 24 Topic 5 All sorts of animals 30 Topic 6 Animals move and feed 34 Topic 7 Caring for animals 38 Topic 8 My body 44 Topic 9 Caring for my body 48 Topic 10 Different materials 54 Topic 11 Using materials 58 Topic 12 Solids and liquids 62 Topic 13 The Earth and the sun 68 Topic 14 Weather and the seasons 72
3 Introduction Preface The Macmillan Science series is a comprehensive science course for all students in primary schools. Building on practical experience and investigation, the books follow current best practice in science education. Through engaging content and carefully graded activities and exercises, students are guided to develop a sound framework of scientific knowledge, understanding and skills. Discussing ideas with partners and then with the whole class is central to the approach used throughout. In this way, the children acquire and improve their spoken English, but are also active learners throughout each science lesson. There are six full-colour Pupil s Books from the level 1 to the final year of primary school. The main strands of living things (plants, animals and humans), materials, and the physical world are repeated at each grade, reinforcing ideas learnt earlier and developing these to a higher level. Science teaching, especially when it is hands-on, can be highly enjoyable and rewarding for teachers and students alike. We hope that Macmillan Science will contribute both to the effectiveness of your teaching and to the pleasure that you and your class gain from studying science. David and Penny Glover Components For each level there is a Pupil s Book, Workbook and CD-ROM, accompanied by a Teacher s Book which gives clear instructions on how to plan lessons. The Pupil s Book contains clear illustrations and instructions for carrying out practical investigations, discussion activities and sections for the assessment of learning. The Workbook contains a range of different activities that enable children to review and consolidate their learning. The CD-ROM packaged with each Pupil s Book, provides further reinforcement and assessment of skills and concepts developed in each unit through interactive activities. The scope and sequence is displayed at the beginning of the Pupil s Book, together with the objectives for each unit. Each of the five main areas of science is colour-coded for easy reference from one book to another. Teacher s Book structure Each topic is divided into three sections: Lesson preparation, Lesson plan and After the lesson. Lesson preparation: outlines the topic objectives, equipment needed, key words with definitions and teaching ideas and background information, linking theory with practice. Lesson plan: detailed lesson plans including ideas for warm-up and extension activities. After the lesson: Workbook and CD-ROM answers. 3
4 Introduction Why teach science in the primary school? Today, the case for teaching primary science hardly needs to be stated. Science, alongside numeracy and literacy, is a core component of the primary school curriculum in schools around the world. The reasons for teaching science at the primary level may be summarised as follows: investigation-based science learning develops children s curiosity, problem-solving, practical and communication skills basic scientific knowledge of the human body, diet, living things, the environment, materials, forces and energy contributes to children s developing awareness of themselves and their relationship to their surroundings; this knowledge will help them to make healthy choices, to keep safe and to solve problems as they move through life scientific values and attitudes such as respect for evidence, questioning, flexible thinking and the willingness to share knowledge and ideas are relevant in all areas of children s learning, not just science through science, children become aware of environmental issues and the impact that they as individuals can have on their surroundings; they develop respect for living things and their environment and become aware of the harm that simple actions such as littering, wasting energy or contaminating water supplies can cause in the majority of countries, science is an examination subject at the end of the final year of primary school. Children may need to perform well in science to gain a place at the secondary school of their choice a good knowledge of science gained in the primary school prepares children to do well in their more formal science education at secondary school. Good results in secondary school science examinations open up a wide range of career opportunities. Successful teaching and learning with Macmillan Science Effective science teaching should incorporate the following components: 1 Plan well-resourced lessons that engage all pupils, so each one is able to participate in the discussion and the practical tasks. Most of the equipment needed for the lessons is easy to obtain, but specific measuring equipment and an assortment of containers are essential for scientific investigations. 2 Allow children to reflect on their prior knowledge, articulating their views about scientific ideas. Sometimes these ideas may be quite different to accepted scientific ones but are often valid from a child s point of view. They provide a key to developing scientific concepts. 3 Encourage children to discuss their ideas with their partners and the rest of the class so that they learn to be active learners, articulating their own ideas and listening to those of others. 4 Introduce the key words shown in each unit, developing a shared understanding of these and encouraging children to use them when they express their ideas. Developing working definitions for new vocabulary and using the glossary can help children to clarify meanings of scientific terms. 5 Try to ask open questions so that children are encouraged to think through their ideas in depth rather than just recalling information. Often, inserting do you think into a question can elicit a more meaningful response. 6 Teach scientific recording, using charts and graphic organisers. These enable comparisons to be made and reduce the amount of writing required, leaving more time for discussion and practical work. 4
5 Introduction 7 Use the school grounds and the neighbourhood as an extension of the classroom, encouraging children to observe things that they may otherwise walk past each day. 8 Science is a way of thinking, not just a body of knowledge, so encourage the children to think of themselves as scientists so that they develop a wonder of the natural world and an excitement for exploring the world around them. Teaching a lesson 1 Look through the learning objectives and key words to decide how the children can be supported during the topic. The language boxes give additional ideas for how children s language needs can be addressed. 2 Check the resources list and ensure that there is enough equipment for all the children to participate in the practical work. Resources can be put out on each table or placed nearby so that it does not cause a distraction during the introduction to the lesson. Ideally, children should work in pairs or small groups so that each person can play an active part. 3 Arrange the classroom to ensure easy movement, making sure that bags and clothing are not trailing from chairs. 4 If an interactive white board is available, look for visual materials and video sequences that will help to reinforce vocabulary and aid concentration. 5 Let the children decide on their own working definitions for new vocabulary and try to develop these during the lesson, refer to the glossary for more precise meanings. Write new vocabulary and summarise children s ideas on the board to reinforce learning, especially for visual learners. 7 Encourage children to be active listeners, responding to the ideas of others, saying if they agree or disagree and giving reasons why. Try to develop a sense that the children are talking to each other. Get children to give reasons for their thinking rather than giving short answers to questions. 8 At the end of the lesson, encourage the children to reflect on their learning, saying what they found particularly interesting or perhaps difficult. Look at the objectives again and ask the class to assess whether they managed to achieve these. Invite questions about any difficulties or puzzles they may still have. Close the lesson with Check your progress. 9 Set the children the Workbook and CD-ROM activities as homework to consolidate their learning. Developing children s scientific vocabulary To become scientifically literate, children must acquire the vocabulary they need to describe their observations and ideas. To aid with this aspect of their learning, new key words are identified in every lesson. Simple definitions for all the key words are given in the glossary at the back of the Pupil s Book, and the Teacher s Guide offers suggestions for helping children to learn these new words. During the lesson, you could write the key words on the board as they are introduced. Children could copy the key words into their notebooks. If you print the key words on individual cards, they can be used as flashcards for reading practice. Key word cards can also be used to label displays and to play word games. 5
6 Introduction General safety rules for students Hazardous laboratory chemicals such as strong acids and alkalis should not be used in the primary school, but common household chemicals such as cleaners and paints are often introduced for various activities. These must be treated as potentially hazardous, and any safety instructions on the container followed. In general, anything which is irritating, toxic or corrosive (bleach, for example) should be handled only by the teacher. Particular care should be taken with matches, candles and other naked flames and heat sources. In lower primary, children should not use heat sources themselves; these should only be demonstrated by the teacher. We advise against the use of spirit burners by pupils in the primary school because of the fire risk posed by fuel spills. Safety equipment There is some basic safety equipment that you should have when you do an experiment. Make sure you have the following nearby: First Aid box. Keep your First Aid box complete at all times if you use something up, replace it. The most important things to have in your First Aid box are First Aid instructions, plasters, small bandages, large bandages and safety pins. Bucket of water (with cup). Burns or chemical poisoning (either swallowed, on the skin, or in the eyes) need water. Near the water, keep a cup with which to pour the water more effectively. Fire blanket. A blanket should be kept for smothering fires. If someone s clothes catch fire, quickly lay the person on the floor and smother the flames with the blanket. Fire bucket. Fill a metal bucket with clean, dry sand and keep a long-handled scoop or ladle in it. Sand is very good for putting out fires. NEVER put out a spirit or kerosene fire with water ALWAYS use sand. Field work and visits Nothing is as effective as first-hand experience in promoting curiosity and developing an understanding of the natural world. As with any learning experience, preparation is the key to a successful field trip. Visit the site yourself in advance to explore what it has to offer If there is a warden or an education officer, discuss what he or she will show the children on the day of the visit. Brief them about the topics the children have been studying in recent lessons It is often helpful to prepare worksheets for the trip. These should prompt the children to find and answer questions about the important specimens/features you want them to see and understand Make a safety assessment before committing yourself to the trip. How many adults will you need to accompany the class? Are there any particular hazards at the site? Follow up the trip with a lesson in which children talk and write about their experiences. 6
