Student Workbook SCIENCE PRACTICAL INVESTIGATIONS YEAR AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM EDITION
|
|
|
- Jonah Hodge
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SCIENCE PRACTICAL INVESTIGATIONS AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM EDITION YEAR 8 Name Class 21 PRACTICAL INVESTIGATIONS ASSESSMENT RUBRICS FOR EVERY PRACTICAL Student Workbook
2 Contents Curriculum Overview... 7 Science understanding... 7 Science as a human endeavour... 7 Science inquiry skills... 8 Safety in the Science Laboratory... 9 Equipment Light microscope Bunsen burner Other lab equipment Working Scientifically Variables and investigatable questions Conclusions Graphing Measurement PRACTICALS Science Inquiry Skills Practical 1 - Sweet cuppa Practical 2 - Viscosity Biological Sciences Practical 3 - Introduction to the microscope Practical 4 - Cheek and onion cells Practical 5 - Size matters Practical 6 - Fantastic yeast Practical 7 - Lung capacity Chemical Sciences Practical 8 - What s the matter? Practical 9 - Energy of particles Practical 10 - A diffuse problem Practical 11 - Is that pure? Practical 12 - Let s make a compound Practical 13 - It s quite elemental Practical 14 - Physical or chemical change
3 Earth and Space Sciences Practical 15 - What s that rock? Practical 16 - The crayon rock cycle Practical 17 - Cooling rate and crystal size Physical Sciences Practical 18 - Egg bungee jump Practical 19 - Windchill Practical 20 - Splash! Practical 21 - Which kettle?
4 Curriculum Overview SCIENCE UNDERSTANDING Australian Curriculum Practical Science Understanding Biological sciences Cells are the basic units of living things; they have specialised structures and functions (ACSSU149) Multi cellular organisms contain systems of organs carrying out specialised functions that enable them to survive and reproduce (ACSSU150) Chemical sciences Properties of the different states of matter can be explained in terms of the motion and arrangement of particles (ACSSU151) Differences between elements, compounds and mixtures can be described at a particle level (ACSSU152) Chemical change involves substances reacting to form new substances (ACSSU225) Earth and space science Sedimentary, igneous and metamorphic rocks contain minerals and are formed by processes that occur within Earth over a variety of timescales (ACSSU153) Physical science Energy appears in different forms, including movement (kinetic energy), heat and potential energy, and energy transformations and transfers cause change within systems (ACSSU155) Curriculum Overview SCIENCE AS A HUMAN ENDEAVOUR Australian Curriculum Practical Science as a Human Endeavour Nature and development of science Scientific knowledge has changed peoples understanding of the world and is refined as new evidence becomes available (ACSHE134) Science knowledge can develop through collaboration across the disciplines of science and the contributions of people from a range of cultures (ACSHE226) Use and influence of science Solutions to contemporary issues that are found using science and technology, may impact on other areas of society and may involve ethical considerations (ACSHE135) People use science understanding and skills in their occupations and these have influenced the development of practices in areas of human activity (ACSHE136) 7
5 Curriculum Overview SCIENCE INQUIRY SKILLS Australian Curriculum Practical Science Inquiry Skills Questioning and predicting Identify questions and problems that can be investigated scientifically and make predictions based on scientific knowledge (ACSIS139) Planning and conducting Collaboratively and individually plan and conduct a range of investigation types, including fieldwork and experiments, ensuring safety and ethical guidelines are followed (ACSIS140) Measure and control variables, select equipment appropriate to the task and collect data with accuracy (ACSIS141) Processing and analysing data and information Construct and use a range of representations, including graphs, keys and models to represent and analyse patterns or relationships in data using digital technologies as appropriate (ACSIS144) Summarise data, from students own investigations and secondary sources, and use scientific understanding to identify relationships and draw conclusions based on evidence (ACSIS145) Evaluating Reflect on scientific investigations including evaluating the quality of the data collected, and identifying improvements (ACSIS146) Use scientific knowledge and findings from investigations to evaluate claims based on evidence (ACSIS234) Communicating Communicate ideas, findings and evidence based solutions to problems using scientific language, and representations, using digital technologies as appropriate (ACSIS148) 8
6 Equipment Light Microscope 10
7 Equipment The Bunsen Burner 1. Put the Bunsen burner on a heat proof mat. 2. Connect the gas hose to the gas supply. 3. Use the ring to close the Bunsen burner air hole. 4. Get a match and light it. 5. Turn on the gas. 6. Hold the burning end of the match about 3 cm above the top of the burner barrel to light the gas. 7. Leave the air hole closed for a visible, yellow flame (the safety flame). 8. Open the air hole for a hotter, blue flame. SAFETY When you are not using the Bunsen burner, switch it off or close the air hole so that other people can see the yellow flame. The burner gets hot! Leave it to cool down before picking it up. Always use a heat-resistant mat and wear safety glasses. 11
