SCIENCE TEST FOR TEACHERS ONLY RATING GUIDE FOR PART II
|
|
|
- Lionel Blake
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK GRADE 8 INTERMEDIATE-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST SPRING 2009 WRITTEN TEST FOR TEACHERS ONLY RATING GUIDE FOR PART II This rating guide contains detailed directions for rating student responses to Part II of the written test in Intermediate-Level Science. All raters should become familiar with the detailed directions before beginning to rate student responses. Appendix A provides a chart that translates final scores into four performance levels. A conversion chart is needed to translate a student s raw score on the written and performance tests to a final score. This chart will be posted on the Department s web site Conversion charts provided for previous administrations of this test must not be used to determine student s final scores for the 2009 administration of this test. Appendix B provides several charts that link the individual items on the test to the Intermediate-Level Science Core Curriculum Grades 5 8. This core curriculum is based on the New York State Learning Standards in Mathematics, Science, and Technology. Any clarifications or changes to this rating guide will be posted on the New York State Education Department website at the end of the test administration period. Check this website before starting the rating process and several times during the rating period. Questions regarding this test should be directed to the Office of State Assessment at (518) or the Office of Curriculum, Instruction, and Instructional Technology at (518) Note: Retain this guide for future use. Do not return it to SED with the performance test materials. COPYRIGHT 2009 THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT ALBANY, NEW YORK 1224
2
3 Detailed Directions for Rating Part II of the Written Test This guide contains detailed directions and criteria for scoring student responses to the questions in Part II of the written test. Raters should become familiar with the detailed directions and scoring criteria before beginning to score the student responses. In rating the student responses, follow the procedure outlined below. 1. Familiarize yourself with the system your school is using for processing the answer papers and recording the test scores. 2. Have a test booklet on hand. Read each Part II question carefully. Note exactly what is required.. Carefully read the criteria provided in this guide for scoring each question. Look at the acceptable responses for each point value. 4. For most questions, examples of acceptable responses are provided. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to, the examples given. Other responses that convey the same general meaning as those given in this guide should also receive credit. Raters must use their judgment to decide if the student s answer meets the criteria. You may find it helpful to discuss questionable student responses with other raters. 5. Discuss with other raters the requirements of each question and the scoring criteria. When you are certain that you clearly understand the requirements and criteria, you are ready to begin scoring the student responses. 6. It is recommended that you score all the student responses to one question before proceeding to the next question. This method helps ensure that the scoring criteria are applied consistently. 7. Students should not lose credit for incorrect spelling, grammar, capitalization, or punctuation. 8. In responses to questions where a specific number of answers are required (e.g., identify three materials, give two examples), if the student provides more than the required number of answers, score only the required number, in the order in which they appear. 9. Record the number of credits you allow for each question in the table provided on the back cover of the test booklet. The maximum number of credits for each question appears in the table. Int.-Lev. Sci. Spring 09 Rating Guide [] [OVER]
4 10. When you have finished scoring all the Part II questions, add the credits allowed for each question to obtain the total raw score for Part II. 11. The total raw score for Part II can be transferred to the student s scannable answer sheet. Check to be certain that the student name on the test booklet matches the name on the answer sheet. 12. Add the student s raw score for Part II to the raw score for Part I to determine the student s total raw score for the written test. Use the conversion chart to convert the written and performance test raw scores to a final score for the student. This chart will be provided on the Department s web site Online Submission of Teacher Evaluations of the Test to the Department Suggestions and feedback from teachers provide an important contribution to the test development process. The Department provides an online evaluation form for State assessments. It contains spaces for teachers to respond to several specific questions and to make suggestions. Instructions for completing the evaluation form are as follows: 1. Go to 2. Select the test title.. Complete the required demographic fields. 4. Complete each evaluation question and provide comments in the space provided. 5. Click the SUBMIT button at the bottom of the page to submit the completed form. Int.-Lev. Sci. Spring 09 Rating Guide [4]
5 46 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: A hard mineral cannot be scratched easily by other Earth materials. They can be used for tools. They can be cut and polished and used for gems. durability can be used for a long time 47 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: color luster ability to reflect light crystal size crystal shape sparkle shiny clarity transparency 48 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: The diamonds might scratch each other if not protected by the wrapping. Diamonds are very hard, so they can scratch each other. Diamonds may be chipped. The diamonds may be broken. 49 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: The trilobites are located in the bottom layer. They are located in the layer that formed first. 50 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: Fossils from different time periods were found in different layers. because there are several different rock layers Int.-Lev. Sci. Spring 09 Rating Guide [5] [OVER]
6 51 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: The plates collide. Plates slide by each other. plates move faulting separation of crustal plates 52 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: volcano formation/volcanoes volcanic activity/eruption subduction rifting tsunami (seismic sea wave) mountain building/mountains trench formation/trenches landslides flooding faulting/folding 5 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: precipitation rain cloudy skies unstable weather 54 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: east northeast north northeast southeast Int.-Lev. Sci. Spring 09 Rating Guide [6]
7 55 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: Increased concentrations of carbon dioxide may lead to global warming. Increased amounts of CO 2 may affect weather and climate. Unacceptable responses include: destruction of the ozone layer (This problem is not due to increased concentration of CO 2.) 56 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: reduce use of fossil fuels plant more trees drive less use other forms of energy (wind, geothermal, water, etc.) save the rain forest conserve energy Unacceptable responses include: don t pollute (This response not specific enough.) recycling (This response not specific enough.) 57 [1] Allow 1 credit for a volume of 10 cm. 58 [2] Allow a maximum of 2 credits, 1 credit for each acceptable response. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: stir the contents of the beaker heat the contents of the beaker heat the water grind/crush the sugar cube shake the contents of the beaker 59 [1] Allow 1 credit for lake. Int.-Lev. Sci. Spring 09 Rating Guide [7] [OVER]
8 60 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: cool the metal ball heat the metal ring 61 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: the higher the temperature, the faster the motion direct relationship the lower the temperature, the slower the motion 62 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: mechanical kinetic energy 6 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: use a thicker/thinner rubber band turn the propeller more times change the mass/weight of the airplane 64 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: Once the plant is mature, it can carry out photosynthesis. After it is mature, the plant can make its own food. The mature plant produces chlorophyll and makes its own food. When the plant matures, it will have leaves, allowing it to make food for itself through photosynthesis. 65 [1] Allow 1 credit for 4 or four. 66 [1] Allow 1 credit for 2 or two. Int.-Lev. Sci. Spring 09 Rating Guide [8]
9 67 [1] Allow 1 credit for grass. 68 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: Mice eat both plants and animals. Mice eat both grass and crickets. 69 [1] Allow 1 credit for crickets or mice. 70 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: Test tube A is a control. Test tube A is used as a comparison for the other two tubes. 71 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: Carbon dioxide from the student s breath dissolves in the water, making it slightly acidic. The student blows carbon dioxide into the water in the tube and it combines with the water. Carbon dioxide mixes with the water to form an acid. 72 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: Acid rain can wear away the details of statues and monuments. Acid rain can cause weathering on the surfaces of statues. Acid rain can destroy monuments. Acid rain causes chemical weathering of limestone. 7 [1] Allow 1 credit for two acceptable responses: bird and shark. Int.-Lev. Sci. Spring 09 Rating Guide [9] [OVER]
10 74 [1] Allow 1 credit. All four cells must be correct to receive credit. Examples of 1-credit responses: R r r Rr rr r Rr rr R r r rr rr r rr rr 75 [1] Allow 1 credit for photosynthesis. 76 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include: Trees provide homes for wildlife. protect animals from predators lumber for homes or other buildings Some trees provide food for other living organisms. Trees are producers in many food chains. reduce erosion fuel source Note: Do not allow credit for benefits that are listed in the introduction to the question (e.g., shade). Int.-Lev. Sci. Spring 09 Rating Guide [10]
11 77 [1] Allow 1 credit for listing 1, 2, 5, 6, and 8 in any order. 78 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: The rock contains fossil shells. Fossil shells are found in some sedimentary rocks. Shells are found in water and most sedimentary rocks form in a water environment. The rock probably formed in a water environment. If the rock is broken, it will probably contain more fossil shells. statement 6 statement 4 statement 7 Int.-Lev. Sci. Spring 09 Rating Guide [11] [OVER]
12 79 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: Average mass increases with age. As age increases in males, so does mass. direct relationship 80 [2] Allow a maximum of 2 credits, allocated as follows: Allow 2 credits if the centers of all five Xs are plotted within the circles shown on the grid below and correctly connected with a line that passes through the circles. Allow 1 credit if the centers of only three or four Xs are plotted within the circles shown on the grid below and correctly connected with a line that passes through the circles. or Allow 1 credit if the centers of all five Xs are plotted within the circles shown on the grid below but are not correctly connected with a line. Note: Allow credit if the student uses something other than an X to plot the points. Example of a 2-credit response: 170 Average Height of Female Students Age 8 to 16 in the United States in Average Height (cm) Age (years) 81 [1] Allow 1 credit for a value from 145 cm to 147 cm or a response that is consistent with the student s graph in question 80. Int.-Lev. Sci. Spring 09 Rating Guide [12]
13 82 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: type of paper towel used how much of the towel is in the water amount of water in the glass the temperature of the water size of the paper towel strips Unacceptable responses include: time (independent variable) height of water on towel (dependent variable) 8 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: Capillary action does occur in the paper towel. The longer the time, the higher the water rose. The water rises fastest when the towel is first placed in the water. Int.-Lev. Sci. Spring 09 Rating Guide [1] [OVER]
14 Appendix A New York State Grade 8 Intermediate-Level Science Test Spring 2009 Performance Levels Chart The chart on the next page defines the four performance levels for this test. The State-designated level of performance for this test is a final score of 65 or higher (level and 4). Students scoring below 65 (levels 1 and 2) must be provided with academic intervention services according to section 100.2(ee)(i ) of the Regulations of the Commissioner of Education. The chart provides the score intervals and a brief description of student abilities at each level. The conversion chart will be posted on the Department s website at Note: Conversion charts provided for previous administrations of this test must not be used to determine students final scores for the 2009 administration.