7 Being a scientist Lesson preparation ObjECTIvES 4 list some of the things a scientist studies 4 describe some of the things a scientist does EqUIPMEnt What do scientists study? Warm up everyday objects that will encourage questions, eg a coconut, an ice balloon (a balloon filled with water and frozen overnight), a rock or a seed Activity 2 paper, coloured pencils What do scientists study? Extension for each child: a magnifying glass, everyday objects BACkgrOUnD InforMATIOn Science is about exploring the world by asking questions and carrying out investigations. It is important for children to understand this for themselves by exploring their world at first-hand. Using science skills such as observing, measuring, recording and investigating should form an important part of science lessons. Whenever possible, children should explore materials, plants and animals, carrying out investigations and raising their own questions. Not all questions can be easily answered, but it is helpful to convey the idea that there are many things we do not know, so scientists try to find answers and explanations. It would be useful for children to start this science course by looking at one or two objects and raising their own questions, and then thinking how they could find out some of the answers. For example, you could bring in a coconut in its shell, or make an ice balloon. Tell the children that they are going to be scientists, doing the same sort of things that real scientists do. They can think of their own questions about the objects and then suggest some possible investigations. Language support Key word Elicitation ideas Quick concept check experiment (v) measure (v) observe (v) record (v) Show a picture of children doing a simple experiment. Show pictures of a measuring jug, scales or a ruler. Show a picture of children looking at an experiment. Show a picture of a simple chart or table. Are the children seeing what happens? (Yes) Is it a way of seeing how much? (Yes) Are they looking carefully? (Yes) Are they looking quickly? (No) Does it show what happened? (Yes) world (v) Show a picture of Earth. Is it where we live? (Yes) 7
8 Being a scientist Lesson plan What do scientists study? p4 Warm up Ask What is science? What is a scientist? Tell the children to talk in pairs about the answers. Then discuss the answers as a class. Ask Can you draw a picture of a scientist? Display the pictures and discuss how the children have represented scientists. Explain to the class that a scientist can be female or male, young or old, and that during these science lessons they are all going to become scientists. Ask What do scientists study? Tell the children to look at page 4. Discuss the list of things that scientists study. Show an object, eg a coconut, rock, seed or ice balloon. Ask Can you think of some questions about this? (Where does it come from? What is it made of? Why is it that shape?) Ask Can you think of anything we could do to find out more about this object? What will happen if we put it in water? Will it sink/float? Explain that this is the way scientists work asking questions and then carrying out experiments. Activity 1 p4 Tell the children to look at the pictures on page 4. Ask What are the scientists studying? a She is using a magnifying glass to examine a leaf. b She is measuring a liquid using a measuring jug. Extension Give each child a magnifying glass and some everyday objects. Ask them to look closely at each object, choose one, and make a close observational drawing. What do scientists do? p5 Warm up Tell the children to look at the picture on page 5. Ask What do scientists do? Tell the children to look at the list of skills on page 5. Ask them to think of some suggestions for each one. Activity 2 p5 Tell the children to draw and colour a picture of themselves being a scientist. Ask What are you doing? Display the pictures the children have drawn next to those they drew of their ideas of what a scientist looks like. Discuss some of the similarities and differences between them. Extension Ask the children to think of questions that scientists might explore. Give them a few examples, such as Why is the sky blue? Why do we need to sleep? There is no need to answer the questions. Check your progress p5 1 world, experiment 2 Children find pictures of scientists at work and say what they are doing. 8
9 Science safety Lesson preparation ObjECTIvES 4 identify dangers when doing science 4 explain how to do science safely EqUIPMEnt no equipment needed BACkgrOUnD InforMATIOn Science is essentially a practical subject with children carrying out practical investigations and moving around the classroom. It may involve hot water, heating substances, cutting things and weighing things. It is essential to keep any risk to the minimum. This topic outlines dangers in science and ways that children can keep safe during science lessons. There are simple rules here that children need to follow and may need reminding of from time to time. It is helpful to look around the classroom before the start of the lesson, ensuring that clothing and bags are removed to one side of the room. If the children are to collect equipment, make sure that this is distributed around the room so that there is not a scramble in one area. Avoid using glass containers, choosing plastic wherever possible. Language support Key word Elicitation ideas Quick concept check heavy (adj) Show a picture or mime a heavy Is it light? (No) Could you pick it up? (No) object. hot (adj) Show a picture of the sun. Is it cold? (No) poisonous (adj) Show a picture of a snake. Does it bite? (Yes) Will it make you ill? (Yes) sharp (adj) Show a picture of a sharp knife. Will it cut? (Yes) Is it sharp? (Yes) 9
10 Science safety Lesson plan Dangers of science p6 Warm up Ask What kind of things do scientists do? Do you think that any of these are dangerous? Do you think you will be doing anything dangerous in science lessons? Discuss responses with partner. Activity 1 p6 Tell the children to look at the pictures on page 6. Ask them to decide how each of these things could be dangerous. Make sure your discussion includes the danger of things that are hot, heavy, sharp and poisonous. How to stay safe in science p7 Ask the children to think of some simple rules for keeping safe in science, and have a class discussion about their ideas. Tell the children to look at page 7 and read the rules. Discuss each in turn and explain that these must be followed every science lesson. Extension Ask the children to work in pairs on creating a short role play about one of the dangers they have discussed. Look at the list of rules for ideas. Get the class to act out the dramas and discuss some of the main points. Ask the children to design a poster warning about one potential danger. Make sure that the message is clear and that the illustration reinforces the message. Check your progress p7 1 sharp, hot, poisonous 2 Children say some things they must do to stay safe in science. Suggestions should include the main ideas on page 7. 10
11 Plants Topic 1 The things around us PB p8-11 Distinguish living and non-living things Distinguish plants and animals Sort and classify living and non-living things Topic 2 Plants and their parts PB p12-15 Name the parts of a plant Collect and handle specimens Make a leaf print Topic 3 The importance of plants PB p16-19 Identify how some plants and plant parts are used Use good hygiene to handle and prepare food Identify different fruits Topic 4 Seeds PB p20-23 Identify seeds as plant parts from which new plants grow Sort and classify specimens Care for a growing plant Review questions PB p24-25 Level 2 Topic 1 Plant life Topic 2 Plants we eat Topic 3 Making things from plants Topic 4 How do plants grow? Level 3 Topic 1 Plant parts: roots and stems Topic 2 Plant parts: branches and leaves Topic 3 Looking at flowers Topic 4 Germination and growth 11
12 Topic 1 The things around us Lesson preparation ObjECTIvES distinguish living and non-living things distinguish plants and animals sort and classify living and non-living things EqUIPMEnt Activity 3 a collection of pictures and/or objects that the children can sort into living/non-living things, eg plants, animals, common household objects; labels for living and non-living. Living and non-living things Extension a camera BACkgrOUnD InforMATIOn Distinguishing between living and non-living can be difficult for young children. Although they may correctly label things as living or non-living, their reasons for choosing these categories are often not scientific ones. Many psychologists, including Piaget, have carried out research into children s ideas about living things. They found that children are likely to identify things that move as living, but may decide that a clock or a toy car is living because it shows some movement. Children may also choose incorrect reasons such as it is living if it is not broken or it is not living if you can buy it in a shop. The biological criteria for living are things that: feed, move, grow, reproduce, breathe, excrete and respond to stimuli. At this stage it is appropriate for children to understand that living things feed, grow and move. Take children out into the local environment and give them lots of opportunities for sorting and classifying objects. This will help them to understand the idea of classifying things according to given criteria. It is also helpful for children to devise their own criteria for deciding whether objects are living or non-living. For example, if they say a plant is living, encourage them to think of reasons for their choice. Some things are very difficult to classify because they show some of the characteristics of living things, eg fire and a car. Language support Key word Elicitation ideas Quick concept check animal (n) Show pictures of a cat, a giraffe and a Is it a person? (No) hippo. living (adj) Show pictures of people, animals, Do they all need food? (Yes) plants and trees. non-living (adj) Show pictures of rocks and a wall. Do they need food and water? (No) plant (n) Show a picture of a plant. Is it a tree? (No) Is it alive? (Yes) 12
13 1 Lesson plan Living and non-living things p8 Warm up Take the children outside and ask them to name some of the things they see around them. Ask Can you name two things that are the same in some way? They may name two buildings. Ask the children to give reasons for their choices. Ask Can you name two things that are different? Again, ask the children to give reasons for their choices. At this stage it is not necessary to discuss living and non-living things. Activity 1 p8 Look at the picture. What can you see? Tell the children to look at the picture on page 8. Ask What can you see? Ask the children to name some of the things in the picture. Ask the children to talk in pairs, taking it in turns to choose two things in the picture that have something the same. Ask In what ways are the two things the same? Ask the children to share some of their examples with the rest of the class. Draw out the idea that some of the things are living things and others are man-made or non-living. Ask the children to tell you which things in the picture are living things and which are non-living things. Activity 2 p9 Look at the pictures above. Say which things are living. Say which things are non-living. Tell the children that some things are alive (living) and some things are not alive (non-living). Tell the children to look at the pictures on page 9. Ask Which of these are living? Which of these are non-living? Ask the children to talk in pairs and discuss each picture, giving reasons for their choices. Discuss the answers as a class. Talk about each object, asking children to say reasons for their choice. Encourage the children to listen carefully to each other, saying whether they agree or disagree with their classmates ideas. Living: tree, insect, bird, flower, fish, worm, cat Non-living: stone, house, fire, car, radio, boat Activity 3 p10 Make a set of living things. Make a set of things that are non-living. Tell the children to look at the picture on page 10. Ask Which are living things? Which are non-living things? Ask the children to sort pictures and objects into sets of living and non-living things. Ask them to do this in pairs and discuss each item. Encourage the children to think of reasons for their choices. 13
14 1 Activity 4 p10 Look at the picture above. How are the things different? Which things move? Which things grow? Which things stay the same? Tell the children to look at the picture on page 10. Ask How are these things different? Which things move? Which things grow? Which things stay the same? Tell the children that living things move and grow, whereas some non-living things can move but do not grow. Plants can turn towards the light and twine around poles. Ask the children to follow the same procedure, in pairs, with the sets of living and non-living things they made in Activity 3. Discuss the responses as a class. They are different because the boy, girl and plant are living and the other items are non-living. Move: boy, girl; Grow: plant; Stay the same: glasses, book, toothbrush, feather, ball Extension Ask the children to photograph six living and six non-living things in the local area and present them as a slide show. Ask the children to make a chart, with the headings feed, move and grow. Then ask them to write things in the chart, and say whether each thing is living or non-living. Living things p11 Warm up Ask How do you decide if something is living? Can you see any living things? Ask the children to look around the classroom and school grounds, and make a list of living things. Activity 5 p11 Say which of these things are plants. Say which are animals. Tell the children to look at the pictures on page 11. Ask Which things are plants? Which things are animals? Discuss the answers as a class. Plants: c, e, f, i, j; Animals: a, b, d, g, h Extension Take the children to a nearby garden or park. Ask them to list the living and non-living things. Play 20 questions with objects such as a plant, an animal, a rock, a toy car and an apple. Check your progress p11 1 living, non-living 2 Children draw a plant and an animal. 14
15 1 After the lesson Workbook p4-7 1 Living things: b, d, e, g, h, i, k; Non-living things: a, c, f, j, l, m 2 Children draw a living thing and a non-living thing in the boxes. 3 Animals: a, b, d, g, h; Plants: c, e, f, i, j 4 Children draw their favourite animal and their favourite plant in the boxes. 5 a true, b false, c true, d true, e false 6 Children draw a bigger tree and a bigger cat in the boxes. 7 Children complete the arrows on the chart. 8 Children chant the sentences and add more themselves. 15
About this unit. Lesson one
 Unit 30 Abuja Carnival About this unit This unit revises language and phonics done throughout the year. The theme of the unit is Abuja carnival. Pupils describe a happy carnival picture and read a story
Unit 30 Abuja Carnival About this unit This unit revises language and phonics done throughout the year. The theme of the unit is Abuja carnival. Pupils describe a happy carnival picture and read a story
Unit 14 Dangerous animals
 Unit 14 Dangerous About this unit In this unit, the pupils will look at some wild living in Africa at how to keep safe from them, at the sounds they make and at their natural habitats. The unit links with
Unit 14 Dangerous About this unit In this unit, the pupils will look at some wild living in Africa at how to keep safe from them, at the sounds they make and at their natural habitats. The unit links with
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15
 Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments Plants Are Producers... 17 Producing a Producer... 19 The Part Plants Play...
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments Plants Are Producers... 17 Producing a Producer... 19 The Part Plants Play...
Contents. Foreword... 5
 Contents Foreword... 5 Chapter 1: Addition Within 0-10 Introduction... 6 Two Groups and a Total... 10 Learn Symbols + and =... 13 Addition Practice... 15 Which is More?... 17 Missing Items... 19 Sums with
Contents Foreword... 5 Chapter 1: Addition Within 0-10 Introduction... 6 Two Groups and a Total... 10 Learn Symbols + and =... 13 Addition Practice... 15 Which is More?... 17 Missing Items... 19 Sums with
Physical Features of Humans
 Grade 1 Science, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Physical Features of Humans Overview Number of instructional days: 11 (1 day = 20 30 minutes) Content to be learned Observe, identify, and record the external features
Grade 1 Science, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Physical Features of Humans Overview Number of instructional days: 11 (1 day = 20 30 minutes) Content to be learned Observe, identify, and record the external features
Unit: Human Impact Differentiated (Tiered) Task How Does Human Activity Impact Soil Erosion?
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Creating and Thinking critically
 Creating and Thinking critically Having their own ideas Thinking of ideas Finding ways to solve problems Finding new ways to do things Making links Making links and noticing patterns in their experience
Creating and Thinking critically Having their own ideas Thinking of ideas Finding ways to solve problems Finding new ways to do things Making links Making links and noticing patterns in their experience
THE HEAD START CHILD OUTCOMES FRAMEWORK
 THE HEAD START CHILD OUTCOMES FRAMEWORK Released in 2000, the Head Start Child Outcomes Framework is intended to guide Head Start programs in their curriculum planning and ongoing assessment of the progress
THE HEAD START CHILD OUTCOMES FRAMEWORK Released in 2000, the Head Start Child Outcomes Framework is intended to guide Head Start programs in their curriculum planning and ongoing assessment of the progress
A Pumpkin Grows. Written by Linda D. Bullock and illustrated by Debby Fisher
 GUIDED READING REPORT A Pumpkin Grows Written by Linda D. Bullock and illustrated by Debby Fisher KEY IDEA This nonfiction text traces the stages a pumpkin goes through as it grows from a seed to become
GUIDED READING REPORT A Pumpkin Grows Written by Linda D. Bullock and illustrated by Debby Fisher KEY IDEA This nonfiction text traces the stages a pumpkin goes through as it grows from a seed to become
been each get other TASK #1 Fry Words TASK #2 Fry Words Write the following words in ABC order: Write the following words in ABC order:
 TASK #1 Fry Words 1-100 been each called down about first TASK #2 Fry Words 1-100 get other long people number into TASK #3 Fry Words 1-100 could part more find now her TASK #4 Fry Words 1-100 for write
TASK #1 Fry Words 1-100 been each called down about first TASK #2 Fry Words 1-100 get other long people number into TASK #3 Fry Words 1-100 could part more find now her TASK #4 Fry Words 1-100 for write
Cognitive Development Facilitator s Guide
 Cognitive Development Facilitator s Guide Competency-Based Learning Objectives Description of Target Audience Training Methodologies/ Strategies Utilized Sequence of Training By the end of this module,
Cognitive Development Facilitator s Guide Competency-Based Learning Objectives Description of Target Audience Training Methodologies/ Strategies Utilized Sequence of Training By the end of this module,
Readyman Activity Badge Outline -- Community Group
 Readyman Activity Badge Outline -- Community Group The Readyman Activity Badge is recommended to be presented in a one month format, as outlined in the Webelos Program Helps booklet. This example outline
Readyman Activity Badge Outline -- Community Group The Readyman Activity Badge is recommended to be presented in a one month format, as outlined in the Webelos Program Helps booklet. This example outline
SESSION 2: HELPING HAND
 SESSION 2: HELPING HAND Ready for the next challenge? Build a device with a long handle that can grab something hanging high! This week you ll also check out your Partner Club s Paper Structure designs.