15 Level Score Range Performance Levels Grade 8 Intermediate-Level Science Test Description of Student Performance Meeting the Standards with Distinction Student demonstrates superior understanding of the intermediate-level science content and concepts for each of the learning standards and key ideas assessed. Student demonstrates superior intermediate-level science skills related to each of the learning standards and key ideas assessed. Student demonstrates superior understanding of the intermediate-level science content, concepts, and skills required for a secondary academic environment Meeting the Standards Student demonstrates understanding of the intermediate-level science content and concepts for each of the learning standards and key ideas assessed. Student demonstrates the science skills required for intermediate-level achievement in each of the learning standards and key ideas assessed. Student demonstrates understanding of the intermediate-level science content, concepts, and skills required for a secondary academic environment Not Fully Meeting the Standards Student demonstrates only minimal proficiency in intermediate-level science content and concepts in most of learning standards and key ideas assessed. Student demonstrates only minimal proficiency in the skills required for intermediate-level achievement in most of the learning standards and key ideas assessed. Student demonstrates marginal understanding of the science content, concepts, and skills required for a secondary academic environment Not Meeting the Standards Student is unable to demonstrate understanding of the intermediate-level science content and concepts in most of the learning standards and key ideas assessed. Student is unable to demonstrate the science skills required for intermediate-level achievement in most of the learning standards and key ideas assessed. Student is unable to demonstrate evidence of the basic science knowledge and skills required for a secondary academic environment.
16 Appendix B Item Maps New York State Grade 8 Intermediate-Level Science Test Spring 2009 Written Test Performance Test Form A Item maps contained in this appendix: Reference to Intermediate-Level Science Core Curriculum Grades 5-8 Spring 2009 Written Test and Performance Test, Form A Reference to Process Skills Based on Standard 4 Spring 2009 Written Test and Performance Test, Form A Reference to Core Curriculum for Individual Test Questions Spring 2009 Written Test Reference to Core Curriculum for Individual Test Questions Performance Test, Form A Note: Core curriculum is based on NYS Learning Standards for Mathematics, Science and Technology.
17 NYS Learning Standards for Mathematics, Science, and Technology Standard/Area Standard 1 Scientific Inquiry Key Idea 1 The central purpose of scientific inquiry is to develop explanations of natural phenomena in a continuing, creative process. Standard 1 Scientific Inquiry Key Idea 2 Beyond the use of reasoning and consensus, scientific inquiry involves the testing of proposed explanations involving the use of conventional techniques and procedures and usually requiring considerable ingenuity. Reference to Intermediate-Level Science Core Curriculum Key Idea or Performance Indicator 1.1 Formulate questions independently with the aid of references appropriate for guiding the search for explanations of everyday observations. 1.2 Construct explanations independently for natural phenomena, especially by proposing preliminary visual models of phenomena. 1. Represent, present, and defend their proposed explanations of everyday observations so that they can be understood and assessed by others. 1.4 Seek to clarify, to assess critically, and to reconcile with their own thinking the ideas presented by others, including peers, teachers, authors, and scientists. 2.1 Use conventional techniques and those of their own design to make further observations and refine their explanations, guided by a need for more information. 2.2 Develop, present, and defend formal research proposals for testing their own explanations of common phenomena, including ways of obtaining needed observations and ways of conducting simple controlled experiments. 2. Carry out their research proposals, recording observations and measurements (e.g., lab notes, audiotape, computer disk, videotape) to help assess the explanation. Station Performance Test Form A Question Number Station 2 Station Spring 2009 Written Test Question Number , 71, , 81 70, 82 Standard 1 Scientific Inquiry Key Idea The observations made while testing proposed explanations, when analyzed using conventional and invented methods, provide new insights into phenomena. Standard 1 Mathematical Analysis.1 Design charts, tables, graphs and other representations of observations in conventional and creative ways to help them address their research question or hypothesis..2 Interpret the organized data to answer the research question or hypothesis and to gain insight into the problem.. Modify their personal understanding of phenomena based on evaluation of their hypothesis. 5 1 Abstraction and symbolic representation are used to communicate mathematically. 2 Deductive and inductive reasoning are used to reach mathematical conclusions. Critical thinking skills are used in the solution of mathematical problems , 5, 6, 7 4, 5, 6, 7 80, 44, 45, 55, 81, 8 61, 79 19, 4, 44 18
18 NYS Learning Standards for Mathematics, Science, and Technology Standard/Area Standard 1 Engineering Design Standard 2 Information Systems Standard 4 Physical Setting Reference to Intermediate-Level Science Core Curriculum Key Idea or Performance Indicator Station 1 Performance Test Form A Question Number Station 2 Station Spring 2009 Written Test Question Number T 1.1 T 1.5 Engineering design is an iterative process involving modeling and optimization to develop technological solutions to problems within given constraints Information technology is used to retrieve, process, and communicate information as a tool to enhance learning Knowledge of the impacts and limitations of information systems is essential to its effectiveness and ethical use..1. Information technology can have positive and negative impacts on society, depending upon how it is used. 1 Earth and celestial phenomena can be described by principles of relative motion and perspective. 1, 2, 2 Many of the phenomena that we observe on Earth involve interactions among components of air, water, and land. Matter is made up of particles whose properties determine the observable characteristics of matter and its reactivity. 4 Energy exists in many forms, and when these forms change energy is conserved. 4, 5, 12, 1, 14, 46, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 5, 54, 55, 59, 72, 78 5, 6, 15, 16, 17, 47, 57, 58, 61 7, 8, 9, 10, 60, 62 5 Energy and matter interact through forces that result in changes in motion. 11, 18, 19, 6 1 Living things are both similar to and different from each other and from nonliving things. 2 Organisms inherit genetic information in a variety of ways that result in continuity of structure and function between parents and offspring. 20, 21, 22, 2, 24, 25, 27, 2,, 9, 71, 7 28, 65, 66, 74 Standard 4 Living Environment Individual organisms and species change over time. 26, 29, 6, 49, 50 4 The continuity of life is sustained through reproduction and development. 0, 41, 4, 64 5 Organisms maintain a dynamic equilibrium that sustains life. 1, 4, 5, 8, 44, 45, 68 6 Plants and animals depend on each other and their physical environment. 64, 67, 69, 75 7 Human decisions and activities have had a profound impact on the physical and living environment. 26, 7, 40, 41, 42, 56, 76