SESSION 2: HELPING HAND Ready for the next challenge? Build a device with a long handle that can grab something hanging high! This week you ll also check out your Partner Club s Paper Structure designs.
Let's Learn English Lesson Plan
 Let's Learn English Lesson Plan Introduction: Let's Learn English lesson plans are based on the CALLA approach. See the end of each lesson for more information and resources on teaching with the CALLA
Let's Learn English Lesson Plan Introduction: Let's Learn English lesson plans are based on the CALLA approach. See the end of each lesson for more information and resources on teaching with the CALLA
Ocean Exploration: Diving Deep into Ocean Science. Developed by: Sierra Tobiason, Lynn Fujii and Noe Taum
 Ocean Exploration: Diving Deep into Ocean Science Grade Level: Sixth Grade Developed by: Sierra Tobiason, Lynn Fujii and Noe Taum Purpose: This curriculum is designed to communicate: I. Methods scientist
Ocean Exploration: Diving Deep into Ocean Science Grade Level: Sixth Grade Developed by: Sierra Tobiason, Lynn Fujii and Noe Taum Purpose: This curriculum is designed to communicate: I. Methods scientist
TWO OLD WOMEN (An Alaskan Legend of Betrayal, Courage and Survival) By Velma Wallis
 TWO OLD WOMEN (An Alaskan Legend of Betrayal, Courage and Survival) By Velma Wallis Sample Lesson meeting the Alaska English/Language Arts Standards Grade 4 By Nita Rearden Vocabulary List: Pick words
TWO OLD WOMEN (An Alaskan Legend of Betrayal, Courage and Survival) By Velma Wallis Sample Lesson meeting the Alaska English/Language Arts Standards Grade 4 By Nita Rearden Vocabulary List: Pick words
Case study Norway case 1
 Case study Norway case 1 School : B (primary school) Theme: Science microorganisms Dates of lessons: March 26-27 th 2015 Age of students: 10-11 (grade 5) Data sources: Pre- and post-interview with 1 teacher
Case study Norway case 1 School : B (primary school) Theme: Science microorganisms Dates of lessons: March 26-27 th 2015 Age of students: 10-11 (grade 5) Data sources: Pre- and post-interview with 1 teacher
Peterborough Eco Framework
 We would expect you to carry out an review at the start of each year to allow you to assess what progress has been made and decide which area or areas you would like to focus on. It is up to you how you
We would expect you to carry out an review at the start of each year to allow you to assess what progress has been made and decide which area or areas you would like to focus on. It is up to you how you
Planting Seeds, Part 1: Can You Design a Fair Test?
 Planting Seeds, Part 1: Can You Design a Fair Test? In this investigation, your team will choose 2 or 3 seeds in order to design an investigation to learn something more about them. First, you will need
Planting Seeds, Part 1: Can You Design a Fair Test? In this investigation, your team will choose 2 or 3 seeds in order to design an investigation to learn something more about them. First, you will need
Characteristics of the Text Genre Informational Text Text Structure
 LESSON 4 TEACHER S GUIDE by Taiyo Kobayashi Fountas-Pinnell Level C Informational Text Selection Summary The narrator presents key locations in his town and why each is important to the community: a store,
LESSON 4 TEACHER S GUIDE by Taiyo Kobayashi Fountas-Pinnell Level C Informational Text Selection Summary The narrator presents key locations in his town and why each is important to the community: a store,
Spanish III Class Description
 Spanish III Class Description Spanish III is an elective class. It is also a hands on class where students take all the knowledge from their previous years of Spanish and put them into practical use. The
Spanish III Class Description Spanish III is an elective class. It is also a hands on class where students take all the knowledge from their previous years of Spanish and put them into practical use. The
PART C: ENERGIZERS & TEAM-BUILDING ACTIVITIES TO SUPPORT YOUTH-ADULT PARTNERSHIPS
 PART C: ENERGIZERS & TEAM-BUILDING ACTIVITIES TO SUPPORT YOUTH-ADULT PARTNERSHIPS The following energizers and team-building activities can help strengthen the core team and help the participants get to
PART C: ENERGIZERS & TEAM-BUILDING ACTIVITIES TO SUPPORT YOUTH-ADULT PARTNERSHIPS The following energizers and team-building activities can help strengthen the core team and help the participants get to
PREP S SPEAKER LISTENER TECHNIQUE COACHING MANUAL
 1 PREP S SPEAKER LISTENER TECHNIQUE COACHING MANUAL IMPORTANCE OF THE SPEAKER LISTENER TECHNIQUE The Speaker Listener Technique (SLT) is a structured communication strategy that promotes clarity, understanding,
1 PREP S SPEAKER LISTENER TECHNIQUE COACHING MANUAL IMPORTANCE OF THE SPEAKER LISTENER TECHNIQUE The Speaker Listener Technique (SLT) is a structured communication strategy that promotes clarity, understanding,
SOCIAL STUDIES GRADE 1. Clear Learning Targets Office of Teaching and Learning Curriculum Division FAMILIES NOW AND LONG AGO, NEAR AND FAR
 SOCIAL STUDIES FAMILIES NOW AND LONG AGO, NEAR AND FAR GRADE 1 Clear Learning Targets 2015-2016 Aligned with Ohio s Learning Standards for Social Studies Office of Teaching and Learning Curriculum Division
SOCIAL STUDIES FAMILIES NOW AND LONG AGO, NEAR AND FAR GRADE 1 Clear Learning Targets 2015-2016 Aligned with Ohio s Learning Standards for Social Studies Office of Teaching and Learning Curriculum Division
Maryland Science Voluntary State Curriculum Grades K-6
 A Correlation of 2006 to the Maryland Science Voluntary State Curriculum Grades K-6 O/S-60 Introduction This document demonstrates how Scott Foresman Science meets the Maryland Science Voluntary State
A Correlation of 2006 to the Maryland Science Voluntary State Curriculum Grades K-6 O/S-60 Introduction This document demonstrates how Scott Foresman Science meets the Maryland Science Voluntary State
We are going to talk about the meaning of the word weary. Then we will learn how it can be used in different sentences.
 Vocabulary Instructional Routine: Make Connections with New Vocabulary Preparation/Materials: several words selected from Hansel and Gretel (e.g.,, glorious, scare) 1 Italicized sentences are what the
Vocabulary Instructional Routine: Make Connections with New Vocabulary Preparation/Materials: several words selected from Hansel and Gretel (e.g.,, glorious, scare) 1 Italicized sentences are what the
TEAM-BUILDING GAMES, ACTIVITIES AND IDEAS
 1. Drop the Ball Time: 10 12 minutes Purpose: Cooperation and healthy competition Participants: Small groups Materials needed: Golf balls, straws, tape Each small group receives 12 straws and 18 inches
1. Drop the Ball Time: 10 12 minutes Purpose: Cooperation and healthy competition Participants: Small groups Materials needed: Golf balls, straws, tape Each small group receives 12 straws and 18 inches
Name of Course: French 1 Middle School. Grade Level(s): 7 and 8 (half each) Unit 1
 Name of Course: French 1 Middle School Grade Level(s): 7 and 8 (half each) Unit 1 Estimated Instructional Time: 15 classes PA Academic Standards: Communication: Communicate in Languages Other Than English
Name of Course: French 1 Middle School Grade Level(s): 7 and 8 (half each) Unit 1 Estimated Instructional Time: 15 classes PA Academic Standards: Communication: Communicate in Languages Other Than English
First Grade Curriculum Highlights: In alignment with the Common Core Standards
 First Grade Curriculum Highlights: In alignment with the Common Core Standards ENGLISH LANGUAGE ARTS Foundational Skills Print Concepts Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features
First Grade Curriculum Highlights: In alignment with the Common Core Standards ENGLISH LANGUAGE ARTS Foundational Skills Print Concepts Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features
Story Problems with. Missing Parts. s e s s i o n 1. 8 A. Story Problems with. More Story Problems with. Missing Parts
 s e s s i o n 1. 8 A Math Focus Points Developing strategies for solving problems with unknown change/start Developing strategies for recording solutions to story problems Using numbers and standard notation
s e s s i o n 1. 8 A Math Focus Points Developing strategies for solving problems with unknown change/start Developing strategies for recording solutions to story problems Using numbers and standard notation
The Ontario Curriculum
 The Ontario Curriculum GRADE 1 checklist format compiled by: The Canadian Homeschooler using the current Ontario Curriculum Content Introduction... Page 3 Mathematics... Page 4 Language Arts... Page 9
The Ontario Curriculum GRADE 1 checklist format compiled by: The Canadian Homeschooler using the current Ontario Curriculum Content Introduction... Page 3 Mathematics... Page 4 Language Arts... Page 9
Lesson 1 Taking chances with the Sun
 P2 Radiation and life Lesson 1 Taking chances with the Sun consider health benefits as well as risks that sunlight presents introduce two ideas: balancing risks and benefits, reducing risks revisit the
P2 Radiation and life Lesson 1 Taking chances with the Sun consider health benefits as well as risks that sunlight presents introduce two ideas: balancing risks and benefits, reducing risks revisit the
Prewriting: Drafting: Revising: Editing: Publishing:
 Prewriting: children begin to plan writing. Drafting: children put their ideas into writing and drawing. Revising: children reread the draft and decide how to rework and improve it. Editing: children polish
Prewriting: children begin to plan writing. Drafting: children put their ideas into writing and drawing. Revising: children reread the draft and decide how to rework and improve it. Editing: children polish
Grade 6: Module 4: Unit 1: Lesson 3 Tracing a Speaker s Argument: John Stossel DDT Video
 Grade 6: Module 4: Unit 1: Lesson 3 Tracing a Speaker s Argument: John Stossel DDT Video This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt
Grade 6: Module 4: Unit 1: Lesson 3 Tracing a Speaker s Argument: John Stossel DDT Video This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt
Airplane Rescue: Social Studies. LEGO, the LEGO logo, and WEDO are trademarks of the LEGO Group The LEGO Group.
 Airplane Rescue: Social Studies LEGO, the LEGO logo, and WEDO are trademarks of the LEGO Group. 2010 The LEGO Group. Lesson Overview The students will discuss ways that people use land and their physical
Airplane Rescue: Social Studies LEGO, the LEGO logo, and WEDO are trademarks of the LEGO Group. 2010 The LEGO Group. Lesson Overview The students will discuss ways that people use land and their physical
Gifted/Challenge Program Descriptions Summer 2016
 Gifted/Challenge Program Descriptions Summer 2016 (Please note: Select courses that have your child s current grade for the 2015/2016 school year, please do NOT select courses for any other grade level.)
Gifted/Challenge Program Descriptions Summer 2016 (Please note: Select courses that have your child s current grade for the 2015/2016 school year, please do NOT select courses for any other grade level.)
172_Primary 4 Comprehension & Vocabulary-7th Pass 07/11/14. Practice. Practice. Study the flyer carefully and then answer questions 1 8.
 omprehensi on & Vocabulary Primary Comprehensi abulary Primary Comprehension & Vocabulary Primary Comprehe y Primary Comprehension & Vocabulary Primary Comprehension & Vocabulary Primary Com Comprehension
omprehensi on & Vocabulary Primary Comprehensi abulary Primary Comprehension & Vocabulary Primary Comprehe y Primary Comprehension & Vocabulary Primary Comprehension & Vocabulary Primary Com Comprehension
Cheeky Monkey COURSES FOR CHILDREN. Kathryn Harper and Claire Medwell
 AUDIO CD FREE MULTI-ROM Cheeky Monkey Kathryn Harper and Claire Medwell Cheeky Monkey is a flexible new two-level course for pre-primary which adapts to different teaching situations and styles. Children
AUDIO CD FREE MULTI-ROM Cheeky Monkey Kathryn Harper and Claire Medwell Cheeky Monkey is a flexible new two-level course for pre-primary which adapts to different teaching situations and styles. Children
Unit 1: Scientific Investigation-Asking Questions
 Unit 1: Scientific Investigation-Asking Questions Standards: OKC 3 Process Standard 3: Experimental design - Understanding experimental designs requires that students recognize the components of a valid
Unit 1: Scientific Investigation-Asking Questions Standards: OKC 3 Process Standard 3: Experimental design - Understanding experimental designs requires that students recognize the components of a valid
ENGAGE. Daily Routines Common Core. Essential Question How can you use the strategy draw a diagram to solve multistep division problems?
 LESSON 4.12 Problem Solving Multistep Division Problems FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards 4.OA.A.2 Multiply or divide to solve word problems involving multiplicative
LESSON 4.12 Problem Solving Multistep Division Problems FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards 4.OA.A.2 Multiply or divide to solve word problems involving multiplicative
MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm
 MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm Why participate in the Science Fair? Science fair projects give students
MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm Why participate in the Science Fair? Science fair projects give students
KS1 Transport Objectives
 KS1 Transport Y1: Number and Place Value Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals; count in multiples
KS1 Transport Y1: Number and Place Value Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals; count in multiples
Grade 4: Module 2A: Unit 1: Lesson 3 Inferring: Who was John Allen?