19 NYS Learning Standards for Mathematics, Science, and Technology Standard/Area Standard 6 Interconnectedness: Common Themes Standard 6 Systems Thinking Standard 6 Models Standard 6 Magnitude and Scale Standard 6 Equilibrium and Stability Standard 6 Patterns of Change Standard 6 Optimization Standard 7 Interdisciplinary Problem Solving Reference to Intermediate-Level Science Core Curriculum Key Idea or Performance Indicator Students will understand the relationships and common themes that connect mathematics, science, and technology and apply the themes to these and other areas of learning Through systems thinking, people can recognize the commonalities that exist among all systems and how parts of a system interrelate and combine to perform specific functions Models are simplified representations of objects, structures, or systems used in analysis, explanation, interpretation, or design..1.2 The grouping of magnitudes of size, time, frequency, and pressures or other units of measurement into a series of relative order provides a useful way to deal with the immense range and the changes in scale that affect the behavior and design of systems Equilibrium is a state of stability due either to a lack of change (static equilibrium) or a balance between opposing forces (dynamic equilibrium) Identifying patterns of change is necessary for making predictions about future behavior and conditions In order to arrive at the best solution that meets criteria within constraints, it is often necessary to make trade-offs. 1 Connections The knowledge and skills of mathematics, science, and technology are used together to make informed decisions and solve problems, especially those related to issues of science/technology/society, consumer decision making, design, and inquiry into phenomena. 2 Strategies Solving interdisciplinary problems involves a variety of skills and strategies, including effective work habits; gathering and processing information; generating and analyzing ideas; realizing ideas; making connections among the common themes of mathematics, science, and technology; and presenting results. Station 1 1, 2,, 4 Performance Test Form A Question Number Station 2 Station, 8 4, 4, 5, 6, 7 Spring 2009 Written Test Question Number 51 8, 1, 14, 15, 16, 17, 0, 2, 6, 8, 40, 42, 4, 49, 50, 52, 5, 54, 57, 58, 59, 60, 62, 6, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, , 79 56
20 Intermediate-Level Science Core Curriculum Grades 5-8 Process Skills Based On Standard 4 General Skills Living Environment Skills Physical Setting Skills Process Skills 1. follow safety procedures in the classroom and laboratory 2. safely and accurately use the following measurement tools: metric ruler, balance, stopwatch, graduated cylinder, thermometer, spring scale, voltmeter Performance Test Form A Question Number Station Station Station Spring 2009 Written Test Question Number. use appropriate units for measured or calculated values 1, 2, 4. recognize and analyze patterns and trends 7, classify objects according to an established scheme and a 7, 78 student-generated scheme 6. develop and use a dichotomous key 1 5, 9 7. sequence events 8. identify cause-and-effect relationships 4, 5, 6 6, 7 48, 71, 75, use indicators and interpret results 1. manipulate a compound microscope to view microscopic objects 2. determine the size of a microscopic object, using a compound microscope. prepare a wet mount slide 4. use appropriate staining techniques 5. design and use a Punnett square or a pedigree chart to predict the probability of certain traits 6. classify living things according to a student-generated scheme and an established scheme 7. interpret and/or illustrate the energy flow in a food chain, energy pyramid, or food web 8. identify pulse points and pulse rates 9. identify structure and function relationships in organisms 1. given the latitude and longitude of a location, indicate its position on a map and determine the latitude and longitude of a given location on a map 2. using identification tests and a flow chart, identify mineral samples. use a diagram of the rock cycle to determine geological processes that led to the formation of a specific rock type 4. plot the location of recent earthquake and volcanic activity on a map and identify patterns of distribution 5. use a magnetic compass to find cardinal directions 6. measure the angular elevation of an object, using appropriate instruments 7. generate and interpret field maps including topographic and weather maps 8. predict the characteristics of an air mass based on the origin of the air mass 9. measure weather variables such as wind speed and direction, relative humidity, barometric pressure, etc. 10. determine the density of liquids, and regular- and irregular-shaped solids 11. determine the volume of a regular- and an irregular-shaped solid, using water displacement 12. using the periodic table, identify an element as a metal, nonmetal, or noble gas 1. determine the identity of an unknown element, using physical and chemical properties 14. using appropriate resources, separate the parts of a mixture 15. determine the electrical conductivity of a material, using a simple circuit 6, , 66, 74 67, 68, , determine the speed and acceleration of a moving object 18, 19 57
21 Grade 8 Intermediate-Level Science Reference to Core Curriculum for Individual Test Questions on Written Test Spring 2009 Question Number MST Learning Standard Area within Standard 4 (PS or LE) Key Idea or Major Understanding Other Standards, Key Ideas, or Major Understandings Process Skills Based on Standard PS 1.1b 2 4 PS 1.1h 4 PS 1.1h 4 4 PS 2.2q 5 4 PS.2a 2.1j 6 4 PS.a 7 4 PS 4.1c 4.1d 8 4 PS 4.4g St 6 KI PS 4.1b 10 4 PS 4.4f 11 4 PS 5.2a 12 4 PS 2.2g 2.2h 1 4 PS 2.2b St 6 KI PS 2.2e St 6 KI PS.1c St 6 KI PS.2e St 6 KI PS.2c St 6 KI PS 5.1d St 1 M.1 PS skill PS 5.1b St 1 M 2.1a PS skill LE 1.1a 21 4 LE 1.1b 1.1f 1.1g 22 4 LE 1.2e 2 4 LE 1.2g 24 4 LE 1.2h 1.2a 25 4 LE 1.2j 26 4 LE.2a 7.1c 27 4 LE 1.1c 28 4 LE 2.1b 29 4 LE.2d 0 4 LE 4.d 4.c; St 6 KI LE 5.1c 2 4 LE 1.1g St 6 KI LE 1.2d S.2h 4 4 LE 5.1f 5 4 LE 5.2e 5.2f 6 4 LE intro.1b; St 6 KI LE 7.1c St 6 KI LE 5.1d St 6 KI LE 1.1e 40 4 LE 7.1b St 6 KI LE 7.2c 4.1b 42 4 LE 7.2d St 1 S 1.2, St 6 KI 2.2
22 Grade 8 Intermediate-Level Science Reference to Core Curriculum for Individual Test Questions on Written Test Spring 2009 MST Area within Key Idea or Process Skills Other Standards, Key Ideas, Learning Standard 4 Major Based on or Major Understandings Standard (PS or LE) Understanding Standard 4 Question Number 4 4 LE 4.1b St 6 KI 2.2; St 1 M 2.1b 44 1 S.2h M 2.1a; LE 5.2d 45 1 S.2h LE 5.2d 46 4 PS 2.1e St 1 S PS.1a PS skill PS 2.1e General skill LE.2c.2b; PS 2.1f; St 6 KI PS 2.2g LE.2c; St 6 KI PS 2.2f St 6 KI 1 and KI PS 2.2a St 6 KI PS 2.2o St 6 KI 2.2 PS skill PS 2.2p St 6 KI 2.2 PS skill PS 2.2r 56 7 KI 1 LE 7.2d 57 4 PS PS skill 11 PS.1f; St 6 KI 2.2 PS skill PS.1b St 6 KI PS 2.1d St 6 KI PS 4.2d St 6 KI PS.b St 1 M 1.1b 62 4 PS 4.1e 4.1d; St 6 KI PS 5 intro 5.1d; St 6 KI LE 4.e 6.2a; St 6 KI LE LE skill 5 LE 2.2c; St 6 KI 2.2 LE skill LE LE skill 5 LE 2.2c; St 6 KI 2.2 LE skill LE 6.1b St 6 KI 2.2 LE skill LE 5.1e St 6 KI 2.2 LE skill LE 6.1a St 6 KI 2.2 LE skill S 2.2b PS 71 4 LE 1.2d St 1 S 1.2b General skill PS 2.1g St 1 S LE 1.1h General skill KI 2.2 LE 2.2c LE skill LE 6.2b General skill LE 7.1c General skill S 1.2c S 2.1d; PS 78 4 PS 2.1f General skill M 1.1b LE, St 6 KI 5.2 General skill S.1a LE 81 1 M 2.1a S.2h; LE 82 1 S 2.2d PS 8 1 S.2d PS
23 Grade 8 Intermediate-Level Science Reference to Core Curriculum for Individual Test Questions on Performance Test Form A Reference to Grade 8 Intermediate-Level Science Core Curriculum Station Question Number pts MST Standard 1 (Mathematical Analysis, Scientific Inquiry and Engineering Design) Key Idea/Performance Indicator MST Standard 6 Interconnected/ Common Themes Process Skills Based on MST Standard 4 1 S 2., S.1, S.2 KI 2 General Skill S 1.1, S 2.2 KI 2 General Skill 6 2 S 1.1, S 2.1, S 2.2, S 2., S.1 KI 2 General Skill S 2.1, S 2.2, S 2. KI 2 General Skill S 2.1, S.1 General Skill S 2.1 LE Skill LE Skill LE Skill General Skill 6 LE Skill S 2. General Skill 2 2 S 2., S.1 1 S 2. KI 2 M 1 KI S.2 M 2 KI 5 General Skill S.2 M 2 KI 5 General Skill S.2 M 2 KI 5 General Skill S 1., S 1.4 M 2 KI 5 General Skill 4 8 S 1.2, S 1., S.1 M 1 KI 2 General Skill 4 1 S 2.1, S 2. General Skill 2 4 S 2.1, S 2. General Skill 4 General Skill 4 1 S 1.2, S 2., S.2 KI S 1., S.2, S. 6 2 S 1., S.2 KI 5 General Skill S.2 General Skill 8
For information only, correct responses are listed in the chart below. Question Number. Correct Response
 THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK 4GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST JUNE 207 WRITTEN TEST FOR TEACHERS ONLY SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Note: All schools (public, nonpublic, and charter) administering
THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK 4GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST JUNE 207 WRITTEN TEST FOR TEACHERS ONLY SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Note: All schools (public, nonpublic, and charter) administering
SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE
 FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York Le REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION LIVING ENVIRONMENT Wednesday, June 19, 2002 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Directions
FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York Le REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION LIVING ENVIRONMENT Wednesday, June 19, 2002 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Directions
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15
 Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments Plants Are Producers... 17 Producing a Producer... 19 The Part Plants Play...