 Grade 4: Module 2A: Unit 1: Lesson 3 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content is indicated by the footer: (name
Grade 4: Module 2A: Unit 1: Lesson 3 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content is indicated by the footer: (name
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Trophies Grade 5
 Unit 6/Week 2 Title: The Golden Lion Tamarin Comes Home Suggested Time: 5 days (45 minutes per day) Common Core ELA Standards: RI.5.1, RI.5.3, RL.5.4, RI.5.8; RF.5.3, RF.5.4; W.5.2, W.5.4, W.5.9; SL.5.1,
Unit 6/Week 2 Title: The Golden Lion Tamarin Comes Home Suggested Time: 5 days (45 minutes per day) Common Core ELA Standards: RI.5.1, RI.5.3, RL.5.4, RI.5.8; RF.5.3, RF.5.4; W.5.2, W.5.4, W.5.9; SL.5.1,
Multiple Intelligence Teaching Strategy Response Groups
 Multiple Intelligence Teaching Strategy Response Groups Steps at a Glance 1 2 3 4 5 Create and move students into Response Groups. Give students resources that inspire critical thinking. Ask provocative
Multiple Intelligence Teaching Strategy Response Groups Steps at a Glance 1 2 3 4 5 Create and move students into Response Groups. Give students resources that inspire critical thinking. Ask provocative
Characteristics of the Text Genre Realistic fi ction Text Structure
 LESSON 14 TEACHER S GUIDE by Oscar Hagen Fountas-Pinnell Level A Realistic Fiction Selection Summary A boy and his mom visit a pond and see and count a bird, fish, turtles, and frogs. Number of Words:
LESSON 14 TEACHER S GUIDE by Oscar Hagen Fountas-Pinnell Level A Realistic Fiction Selection Summary A boy and his mom visit a pond and see and count a bird, fish, turtles, and frogs. Number of Words:
Grade 3 Science Life Unit (3.L.2)
 Grade 3 Science Life Unit (3.L.2) Decision 1: What will students learn in this unit? Standards Addressed: Science 3.L.2 Understand how plants survive in their environments. Ask and answer questions to
Grade 3 Science Life Unit (3.L.2) Decision 1: What will students learn in this unit? Standards Addressed: Science 3.L.2 Understand how plants survive in their environments. Ask and answer questions to
SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE
 FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York Le REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION LIVING ENVIRONMENT Wednesday, June 19, 2002 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Directions
FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York Le REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION LIVING ENVIRONMENT Wednesday, June 19, 2002 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Directions
National Literacy and Numeracy Framework for years 3/4
 1. Oracy National Literacy and Numeracy Framework for years 3/4 Speaking Listening Collaboration and discussion Year 3 - Explain information and ideas using relevant vocabulary - Organise what they say
1. Oracy National Literacy and Numeracy Framework for years 3/4 Speaking Listening Collaboration and discussion Year 3 - Explain information and ideas using relevant vocabulary - Organise what they say
5.1 Sound & Light Unit Overview
 5.1 Sound & Light Unit Overview Enduring Understanding: Sound and light are forms of energy that travel and interact with objects in various ways. Essential Question: How is sound energy transmitted, absorbed,
5.1 Sound & Light Unit Overview Enduring Understanding: Sound and light are forms of energy that travel and interact with objects in various ways. Essential Question: How is sound energy transmitted, absorbed,
Using a topic-based approach for Cambridge English: Young Learners classroom activities
 Using a topic-based approach for Cambridge English: Young Learners classroom activities Handout: Topic list for Cambridge English: Starters Write the examples of vocabulary items from the word cloud on
Using a topic-based approach for Cambridge English: Young Learners classroom activities Handout: Topic list for Cambridge English: Starters Write the examples of vocabulary items from the word cloud on
Genevieve L. Hartman, Ph.D.
 Curriculum Development and the Teaching-Learning Process: The Development of Mathematical Thinking for all children Genevieve L. Hartman, Ph.D. Topics for today Part 1: Background and rationale Current
Curriculum Development and the Teaching-Learning Process: The Development of Mathematical Thinking for all children Genevieve L. Hartman, Ph.D. Topics for today Part 1: Background and rationale Current
Kindergarten Lessons for Unit 7: On The Move Me on the Map By Joan Sweeney
 Kindergarten Lessons for Unit 7: On The Move Me on the Map By Joan Sweeney Aligned with the Common Core State Standards in Reading, Speaking & Listening, and Language Written & Prepared for: Baltimore
Kindergarten Lessons for Unit 7: On The Move Me on the Map By Joan Sweeney Aligned with the Common Core State Standards in Reading, Speaking & Listening, and Language Written & Prepared for: Baltimore
Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium:
 Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium: ELA Practice Test Scoring Guide Grade 5 04/25/2014 G5_PracticeTest_ScoringGuide_ELA.docx 0 1 5 1 1 2 RI-1 The student will identify text evidence to support a given
Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium: ELA Practice Test Scoring Guide Grade 5 04/25/2014 G5_PracticeTest_ScoringGuide_ELA.docx 0 1 5 1 1 2 RI-1 The student will identify text evidence to support a given
MATH Study Skills Workshop
 MATH Study Skills Workshop Become an expert math student through understanding your personal learning style, by incorporating practical memory skills, and by becoming proficient in test taking. 11/30/15
MATH Study Skills Workshop Become an expert math student through understanding your personal learning style, by incorporating practical memory skills, and by becoming proficient in test taking. 11/30/15
Learning Fields Unit and Lesson Plans
 Learning Fields Unit and Lesson Plans UNIT INTRODUCTION Learning Fields seeks to connect people with agriculture and rural life today. The lessons in this unit will help students to understand how agriculture
Learning Fields Unit and Lesson Plans UNIT INTRODUCTION Learning Fields seeks to connect people with agriculture and rural life today. The lessons in this unit will help students to understand how agriculture
TEACHING Simple Tools Set II
 TEACHING GUIDE TEACHING Simple Tools Set II Kindergarten Reading Level ISBN-10: 0-8225-6880-2 Green ISBN-13: 978-0-8225-6880-3 2 TEACHING SIMPLE TOOLS SET II Standards Science Mathematics Language Arts
TEACHING GUIDE TEACHING Simple Tools Set II Kindergarten Reading Level ISBN-10: 0-8225-6880-2 Green ISBN-13: 978-0-8225-6880-3 2 TEACHING SIMPLE TOOLS SET II Standards Science Mathematics Language Arts
English Nexus Offender Learning
 Working as a catering assistant Topic Vocabulary and functional language for a catering assistant s role. Level: Entry 3 / National 4 Time: 90 minutes Aim To become more familiar with the job description
Working as a catering assistant Topic Vocabulary and functional language for a catering assistant s role. Level: Entry 3 / National 4 Time: 90 minutes Aim To become more familiar with the job description
FCE Speaking Part 4 Discussion teacher s notes
 Description Brainstorming activity designed to raise students awareness of discussion questions followed by controlled practice and a True/False activity. Time required: Additional materials required:
Description Brainstorming activity designed to raise students awareness of discussion questions followed by controlled practice and a True/False activity. Time required: Additional materials required:
UDL Lesson Plan Template : Module 01 Group 4 Page 1 of 5 Shannon Bates, Sandra Blefko, Robin Britt
 Page 1 of 5 Shannon Bates, Sandra Blefko, Robin Britt Objective/s: Demonstrate physical care in relation to needs. Assessment/s: Demonstrations, formative assessments, personal reflections Learner Objectives:
Page 1 of 5 Shannon Bates, Sandra Blefko, Robin Britt Objective/s: Demonstrate physical care in relation to needs. Assessment/s: Demonstrations, formative assessments, personal reflections Learner Objectives:
Universal Design for Learning Lesson Plan
 Universal Design for Learning Lesson Plan Teacher(s): Alexandra Romano Date: April 9 th, 2014 Subject: English Language Arts NYS Common Core Standard: RL.5 Reading Standards for Literature Cluster Key
Universal Design for Learning Lesson Plan Teacher(s): Alexandra Romano Date: April 9 th, 2014 Subject: English Language Arts NYS Common Core Standard: RL.5 Reading Standards for Literature Cluster Key
Picture It, Dads! Facilitator Activities For. The Mitten
 Picture It, Dads! Facilitator Activities For The Mitten Picture It Dads! The Mitten Goals for Dads: 1. To practice effective read-aloud techniques. 2. To develop strategies to help retell the story. 3.
Picture It, Dads! Facilitator Activities For The Mitten Picture It Dads! The Mitten Goals for Dads: 1. To practice effective read-aloud techniques. 2. To develop strategies to help retell the story. 3.