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments Plants Are Producers... 17 Producing a Producer... 19 The Part Plants Play...
INSTRUCTIONAL FOCUS DOCUMENT Grade 5/Science
 Exemplar Lesson 01: Comparing Weather and Climate Exemplar Lesson 02: Sun, Ocean, and the Water Cycle State Resources: Connecting to Unifying Concepts through Earth Science Change Over Time RATIONALE:
Exemplar Lesson 01: Comparing Weather and Climate Exemplar Lesson 02: Sun, Ocean, and the Water Cycle State Resources: Connecting to Unifying Concepts through Earth Science Change Over Time RATIONALE:
Maryland Science Voluntary State Curriculum Grades K-6
 A Correlation of 2006 to the Maryland Science Voluntary State Curriculum Grades K-6 O/S-60 Introduction This document demonstrates how Scott Foresman Science meets the Maryland Science Voluntary State
A Correlation of 2006 to the Maryland Science Voluntary State Curriculum Grades K-6 O/S-60 Introduction This document demonstrates how Scott Foresman Science meets the Maryland Science Voluntary State
PROJECT LEARNING TREE 4 th grade Language Arts Correlation to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
 PROJECT LEARNING TREE 4 th grade Language Arts Correlation/TEKS Language Arts Students are expected to: Activity 4.3A summarize and explain the lesson or message of a work of fiction as its theme 18, 89
PROJECT LEARNING TREE 4 th grade Language Arts Correlation/TEKS Language Arts Students are expected to: Activity 4.3A summarize and explain the lesson or message of a work of fiction as its theme 18, 89
Unit: Human Impact Differentiated (Tiered) Task How Does Human Activity Impact Soil Erosion?
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Introduction to Forensics: Preventing Fires in the First Place. A Distance Learning Program Presented by the FASNY Museum of Firefighting
 Introduction to Forensics: A Distance Learning Program Presented by the FASNY Museum of Firefighting Educators Overview Introduction to Forensics This Distance Learning Program is a part of the education
Introduction to Forensics: A Distance Learning Program Presented by the FASNY Museum of Firefighting Educators Overview Introduction to Forensics This Distance Learning Program is a part of the education
How to Read the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS)
 How to Read the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) are distinct from prior science standards in three essential ways. 1) Performance. Prior standards
How to Read the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) are distinct from prior science standards in three essential ways. 1) Performance. Prior standards
FOR TEACHERS ONLY. The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING/PHYSICS
 PS P FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING/PHYSICS Thursday, June 21, 2007 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE
PS P FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING/PHYSICS Thursday, June 21, 2007 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL
 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL PART ONE: SHORT-ANSWER
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL PART ONE: SHORT-ANSWER
This Performance Standards include four major components. They are
 Environmental Physics Standards The Georgia Performance Standards are designed to provide students with the knowledge and skills for proficiency in science. The Project 2061 s Benchmarks for Science Literacy
Environmental Physics Standards The Georgia Performance Standards are designed to provide students with the knowledge and skills for proficiency in science. The Project 2061 s Benchmarks for Science Literacy
All Systems Go! Using a Systems Approach in Elementary Science
 All Systems Go! CAST November Tracey Ramirez Professional Learning Facilitator The Charles A. Dana Center What we do and how we do it The Dana Center collaborates with others locally and nationally to
All Systems Go! CAST November Tracey Ramirez Professional Learning Facilitator The Charles A. Dana Center What we do and how we do it The Dana Center collaborates with others locally and nationally to
5.1 Sound & Light Unit Overview
 5.1 Sound & Light Unit Overview Enduring Understanding: Sound and light are forms of energy that travel and interact with objects in various ways. Essential Question: How is sound energy transmitted, absorbed,
5.1 Sound & Light Unit Overview Enduring Understanding: Sound and light are forms of energy that travel and interact with objects in various ways. Essential Question: How is sound energy transmitted, absorbed,
GUIDE CURRICULUM. Science 10
 Science 10 Arts Education Business Education English Language Arts Entrepreneurship Family Studies Health Education International Baccalaureate Languages Mathematics Personal Development and Career Education
Science 10 Arts Education Business Education English Language Arts Entrepreneurship Family Studies Health Education International Baccalaureate Languages Mathematics Personal Development and Career Education
Abc Of Science 8th Grade
 Abc Of 8th Grade Free PDF ebook Download: Abc Of 8th Grade Download or Read Online ebook abc of science 8th grade in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database In addition, some courses such as 7th grade
Abc Of 8th Grade Free PDF ebook Download: Abc Of 8th Grade Download or Read Online ebook abc of science 8th grade in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database In addition, some courses such as 7th grade
MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm
 MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm Why participate in the Science Fair? Science fair projects give students
MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm Why participate in the Science Fair? Science fair projects give students
Environmental Science Curriculum Guide NMHZHS
 MOUNT VERNON CITY SCHOOL DISTRICT Environmental Science Curriculum Guide NMHZHS THIS HANDBOOK IS FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE CURRICULUM IN MOUNT VERNON. 2015-16 Mount Vernon City
MOUNT VERNON CITY SCHOOL DISTRICT Environmental Science Curriculum Guide NMHZHS THIS HANDBOOK IS FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE CURRICULUM IN MOUNT VERNON. 2015-16 Mount Vernon City
Rendezvous with Comet Halley Next Generation of Science Standards
 Next Generation of Science Standards 5th Grade 6 th Grade 7 th Grade 8 th Grade 5-PS1-3 Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties. MS-PS1-4 Develop a model that
Next Generation of Science Standards 5th Grade 6 th Grade 7 th Grade 8 th Grade 5-PS1-3 Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties. MS-PS1-4 Develop a model that
Teaching NGSS in Elementary School Third Grade
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Teaching NGSS in Elementary School Third Grade Presented by: Ted Willard, Carla Zembal-Saul, Mary Starr, and Kathy Renfrew December 17, 2014 6:30 p.m. ET / 5:30
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Teaching NGSS in Elementary School Third Grade Presented by: Ted Willard, Carla Zembal-Saul, Mary Starr, and Kathy Renfrew December 17, 2014 6:30 p.m. ET / 5:30
Lesson 1 Taking chances with the Sun
 P2 Radiation and life Lesson 1 Taking chances with the Sun consider health benefits as well as risks that sunlight presents introduce two ideas: balancing risks and benefits, reducing risks revisit the
P2 Radiation and life Lesson 1 Taking chances with the Sun consider health benefits as well as risks that sunlight presents introduce two ideas: balancing risks and benefits, reducing risks revisit the
Paper 2. Mathematics test. Calculator allowed. First name. Last name. School KEY STAGE TIER
 259574_P2 5-7_KS3_Ma.qxd 1/4/04 4:14 PM Page 1 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 5 7 2004 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you
259574_P2 5-7_KS3_Ma.qxd 1/4/04 4:14 PM Page 1 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 5 7 2004 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you
Measuring physical factors in the environment
 B2 3.1a Student practical sheet Measuring physical factors in the environment Do environmental conditions affect the distriution of plants? Aim To find out whether environmental conditions affect the distriution
B2 3.1a Student practical sheet Measuring physical factors in the environment Do environmental conditions affect the distriution of plants? Aim To find out whether environmental conditions affect the distriution
Program Alignment Worksheet High School
 Program Alignment Worksheet High School Publisher Name Pearson Program Title Prentice Hall Biology (Miler/Levine) 2010; Event Based Science 2005 Computer Based? Requires Internet? Target Grades 9 12 Steps
Program Alignment Worksheet High School Publisher Name Pearson Program Title Prentice Hall Biology (Miler/Levine) 2010; Event Based Science 2005 Computer Based? Requires Internet? Target Grades 9 12 Steps
Physical Features of Humans
 Grade 1 Science, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Physical Features of Humans Overview Number of instructional days: 11 (1 day = 20 30 minutes) Content to be learned Observe, identify, and record the external features
Grade 1 Science, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Physical Features of Humans Overview Number of instructional days: 11 (1 day = 20 30 minutes) Content to be learned Observe, identify, and record the external features
Friction Stops Motion
 activity Friction Stops Motion BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade Quarter Activity SC.C... The student understands that the motion of an object can be described and measured. SC.H...