Kindergarten - Unit One - Connecting Themes
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary for the Kindergarten Social Studies Course. Kindergarten
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary for the Kindergarten Social Studies Course. Kindergarten
Master of Motivation & Influence. Barbara Jordan, MS, LPC, CSAC
 Master of Motivation & Influence Barbara Jordan, MS, LPC, CSAC Welcome Fast forward to 2:00 http://www.dailymotion.com/video/x8nt4s_poor-listeningskills_fun http://search.yahoo.com/search?p=video+clip+of+good+listening+s
Master of Motivation & Influence Barbara Jordan, MS, LPC, CSAC Welcome Fast forward to 2:00 http://www.dailymotion.com/video/x8nt4s_poor-listeningskills_fun http://search.yahoo.com/search?p=video+clip+of+good+listening+s
Speak with Confidence The Art of Developing Presentations & Impromptu Speaking
 Speak with Confidence The Art of Developing Presentations & Impromptu Speaking Use this system as a guide, but don't be afraid to modify it to fit your needs. Remember the keys to delivering a successful
Speak with Confidence The Art of Developing Presentations & Impromptu Speaking Use this system as a guide, but don't be afraid to modify it to fit your needs. Remember the keys to delivering a successful
Kindergarten SAMPLE MATERIAL INSIDE
 Kindergarten SAMPLE MATERIAL INSIDE About Nelson Science Developed by an experienced team of BC educators, Nelson Science is a comprehensive series built from the ground up to fully align with the new
Kindergarten SAMPLE MATERIAL INSIDE About Nelson Science Developed by an experienced team of BC educators, Nelson Science is a comprehensive series built from the ground up to fully align with the new
Literacy THE KEYS TO SUCCESS. Tips for Elementary School Parents (grades K-2)
 Literacy THE KEYS TO SUCCESS Tips for Elementary School Parents (grades K-2) Randi Weingarten president Lorretta Johnson secretary-treasurer Mary Cathryn Ricker executive vice president OUR MISSION The
Literacy THE KEYS TO SUCCESS Tips for Elementary School Parents (grades K-2) Randi Weingarten president Lorretta Johnson secretary-treasurer Mary Cathryn Ricker executive vice president OUR MISSION The
St Michael s Catholic Primary School
 St Michael s Catholic Primary School Inspection report Unique Reference Number 10477 Local Authority Wolverhampton Inspection number 77076 Inspection dates 19 20 September 2011 Reporting inspector Sharona
St Michael s Catholic Primary School Inspection report Unique Reference Number 10477 Local Authority Wolverhampton Inspection number 77076 Inspection dates 19 20 September 2011 Reporting inspector Sharona
Dear Teacher: Welcome to Reading Rods! Reading Rods offer many outstanding features! Read on to discover how to put Reading Rods to work today!
 Dear Teacher: Welcome to Reading Rods! Your Sentence Building Reading Rod Set contains 156 interlocking plastic Rods printed with words representing different parts of speech and punctuation marks. Students
Dear Teacher: Welcome to Reading Rods! Your Sentence Building Reading Rod Set contains 156 interlocking plastic Rods printed with words representing different parts of speech and punctuation marks. Students
Mississippi Valley Archaeology Center 1725 State Street La Crosse, Wisconsin Phone: Web site:
 Mississippi Valley Archaeology Center 1725 State Street La Crosse, Wisconsin 54601 Phone: 608-785-6473 Web site: http://www.uwlax.edu/mvac This lesson was created by a teacher participating in the Eisenhower
Mississippi Valley Archaeology Center 1725 State Street La Crosse, Wisconsin 54601 Phone: 608-785-6473 Web site: http://www.uwlax.edu/mvac This lesson was created by a teacher participating in the Eisenhower
Grade 5: Module 2A: Unit 1: Lesson 6 Analyzing an Interview with a Rainforest Scientist Part 1
 Grade 5: Module 2A: Unit 1: Lesson 6 Analyzing an Interview with a Rainforest Scientist Part 1 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Grade 5: Module 2A: Unit 1: Lesson 6 Analyzing an Interview with a Rainforest Scientist Part 1 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
P a g e 1. Grade 5. Grant funded by:
 P a g e 1 Grade 5 Grant funded by: P a g e 2 Focus Standard: 5.NF.1, 5.NF.2 Lesson 6: Adding and Subtracting Unlike Fractions Standards for Mathematical Practice: SMP.1, SMP.2, SMP.6, SMP.7, SMP.8 Estimated
P a g e 1 Grade 5 Grant funded by: P a g e 2 Focus Standard: 5.NF.1, 5.NF.2 Lesson 6: Adding and Subtracting Unlike Fractions Standards for Mathematical Practice: SMP.1, SMP.2, SMP.6, SMP.7, SMP.8 Estimated
More ESL Teaching Ideas
 More ESL Teaching Ideas Grades 1-8 Written by Anne Moore and Dana Pilling Illustrated by Tom Riddolls, Alicia Macdonald About the authors: Anne Moore is a certified teacher with a specialist certification
More ESL Teaching Ideas Grades 1-8 Written by Anne Moore and Dana Pilling Illustrated by Tom Riddolls, Alicia Macdonald About the authors: Anne Moore is a certified teacher with a specialist certification
Sight Word Assessment
 Make, Take & Teach Sight Word Assessment Assessment and Progress Monitoring for the Dolch 220 Sight Words What are sight words? Sight words are words that are used frequently in reading and writing. Because
Make, Take & Teach Sight Word Assessment Assessment and Progress Monitoring for the Dolch 220 Sight Words What are sight words? Sight words are words that are used frequently in reading and writing. Because
Consequences of Your Good Behavior Free & Frequent Praise
 Statement of Purpose The aim of this classroom is to be a comfortable, respectful and friendly atmosphere in which we can learn about social studies. It is okay if you make mistakes because it is often
Statement of Purpose The aim of this classroom is to be a comfortable, respectful and friendly atmosphere in which we can learn about social studies. It is okay if you make mistakes because it is often
Medium Term Plan English Year
 Medium Term Plan English Year 12016 17 Comprehension Work through Comprehension Book and guided reading Grammar and punctuation Nelson Grammar International Pupil Book 1. Nelson International Comprehension
Medium Term Plan English Year 12016 17 Comprehension Work through Comprehension Book and guided reading Grammar and punctuation Nelson Grammar International Pupil Book 1. Nelson International Comprehension
Tour. English Discoveries Online
 Techno-Ware Tour Of English Discoveries Online Online www.englishdiscoveries.com http://ed242us.engdis.com/technotms Guided Tour of English Discoveries Online Background: English Discoveries Online is
Techno-Ware Tour Of English Discoveries Online Online www.englishdiscoveries.com http://ed242us.engdis.com/technotms Guided Tour of English Discoveries Online Background: English Discoveries Online is
Stakeholder Debate: Wind Energy
 Activity ENGAGE For Educator Stakeholder Debate: Wind Energy How do stakeholder interests determine which specific resources a community will use? For the complete activity with media resources, visit:
Activity ENGAGE For Educator Stakeholder Debate: Wind Energy How do stakeholder interests determine which specific resources a community will use? For the complete activity with media resources, visit:
Common Core State Standards
 Common Core State Standards Common Core State Standards 7.NS.3 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. Mathematical Practices 1, 3, and 4 are aspects
Common Core State Standards Common Core State Standards 7.NS.3 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. Mathematical Practices 1, 3, and 4 are aspects
Mathematics Success Grade 7
 T894 Mathematics Success Grade 7 [OBJECTIVE] The student will find probabilities of compound events using organized lists, tables, tree diagrams, and simulations. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] Simple probability,
T894 Mathematics Success Grade 7 [OBJECTIVE] The student will find probabilities of compound events using organized lists, tables, tree diagrams, and simulations. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] Simple probability,
Friction Stops Motion
 activity Friction Stops Motion BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade Quarter Activity SC.C... The student understands that the motion of an object can be described and measured. SC.H...
activity Friction Stops Motion BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade Quarter Activity SC.C... The student understands that the motion of an object can be described and measured. SC.H...