activity Friction Stops Motion BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade Quarter Activity SC.C... The student understands that the motion of an object can be described and measured. SC.H...
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SOCIAL STUDIES SYLLABUS FOR BASIC EDUCATION STANDARD III-VI
 THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SOCIAL STUDIES SYLLABUS FOR BASIC EDUCATION STANDARD III-VI THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SOCIAL STUDIES SYLLABUS FOR BASIC EDUCATION STANDARD III-VI THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION SCIENCE AND
PHYSICS 40S - COURSE OUTLINE AND REQUIREMENTS Welcome to Physics 40S for !! Mr. Bryan Doiron
 PHYSICS 40S - COURSE OUTLINE AND REQUIREMENTS Welcome to Physics 40S for 2016-2017!! Mr. Bryan Doiron The course covers the following topics (time permitting): Unit 1 Kinematics: Special Equations, Relative
PHYSICS 40S - COURSE OUTLINE AND REQUIREMENTS Welcome to Physics 40S for 2016-2017!! Mr. Bryan Doiron The course covers the following topics (time permitting): Unit 1 Kinematics: Special Equations, Relative
Statistical Analysis of Climate Change, Renewable Energies, and Sustainability An Independent Investigation for Introduction to Statistics
 5/22/2012 Statistical Analysis of Climate Change, Renewable Energies, and Sustainability An Independent Investigation for Introduction to Statistics College of Menominee Nation & University of Wisconsin
5/22/2012 Statistical Analysis of Climate Change, Renewable Energies, and Sustainability An Independent Investigation for Introduction to Statistics College of Menominee Nation & University of Wisconsin
AGS THE GREAT REVIEW GAME FOR PRE-ALGEBRA (CD) CORRELATED TO CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS
 AGS THE GREAT REVIEW GAME FOR PRE-ALGEBRA (CD) CORRELATED TO CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS 1 CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS: Chapter 1 ALGEBRA AND WHOLE NUMBERS Algebra and Functions 1.4 Students use algebraic
AGS THE GREAT REVIEW GAME FOR PRE-ALGEBRA (CD) CORRELATED TO CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS 1 CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS: Chapter 1 ALGEBRA AND WHOLE NUMBERS Algebra and Functions 1.4 Students use algebraic
Fourth Grade. Reporting Student Progress. Libertyville School District 70. Fourth Grade
 Fourth Grade Libertyville School District 70 Reporting Student Progress Fourth Grade A Message to Parents/Guardians: Libertyville Elementary District 70 teachers of students in kindergarten-5 utilize a
Fourth Grade Libertyville School District 70 Reporting Student Progress Fourth Grade A Message to Parents/Guardians: Libertyville Elementary District 70 teachers of students in kindergarten-5 utilize a
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15
 Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments School Supplies... 17 A Place to Call Home... 21 Paste Up Habitats... 37
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments School Supplies... 17 A Place to Call Home... 21 Paste Up Habitats... 37
The Ontario Curriculum
 The Ontario Curriculum GRADE 1 checklist format compiled by: The Canadian Homeschooler using the current Ontario Curriculum Content Introduction... Page 3 Mathematics... Page 4 Language Arts... Page 9
The Ontario Curriculum GRADE 1 checklist format compiled by: The Canadian Homeschooler using the current Ontario Curriculum Content Introduction... Page 3 Mathematics... Page 4 Language Arts... Page 9
Ocean Exploration: Diving Deep into Ocean Science. Developed by: Sierra Tobiason, Lynn Fujii and Noe Taum
 Ocean Exploration: Diving Deep into Ocean Science Grade Level: Sixth Grade Developed by: Sierra Tobiason, Lynn Fujii and Noe Taum Purpose: This curriculum is designed to communicate: I. Methods scientist
Ocean Exploration: Diving Deep into Ocean Science Grade Level: Sixth Grade Developed by: Sierra Tobiason, Lynn Fujii and Noe Taum Purpose: This curriculum is designed to communicate: I. Methods scientist
Read the passage above. What does Chief Seattle believe about owning land?
 The Great Chief in Washington sends word that he wishes to buy our land. How can you buy or sell the sky the warmth of the land? The idea is strange to us. We do not own the freshness of the air or the
The Great Chief in Washington sends word that he wishes to buy our land. How can you buy or sell the sky the warmth of the land? The idea is strange to us. We do not own the freshness of the air or the
ENVR 205 Engineering Tools for Environmental Problem Solving Spring 2017
 ENVR 205 Engineering Tools for Environmental Problem Solving Spring 2017 Instructor: Dr. Barbara rpin, Professor Environmental Science and Engineering Gillings School of Global Public Health University
ENVR 205 Engineering Tools for Environmental Problem Solving Spring 2017 Instructor: Dr. Barbara rpin, Professor Environmental Science and Engineering Gillings School of Global Public Health University
Study Guide for Right of Way Equipment Operator 1
 Study Guide for Right of Way Equipment Operator 1 Test Number: 2814 Human Resources Talent Planning & Programs Southern California Edison An Edison International Company REV082815 Introduction The 2814
Study Guide for Right of Way Equipment Operator 1 Test Number: 2814 Human Resources Talent Planning & Programs Southern California Edison An Edison International Company REV082815 Introduction The 2814
Igneous Rock Formation
 Igneous Rock Formation *adapted from TOPS Learning Systems 1) Lay down a row of saturated salt water drops along the diameter of an aluminum pie tin. 2) Rest the tin on a jar so a candle fits under the
Igneous Rock Formation *adapted from TOPS Learning Systems 1) Lay down a row of saturated salt water drops along the diameter of an aluminum pie tin. 2) Rest the tin on a jar so a candle fits under the
Scientific Inquiry Test Questions
 Test Questions Free PDF ebook Download: Test Questions Download or Read Online ebook scientific inquiry test questions in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Understandings about scientific inquiry
Test Questions Free PDF ebook Download: Test Questions Download or Read Online ebook scientific inquiry test questions in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Understandings about scientific inquiry
Course outline. Code: ENS281 Title: Introduction to Sustainable Energy Systems
 Course outline Code: ENS281 Title: Introduction to Sustainable Energy Systems Faculty of: Science, Health, Education and Engineering Teaching Session: Semester 1 Year: 2017 Course Coordinator: Dr Damon
Course outline Code: ENS281 Title: Introduction to Sustainable Energy Systems Faculty of: Science, Health, Education and Engineering Teaching Session: Semester 1 Year: 2017 Course Coordinator: Dr Damon
FOR TEACHERS ONLY RATING GUIDE BOOKLET 1 OBJECTIVE AND CONSTRUCTED RESPONSE JUNE 1 2, 2005
 FOR TEACHERS ONLY THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK GRADE 8 INTERMEDIATE-LEVEL TEST SOCIAL STUDIES RATING GUIDE BOOKLET 1 OBJECTIVE AND CONSTRUCTED RESPONSE JUNE 1 2, 2005 Updated information regarding
FOR TEACHERS ONLY THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK GRADE 8 INTERMEDIATE-LEVEL TEST SOCIAL STUDIES RATING GUIDE BOOKLET 1 OBJECTIVE AND CONSTRUCTED RESPONSE JUNE 1 2, 2005 Updated information regarding
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 5: HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS
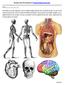 SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 5: HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS NAME: This booklet is an in-class assignment; you must complete all pages during the class work periods provided. You must use full sentences for all sections
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 5: HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS NAME: This booklet is an in-class assignment; you must complete all pages during the class work periods provided. You must use full sentences for all sections
Unit 1: Scientific Investigation-Asking Questions
 Unit 1: Scientific Investigation-Asking Questions Standards: OKC 3 Process Standard 3: Experimental design - Understanding experimental designs requires that students recognize the components of a valid
Unit 1: Scientific Investigation-Asking Questions Standards: OKC 3 Process Standard 3: Experimental design - Understanding experimental designs requires that students recognize the components of a valid
Stakeholder Debate: Wind Energy
 Activity ENGAGE For Educator Stakeholder Debate: Wind Energy How do stakeholder interests determine which specific resources a community will use? For the complete activity with media resources, visit:
Activity ENGAGE For Educator Stakeholder Debate: Wind Energy How do stakeholder interests determine which specific resources a community will use? For the complete activity with media resources, visit:
Evolution in Paradise
 Evolution in Paradise Engaging science lessons for middle and high school brought to you by BirdSleuth K-12 and the most extravagant birds in the world! The Evolution in Paradise lesson series is part
Evolution in Paradise Engaging science lessons for middle and high school brought to you by BirdSleuth K-12 and the most extravagant birds in the world! The Evolution in Paradise lesson series is part
Biome I Can Statements
 Biome I Can Statements I can recognize the meanings of abbreviations. I can use dictionaries, thesauruses, glossaries, textual features (footnotes, sidebars, etc.) and technology to define and pronounce
Biome I Can Statements I can recognize the meanings of abbreviations. I can use dictionaries, thesauruses, glossaries, textual features (footnotes, sidebars, etc.) and technology to define and pronounce
People: Past and Present
 People: Past and Present Field Trip Grade Level: 1 Process Skills: Observation Connections Enduring understanding: There are similarities and differences across cultures. Alignment to Utah Core Curriculum
People: Past and Present Field Trip Grade Level: 1 Process Skills: Observation Connections Enduring understanding: There are similarities and differences across cultures. Alignment to Utah Core Curriculum
Science Fair Project Handbook
 Science Fair Project Handbook IDENTIFY THE TESTABLE QUESTION OR PROBLEM: a) Begin by observing your surroundings, making inferences and asking testable questions. b) Look for problems in your life or surroundings
Science Fair Project Handbook IDENTIFY THE TESTABLE QUESTION OR PROBLEM: a) Begin by observing your surroundings, making inferences and asking testable questions. b) Look for problems in your life or surroundings
Table of Contents. This descriptive guide will assist you in integrating the DVD science and education content into your instructional program.
 Bill Nye the Science Guy Comets & Meteors 1. Implementation Guide........................................ 2 9 This descriptive guide will assist you in integrating the DVD science and education content
Bill Nye the Science Guy Comets & Meteors 1. Implementation Guide........................................ 2 9 This descriptive guide will assist you in integrating the DVD science and education content
Curriculum Design Project with Virtual Manipulatives. Gwenanne Salkind. George Mason University EDCI 856. Dr. Patricia Moyer-Packenham
 Curriculum Design Project with Virtual Manipulatives Gwenanne Salkind George Mason University EDCI 856 Dr. Patricia Moyer-Packenham Spring 2006 Curriculum Design Project with Virtual Manipulatives Table
Curriculum Design Project with Virtual Manipulatives Gwenanne Salkind George Mason University EDCI 856 Dr. Patricia Moyer-Packenham Spring 2006 Curriculum Design Project with Virtual Manipulatives Table
Eggs-periments & Eggs-plorations
 Eggs-periments & Eggs-plorations Dear Educator, The American Egg Board, together with the curriculum experts Young Minds Inspired (YMI), have teamed to bring you this Eggs-periments and Eggsplorations
Eggs-periments & Eggs-plorations Dear Educator, The American Egg Board, together with the curriculum experts Young Minds Inspired (YMI), have teamed to bring you this Eggs-periments and Eggsplorations
Application of Virtual Instruments (VIs) for an enhanced learning environment
 Application of Virtual Instruments (VIs) for an enhanced learning environment Philip Smyth, Dermot Brabazon, Eilish McLoughlin Schools of Mechanical and Physical Sciences Dublin City University Ireland
Application of Virtual Instruments (VIs) for an enhanced learning environment Philip Smyth, Dermot Brabazon, Eilish McLoughlin Schools of Mechanical and Physical Sciences Dublin City University Ireland
If you have problems logging in go to
 Trinity Valley Comm College Chem 1412 Internet Class Fall 2010 Wm Travis Dungan Room A103A, phone number 903 729 0256 ext 251 (Palestine campus) Email address: tdungan@tvcc.edu Getting started: Welcome
Trinity Valley Comm College Chem 1412 Internet Class Fall 2010 Wm Travis Dungan Room A103A, phone number 903 729 0256 ext 251 (Palestine campus) Email address: tdungan@tvcc.edu Getting started: Welcome
Creating Coherent Inquiry Projects to Support Student Cognition and Collaboration in Physics
 Creating Coherent Inquiry Projects to Support Student Cognition and Collaboration in Physics 6 Douglas B. Clark, Arizona State University S. Raj Chaudhury, Christopher Newport University As a physics teacher,
Creating Coherent Inquiry Projects to Support Student Cognition and Collaboration in Physics 6 Douglas B. Clark, Arizona State University S. Raj Chaudhury, Christopher Newport University As a physics teacher,
Kindergarten Foundations of America
 Kindergarten Foundations of America In kindergarten, students begin to understand the foundations of the social studies strands: history, geography, government, and economics. Students begin their introduction
Kindergarten Foundations of America In kindergarten, students begin to understand the foundations of the social studies strands: history, geography, government, and economics. Students begin their introduction
This document has been produced by:
 year 6 This document has been produced by: The All Wales ESDGC Officer Group to support schools introducing the National Literacy and Numeracy Framework through ESDGC activities. With support from: Developing
year 6 This document has been produced by: The All Wales ESDGC Officer Group to support schools introducing the National Literacy and Numeracy Framework through ESDGC activities. With support from: Developing
Grade 3: Module 2B: Unit 3: Lesson 10 Reviewing Conventions and Editing Peers Work
 Grade 3: Module 2B: Unit 3: Lesson 10 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content is indicated by the footer: (name
Grade 3: Module 2B: Unit 3: Lesson 10 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. Exempt third-party content is indicated by the footer: (name
Interpreting Graphs Middle School Science
 Middle School Free PDF ebook Download: Download or Read Online ebook interpreting graphs middle school science in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database. Rain, Rain, Go Away When the student council
Middle School Free PDF ebook Download: Download or Read Online ebook interpreting graphs middle school science in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database. Rain, Rain, Go Away When the student council
4th Grade Science Test Ecosystems
 4th Grade Science Free PDF ebook Download: 4th Grade Science Download or Read Online ebook 4th grade science test ecosystems in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database 4th Grade--LIFE SCIENCE. Unit
4th Grade Science Free PDF ebook Download: 4th Grade Science Download or Read Online ebook 4th grade science test ecosystems in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database 4th Grade--LIFE SCIENCE. Unit
Heredity In Plants For 2nd Grade
 In Plants For 2nd Grade Free PDF ebook Download: In Plants For 2nd Grade Download or Read Online ebook heredity in plants for 2nd grade in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database I Write the letter
In Plants For 2nd Grade Free PDF ebook Download: In Plants For 2nd Grade Download or Read Online ebook heredity in plants for 2nd grade in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database I Write the letter
Characteristics of Functions
 Characteristics of Functions Unit: 01 Lesson: 01 Suggested Duration: 10 days Lesson Synopsis Students will collect and organize data using various representations. They will identify the characteristics
Characteristics of Functions Unit: 01 Lesson: 01 Suggested Duration: 10 days Lesson Synopsis Students will collect and organize data using various representations. They will identify the characteristics
Introducing the New Iowa Assessments Mathematics Levels 12 14
 Introducing the New Iowa Assessments Mathematics Levels 12 14 ITP Assessment Tools Math Interim Assessments: Grades 3 8 Administered online Constructed Response Supplements Reading, Language Arts, Mathematics
Introducing the New Iowa Assessments Mathematics Levels 12 14 ITP Assessment Tools Math Interim Assessments: Grades 3 8 Administered online Constructed Response Supplements Reading, Language Arts, Mathematics
Utilizing Soft System Methodology to Increase Productivity of Shell Fabrication Sushant Sudheer Takekar 1 Dr. D.N. Raut 2
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 2, Issue 04, 2014 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Utilizing Soft System Methodology to Increase Productivity of Shell Fabrication Sushant
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 2, Issue 04, 2014 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Utilizing Soft System Methodology to Increase Productivity of Shell Fabrication Sushant
Introducing the New Iowa Assessments Reading Levels 12 14
 Introducing the New Iowa Assessments Reading Levels 12 14 ITP Assessment Tools Math Interim Assessments: Grades 3 8 Administered online Constructed Response Supplements Reading, Language Arts, Mathematics
Introducing the New Iowa Assessments Reading Levels 12 14 ITP Assessment Tools Math Interim Assessments: Grades 3 8 Administered online Constructed Response Supplements Reading, Language Arts, Mathematics
Julia Smith. Effective Classroom Approaches to.