Fountas-Pinnell Level P Informational Text
 LESSON 7 TEACHER S GUIDE Now Showing in Your Living Room by Lisa Cocca Fountas-Pinnell Level P Informational Text Selection Summary This selection spans the history of television in the United States,
LESSON 7 TEACHER S GUIDE Now Showing in Your Living Room by Lisa Cocca Fountas-Pinnell Level P Informational Text Selection Summary This selection spans the history of television in the United States,
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 5: HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS
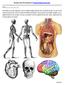 SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 5: HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS NAME: This booklet is an in-class assignment; you must complete all pages during the class work periods provided. You must use full sentences for all sections
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 5: HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS NAME: This booklet is an in-class assignment; you must complete all pages during the class work periods provided. You must use full sentences for all sections
My Identity, Your Identity: Historical Landmarks/Famous Places
 Project Name My Identity, Your Identity: Historical Landmarks/Famous Places Global Project Theme Grade/Age Level Length of Unit Heritage, Identity, & Tradition Grade 5-12 /Ages 10-19 5 weeks Unit Content
Project Name My Identity, Your Identity: Historical Landmarks/Famous Places Global Project Theme Grade/Age Level Length of Unit Heritage, Identity, & Tradition Grade 5-12 /Ages 10-19 5 weeks Unit Content
CLASS EXPECTATIONS Respect yourself, the teacher & others 2. Put forth your best effort at all times Be prepared for class each day
 CLASS EXPECTATIONS 1. Respect yourself, the teacher & others Show respect for the teacher, yourself and others at all times. Respect others property. Avoid touching or writing on anything that does not
CLASS EXPECTATIONS 1. Respect yourself, the teacher & others Show respect for the teacher, yourself and others at all times. Respect others property. Avoid touching or writing on anything that does not
Food Chain Cut And Paste Activities
 Cut And Paste Activities Free PDF ebook Download: Cut And Paste Activities Download or Read Online ebook food chain cut and paste activities in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database CO #3: Organise
Cut And Paste Activities Free PDF ebook Download: Cut And Paste Activities Download or Read Online ebook food chain cut and paste activities in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database CO #3: Organise
Helping at Home ~ Supporting your child s learning!
 Helping at Home ~ Supporting your child s learning! Halcombe School 2014 HELPING AT HOME At Halcombe School, we think teaching your child at school is like coaching your child in a sports team. When your
Helping at Home ~ Supporting your child s learning! Halcombe School 2014 HELPING AT HOME At Halcombe School, we think teaching your child at school is like coaching your child in a sports team. When your
Grade 6: Module 4: Unit 3: Overview
 Grade 6: Module 4: Unit 3: Overview This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content is indicated by the footer: (name
Grade 6: Module 4: Unit 3: Overview This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content is indicated by the footer: (name
Activities. Standards-Based Skill-Builders with Seasonal Themes. Written by Brenda Kaufmann. Sample file. Illustrated by Janet Armbrust
 Spring Math Activities Standards-Based Skill-Builders with Seasonal Themes Written by Brenda Kaufmann Illustrated by Janet Armbrust Teaching & Learning Company 1204 Buchanan St., P.O. Box 10 Carthage,
Spring Math Activities Standards-Based Skill-Builders with Seasonal Themes Written by Brenda Kaufmann Illustrated by Janet Armbrust Teaching & Learning Company 1204 Buchanan St., P.O. Box 10 Carthage,
Holy Family Catholic Primary School SPELLING POLICY
 Holy Family Catholic Primary School SPELLING POLICY 1. The aim of the spelling policy at Holy Family Catholic Primary School is to ensure that the children are encouraged to develop spelling accuracy in
Holy Family Catholic Primary School SPELLING POLICY 1. The aim of the spelling policy at Holy Family Catholic Primary School is to ensure that the children are encouraged to develop spelling accuracy in
Std: III rd. Subject: Morals cw.
 MORALS - CW Std: I rd. Subject: Morals cw. Sl. No Topic Peg No. 1. Being Brave. 2 2. Love of books. 3-4 3. Love hobby. 4 4. Love your Elders. 5 5. Kindness. 5-6 6. Love Mother India. 7 7. Nature loves
MORALS - CW Std: I rd. Subject: Morals cw. Sl. No Topic Peg No. 1. Being Brave. 2 2. Love of books. 3-4 3. Love hobby. 4 4. Love your Elders. 5 5. Kindness. 5-6 6. Love Mother India. 7 7. Nature loves
Includes Activities for all ages CHALLENGE LEVEL 1. Explore STEM with
 Take Our Daughters And Sons To Work Foundation Activity Guide Includes Activities for all ages CHALLENGE LEVEL 1 Explore STEM with WARNING: These STEM activities have been known to cause extreme excitement.
Take Our Daughters And Sons To Work Foundation Activity Guide Includes Activities for all ages CHALLENGE LEVEL 1 Explore STEM with WARNING: These STEM activities have been known to cause extreme excitement.
Fearless Change -- Patterns for Introducing New Ideas
 Ask for Help Since the task of introducing a new idea into an organization is a big job, look for people and resources to help your efforts. The job of introducing a new idea into an organization is too
Ask for Help Since the task of introducing a new idea into an organization is a big job, look for people and resources to help your efforts. The job of introducing a new idea into an organization is too
2 months: Social and Emotional Begins to smile at people Can briefly calm self (may bring hands to mouth and suck on hand) Tries to look at parent
 2 months: Begins to smile at people Can briefly calm self (may bring hands to mouth and suck on hand) Tries to look at parent Coos, makes gurgling sounds Turns head toward sounds Pays attention to faces
2 months: Begins to smile at people Can briefly calm self (may bring hands to mouth and suck on hand) Tries to look at parent Coos, makes gurgling sounds Turns head toward sounds Pays attention to faces
CAFE ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS O S E P P C E A. 1 Framework 2 CAFE Menu. 3 Classroom Design 4 Materials 5 Record Keeping
 CAFE RE P SU C 3 Classroom Design 4 Materials 5 Record Keeping P H ND 1 Framework 2 CAFE Menu R E P 6 Assessment 7 Choice 8 Whole-Group Instruction 9 Small-Group Instruction 10 One-on-one Instruction 11
CAFE RE P SU C 3 Classroom Design 4 Materials 5 Record Keeping P H ND 1 Framework 2 CAFE Menu R E P 6 Assessment 7 Choice 8 Whole-Group Instruction 9 Small-Group Instruction 10 One-on-one Instruction 11
WiggleWorks Software Manual PDF0049 (PDF) Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 WiggleWorks Software Manual PDF0049 (PDF) Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Table of Contents Welcome to WiggleWorks... 3 Program Materials... 3 WiggleWorks Teacher Software... 4 Logging In...
WiggleWorks Software Manual PDF0049 (PDF) Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Table of Contents Welcome to WiggleWorks... 3 Program Materials... 3 WiggleWorks Teacher Software... 4 Logging In...
Grade 3: Module 1: Unit 3: Lesson 5 Jigsaw Groups and Planning for Paragraph Writing about Waiting for the Biblioburro
 Grade 3: Module 1: Unit 3: Lesson 5 Jigsaw Groups and Planning for Paragraph Writing about Waiting for the Biblioburro This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Grade 3: Module 1: Unit 3: Lesson 5 Jigsaw Groups and Planning for Paragraph Writing about Waiting for the Biblioburro This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Lesson Plan Title Aquatic Ecology
 Lesson Plan Title Aquatic Ecology Name (last, first): Larson, Don Scientific Theme(s): C-2: develop an understanding of the structure, function, behavior, development, life cycles, and diversity of living
Lesson Plan Title Aquatic Ecology Name (last, first): Larson, Don Scientific Theme(s): C-2: develop an understanding of the structure, function, behavior, development, life cycles, and diversity of living
Table of Contents. This descriptive guide will assist you in integrating the DVD science and education content into your instructional program.
 Bill Nye the Science Guy Comets & Meteors 1. Implementation Guide........................................ 2 9 This descriptive guide will assist you in integrating the DVD science and education content
Bill Nye the Science Guy Comets & Meteors 1. Implementation Guide........................................ 2 9 This descriptive guide will assist you in integrating the DVD science and education content
ENERGY WORLD: Electricity aro
 ENERGY WORLD: Electricity aro ound us Lesson Plans October December 2008 UNIT 1. WHAT IS ELEC CTRICITY? TEACHING OBJECTIVES - To identify and classify electrical and non electrical appliances. - To know
ENERGY WORLD: Electricity aro ound us Lesson Plans October December 2008 UNIT 1. WHAT IS ELEC CTRICITY? TEACHING OBJECTIVES - To identify and classify electrical and non electrical appliances. - To know