 Julia Smith @tessmaths Effective Classroom Approaches to GCSE Maths resits julia.smith@writtle.ac.uk Agenda The context of GCSE resit in a post-16 setting An overview of the new GCSE Key features of a
Julia Smith @tessmaths Effective Classroom Approaches to GCSE Maths resits julia.smith@writtle.ac.uk Agenda The context of GCSE resit in a post-16 setting An overview of the new GCSE Key features of a
Teaching Literacy Through Videos
 Teaching Literacy Through Videos Elizabeth Stavis Reading Intervention Specialist RR Teacher Santa Clara Unified Jenny Maehara Elementary Literacy Specialist RR Teacher Santa Clara Unified February 9,
Teaching Literacy Through Videos Elizabeth Stavis Reading Intervention Specialist RR Teacher Santa Clara Unified Jenny Maehara Elementary Literacy Specialist RR Teacher Santa Clara Unified February 9,
Biology and Microbiology
 November 14, 2006 California State University (CSU) Statewide Pattern The Lower-Division Transfer Pattern (LDTP) consists of the CSU statewide pattern of coursework outlined below, plus campus-specific
November 14, 2006 California State University (CSU) Statewide Pattern The Lower-Division Transfer Pattern (LDTP) consists of the CSU statewide pattern of coursework outlined below, plus campus-specific
Math-U-See Correlation with the Common Core State Standards for Mathematical Content for Third Grade
 Math-U-See Correlation with the Common Core State Standards for Mathematical Content for Third Grade The third grade standards primarily address multiplication and division, which are covered in Math-U-See
Math-U-See Correlation with the Common Core State Standards for Mathematical Content for Third Grade The third grade standards primarily address multiplication and division, which are covered in Math-U-See
Designing a case study
 Designing a case study Case studies are problem situations based on real life like situations, the outcome of the case is already known (at least to the lecturer). Cees van Westen International Institute
Designing a case study Case studies are problem situations based on real life like situations, the outcome of the case is already known (at least to the lecturer). Cees van Westen International Institute
First Grade Curriculum Highlights: In alignment with the Common Core Standards
 First Grade Curriculum Highlights: In alignment with the Common Core Standards ENGLISH LANGUAGE ARTS Foundational Skills Print Concepts Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features
First Grade Curriculum Highlights: In alignment with the Common Core Standards ENGLISH LANGUAGE ARTS Foundational Skills Print Concepts Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features
ENERGY WORLD: Electricity aro
 ENERGY WORLD: Electricity aro ound us Lesson Plans October December 2008 UNIT 1. WHAT IS ELEC CTRICITY? TEACHING OBJECTIVES - To identify and classify electrical and non electrical appliances. - To know
ENERGY WORLD: Electricity aro ound us Lesson Plans October December 2008 UNIT 1. WHAT IS ELEC CTRICITY? TEACHING OBJECTIVES - To identify and classify electrical and non electrical appliances. - To know
Food Chain Cut And Paste Activities
 Cut And Paste Activities Free PDF ebook Download: Cut And Paste Activities Download or Read Online ebook food chain cut and paste activities in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database CO #3: Organise
Cut And Paste Activities Free PDF ebook Download: Cut And Paste Activities Download or Read Online ebook food chain cut and paste activities in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database CO #3: Organise
End-of-Module Assessment Task K 2
 Student Name Topic A: Two-Dimensional Flat Shapes Date 1 Date 2 Date 3 Rubric Score: Time Elapsed: Topic A Topic B Materials: (S) Paper cutouts of typical triangles, squares, Topic C rectangles, hexagons,
Student Name Topic A: Two-Dimensional Flat Shapes Date 1 Date 2 Date 3 Rubric Score: Time Elapsed: Topic A Topic B Materials: (S) Paper cutouts of typical triangles, squares, Topic C rectangles, hexagons,
Sugar And Salt Solutions Phet Simulation Packet
 Sugar And Salt Solutions Phet Simulation Packet Free PDF ebook Download: Sugar And Salt Solutions Phet Simulation Packet Download or Read Online ebook sugar and salt solutions phet simulation packet in
Sugar And Salt Solutions Phet Simulation Packet Free PDF ebook Download: Sugar And Salt Solutions Phet Simulation Packet Download or Read Online ebook sugar and salt solutions phet simulation packet in
United states panel on climate change. memorandum
 United states panel on climate change memorandum Welcome to the U.S. Convention on Climate Change. Each of you is a member of a delegation (interest group) at an upcoming meeting to debate and vote on
United states panel on climate change memorandum Welcome to the U.S. Convention on Climate Change. Each of you is a member of a delegation (interest group) at an upcoming meeting to debate and vote on
Adaptations and Survival: The Story of the Peppered Moth
 Adaptations and Survival: The Story of the Peppered Moth Teacher: Rachel Card Subject Areas: Science/ELA Grade Level: Fourth Unit Title: Animal Adaptations Lesson Title: Adaptations and Survival: The Story
Adaptations and Survival: The Story of the Peppered Moth Teacher: Rachel Card Subject Areas: Science/ELA Grade Level: Fourth Unit Title: Animal Adaptations Lesson Title: Adaptations and Survival: The Story
CEE 2050: Introduction to Green Engineering
 Green and sustainable are two of the buzzwords of your generation. These words reflect real and widespread challenges related to water, natural resources, transportation, energy, global health, and population.
Green and sustainable are two of the buzzwords of your generation. These words reflect real and widespread challenges related to water, natural resources, transportation, energy, global health, and population.
Create A City: An Urban Planning Exercise Students learn the process of planning a community, while reinforcing their writing and speaking skills.
 Create A City: An Urban Planning Exercise Students learn the process of planning a community, while reinforcing their writing and speaking skills. Author Gale Ekiss Grade Level 4-8 Duration 3 class periods
Create A City: An Urban Planning Exercise Students learn the process of planning a community, while reinforcing their writing and speaking skills. Author Gale Ekiss Grade Level 4-8 Duration 3 class periods
Our Hazardous Environment
 Geography 1110; Spring 2012 Our Hazardous Environment Instructor: Dr. Weimin Feng Office: Nevins Hall, Room 2067 Office phone: 333-7030 E-mail: wfeng@valdosta.edu Office hours: MWF 2-3 pm, or by appt.
Geography 1110; Spring 2012 Our Hazardous Environment Instructor: Dr. Weimin Feng Office: Nevins Hall, Room 2067 Office phone: 333-7030 E-mail: wfeng@valdosta.edu Office hours: MWF 2-3 pm, or by appt.
Large Kindergarten Centers Icons
 Large Kindergarten Centers Icons To view and print each center icon, with CCSD objectives, please click on the corresponding thumbnail icon below. ABC / Word Study Read the Room Big Book Write the Room
Large Kindergarten Centers Icons To view and print each center icon, with CCSD objectives, please click on the corresponding thumbnail icon below. ABC / Word Study Read the Room Big Book Write the Room
MAR Environmental Problems & Solutions. Stony Brook University School of Marine & Atmospheric Sciences (SoMAS)
 MAR 340-01 Environmental Problems & Solutions Stony Brook University School of Marine & Atmospheric Sciences (SoMAS) This course satisfies the DEC category H This course satisfies the SBC category STAS
MAR 340-01 Environmental Problems & Solutions Stony Brook University School of Marine & Atmospheric Sciences (SoMAS) This course satisfies the DEC category H This course satisfies the SBC category STAS
Teaching a Laboratory Section
 Chapter 3 Teaching a Laboratory Section Page I. Cooperative Problem Solving Labs in Operation 57 II. Grading the Labs 75 III. Overview of Teaching a Lab Session 79 IV. Outline for Teaching a Lab Session
Chapter 3 Teaching a Laboratory Section Page I. Cooperative Problem Solving Labs in Operation 57 II. Grading the Labs 75 III. Overview of Teaching a Lab Session 79 IV. Outline for Teaching a Lab Session
Paper Reference. Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1380 Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Foundation Tier. Monday 6 June 2011 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 1 3 8 0 1 F Paper Reference(s) 1380/1F Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1380 Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Foundation Tier Monday 6 June 2011 Afternoon Time: 1 hour
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 1 3 8 0 1 F Paper Reference(s) 1380/1F Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1380 Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Foundation Tier Monday 6 June 2011 Afternoon Time: 1 hour
Summer Workshops STEM EDUCATION // PK-12
 Summer Workshops STEM EDUCATION // PK-12 Attention K-12 Educators! The Center is excited to be offering the following professional development opportunities to teachers this July and August at The College
Summer Workshops STEM EDUCATION // PK-12 Attention K-12 Educators! The Center is excited to be offering the following professional development opportunities to teachers this July and August at The College
SOCIAL STUDIES GRADE 1. Clear Learning Targets Office of Teaching and Learning Curriculum Division FAMILIES NOW AND LONG AGO, NEAR AND FAR
 SOCIAL STUDIES FAMILIES NOW AND LONG AGO, NEAR AND FAR GRADE 1 Clear Learning Targets 2015-2016 Aligned with Ohio s Learning Standards for Social Studies Office of Teaching and Learning Curriculum Division
SOCIAL STUDIES FAMILIES NOW AND LONG AGO, NEAR AND FAR GRADE 1 Clear Learning Targets 2015-2016 Aligned with Ohio s Learning Standards for Social Studies Office of Teaching and Learning Curriculum Division
1. Listen carefully as your teacher assigns you two or more rows of the Biome Jigsaw Chart (page S2) to fill in.
 Biome Bags - Student Guide In this activity, you will explore ecology and biodiversity will be to work cooperatively to: in seven terrestrial biomes. Your task 1. Research and share information to complete
Biome Bags - Student Guide In this activity, you will explore ecology and biodiversity will be to work cooperatively to: in seven terrestrial biomes. Your task 1. Research and share information to complete
Extending Place Value with Whole Numbers to 1,000,000
 Grade 4 Mathematics, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Extending Place Value with Whole Numbers to 1,000,000 Overview Number of Instructional Days: 10 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to Be Learned Recognize that a digit
Grade 4 Mathematics, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Extending Place Value with Whole Numbers to 1,000,000 Overview Number of Instructional Days: 10 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to Be Learned Recognize that a digit
LOUISIANA HIGH SCHOOL RALLY ASSOCIATION
 LOUISIANA HIGH SCHOOL RALLY ASSOCIATION Literary Events 2014-15 General Information There are 44 literary events in which District and State Rally qualifiers compete. District and State Rally tests are
LOUISIANA HIGH SCHOOL RALLY ASSOCIATION Literary Events 2014-15 General Information There are 44 literary events in which District and State Rally qualifiers compete. District and State Rally tests are
KS1 Transport Objectives
 KS1 Transport Y1: Number and Place Value Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals; count in multiples
KS1 Transport Y1: Number and Place Value Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals; count in multiples
Airplane Rescue: Social Studies. LEGO, the LEGO logo, and WEDO are trademarks of the LEGO Group The LEGO Group.
 Airplane Rescue: Social Studies LEGO, the LEGO logo, and WEDO are trademarks of the LEGO Group. 2010 The LEGO Group. Lesson Overview The students will discuss ways that people use land and their physical
Airplane Rescue: Social Studies LEGO, the LEGO logo, and WEDO are trademarks of the LEGO Group. 2010 The LEGO Group. Lesson Overview The students will discuss ways that people use land and their physical
Montana Content Standards for Mathematics Grade 3. Montana Content Standards for Mathematical Practices and Mathematics Content Adopted November 2011
 Montana Content Standards for Mathematics Grade 3 Montana Content Standards for Mathematical Practices and Mathematics Content Adopted November 2011 Contents Standards for Mathematical Practice: Grade
Montana Content Standards for Mathematics Grade 3 Montana Content Standards for Mathematical Practices and Mathematics Content Adopted November 2011 Contents Standards for Mathematical Practice: Grade
Mathematics subject curriculum
 Mathematics subject curriculum Dette er ei omsetjing av den fastsette læreplanteksten. Læreplanen er fastsett på Nynorsk Established as a Regulation by the Ministry of Education and Research on 24 June
Mathematics subject curriculum Dette er ei omsetjing av den fastsette læreplanteksten. Læreplanen er fastsett på Nynorsk Established as a Regulation by the Ministry of Education and Research on 24 June
This document has been produced by:
 year 9 This document has been produced by: The All Wales ESDGC Officer Group to support schools introducing the National Literacy and Numeracy Framework through ESDGC activities. With support from: Developing
year 9 This document has been produced by: The All Wales ESDGC Officer Group to support schools introducing the National Literacy and Numeracy Framework through ESDGC activities. With support from: Developing
Hardhatting in a Geo-World
 Hardhatting in a Geo-World TM Developed and Published by AIMS Education Foundation This book contains materials developed by the AIMS Education Foundation. AIMS (Activities Integrating Mathematics and
Hardhatting in a Geo-World TM Developed and Published by AIMS Education Foundation This book contains materials developed by the AIMS Education Foundation. AIMS (Activities Integrating Mathematics and
Fifth Grade Science Inquiry Questions
 Fifth Inquiry Free PDF ebook Download: Fifth Inquiry Download or Read Online ebook fifth grade science inquiry questions in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Science. Grade-Level Expectations:
Fifth Inquiry Free PDF ebook Download: Fifth Inquiry Download or Read Online ebook fifth grade science inquiry questions in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Science. Grade-Level Expectations:
Applied Science Double Award GCSE. Students Guide
 Applied Science Double Award GCSE Students Guide WJEC CBAC APPLIED SCIENCE DOUBLE AWARD GCSE STUDENTS GUIDE This booklet has been produced for the use of students following the WJEC GCSE Applied Science
Applied Science Double Award GCSE Students Guide WJEC CBAC APPLIED SCIENCE DOUBLE AWARD GCSE STUDENTS GUIDE This booklet has been produced for the use of students following the WJEC GCSE Applied Science
Electromagnetic Spectrum Webquest Answer Key
 Webquest Answer Key Free PDF ebook Download: Webquest Answer Key Download or Read Online ebook electromagnetic spectrum webquest answer key in PDF Format From Best User Guide Database Section:. & Light
Webquest Answer Key Free PDF ebook Download: Webquest Answer Key Download or Read Online ebook electromagnetic spectrum webquest answer key in PDF Format From Best User Guide Database Section:. & Light
Dublin City Schools Mathematics Graded Course of Study GRADE 4
 I. Content Standard: Number, Number Sense and Operations Standard Students demonstrate number sense, including an understanding of number systems and reasonable estimates using paper and pencil, technology-supported
I. Content Standard: Number, Number Sense and Operations Standard Students demonstrate number sense, including an understanding of number systems and reasonable estimates using paper and pencil, technology-supported
Lego Science Lesson Plans
 Lego Science Free PDF ebook Download: Lego Science Download or Read Online ebook lego science lesson plans in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Early Simple Machines Teacher's Guide (59768).
Lego Science Free PDF ebook Download: Lego Science Download or Read Online ebook lego science lesson plans in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Early Simple Machines Teacher's Guide (59768).
Interactive Whiteboard
 50 Graphic Organizers for the Interactive Whiteboard Whiteboard-ready graphic organizers for reading, writing, math, and more to make learning engaging and interactive by Jennifer Jacobson & Dottie Raymer
50 Graphic Organizers for the Interactive Whiteboard Whiteboard-ready graphic organizers for reading, writing, math, and more to make learning engaging and interactive by Jennifer Jacobson & Dottie Raymer