8 Rebound Height (% of drop height) SASTA Year 8 Practical Workbook 2017 Working Scientifically Graphing While there are several variations of each, the two basic types of graphs that you will use to record and display data in science are column graphs and line graphs. For each type of graph, you must place the independent variable on the horizontal axis and the dependent variable on the vertical axis. The type of graph appropriate for your data depends upon the type of observations and measurements recorded. Column Graphs Column graphs are the most appropriate graphs to use when the independent variable is discrete data. Discrete data are categorical (descriptions) or counted (for example gender, months of the year, brands of soccer ball, the count of people in a room). Test for discrete data: If the intervals between values on the horizontal axis cannot be logically divided then the data is generally discrete; for example you can t have 1.33 people in a room and you don t normally say that the current month is 1.5 Februaries. 90 Bounce performance of a selection of commercial elite soccer balls Nike Baden Adidas Brine King Soccer Ball Brand Line Graphs Line graphs are generally used to plot continuous data (measurements associated with a standard scale or continuum). The lines on scientific graphs are usually drawn either straight or curved. These "smoothed" lines do not have to touch all the data points, but they should at least get close to most of them. They are called lines of best fit. In general, scientific graphs are not drawn in connect-the-dot fashion. 16
9 Rebound Height (cm) SASTA Year 8 Practical Workbook 2017 Working Scientifically Test for continuous data: If the intervals between values on the horizontal axis can be logically divided then the data is generally continuous; for example, you can have 1.33 degrees Celsius measured on a digital thermometer and it is possible to measure 1.5 centimetres on a ruler The effect of inflation pressure on the bounce height of a Nike Soccer Ball dropped from a height of 200cm Inflation Pressure (PSI) The parts of a line graph include: 1. Data pairs: Graphs are made using pairs of numbers. Each pair of numbers represents one data point on a graph. The first number in the pair represents the independent variable and is plotted on the x axis. The second number represents the dependent variable and is plotted on the y axis. 2. Axis labels: The label on the x axis is the name of the independent variable. The label on the y axis is the name of the dependent variable. Be sure to write the units of each variable in parentheses after its label. 3. Scale: The scale is the quantity represented per line on the graph. The scale of the graph depends on the number of lines available on your graph paper or grid and the range of the data. Divide the range by the number of lines. To make the calculated scale easy-to-use, round the value to a whole number. 4. Title: The title on the graph should have a meaning that allows the viewer to instantly know what the graph is about without the viewer having to read any other text. 17
10 Working Scientifically Graph Checklist What makes for a good graph? For a good graph, you should answer "yes" with a tick to every question Have you selected the appropriate graph type for the data you are displaying? Does your graph have a title? Have you placed the independent variable on the x axis and the dependent variable on the y axis? Have you labelled the axes correctly and specified the units of measurement? Does your graph have the proper scale (the appropriate high and low values on the axes)? Is your data plotted correctly and clearly? If your graph is a line graph, have you drawn a line of best fit? 18
11 Science Inquiry Skills Practical 1 Sweet cuppa Background A solute is a substance that is dissolved into another substance. A solvent is a substance into which chemicals are dissolved. When a solute and solvent are mixed together, they form a solution. The solute is dissolved in the solvent. When sugar and instant coffee are dissolved in a cup of hot water the sugar and coffee are the solutes and the hot water is the solvent; together they make a sweet coffee solution. Purpose To investigate the effect of water temperature on the solubility of sugar in water. Note that water will be used instead of coffee because it may be too hard so observe the sugar dissolving in coffee. From the information given in the Purpose and by reading through the Procedure, identify the variables in this investigation and construct a question for investigation. Independent variable (include units of measure) Dependent variable (include units of measure) Question for investigation What happens to (dependent variable) When we change (independent variable) What factors will you control to ensure this is a fair test? (A detailed list of all the factors (things) that you expect to affect how fast the sugar dissolves except for the independent variable) Prediction (This is a statement about what you expect to observe for the dependent variable as the independent variable is changed.) 23
12 Science Inquiry Skills Materials 4 x 250 ml beakers stop watch 4 thermometers matches 100 ml measuring cylinder kettle glass stirring rod 4 sugar cubes room temperature water (approx. 22 C) tongs refrigerated water (approx. 4 C) Bunsen burner, heat proof mat, gauze mat, tripod Procedure (Note that you do not have to do the boiling water first. You can choose to do the water temperature treatments in any order) 1. Set up the heat proof mat, Bunsen burner, tripod and gauze mat ready to heat water. 2. Use the measuring cylinder to transfer 100 ml of tap water into one 250 ml beaker 3. Use the Bunsen burner (on blue flame) to heat the water until it boils. 4. Measure the temperature of the water using the thermometer and record this value in the results table. 5. Use the tongs to drop a cube of sugar into the boiling water and simultaneously start the stop watch. 6. Stir the boiling water with the stirring rod and continue timing until all the sugar from the sugar cube appears to have dissolved. 7. Stop the stop watch and record the time taken for the sugar to dissolve in the results table. 8. Repeat steps 2 7 until you have completed the experiments with all four water temperatures. This means that instead of boiling the water using the Bunsen burner at step 3 you will use the refrigerated water, room temperature water, and hot water (from the kettle). Draw a properly formatted scientific diagram of your Bunsen burner set up to heat the water here: 24
13 Science Inquiry Skills Results Table 1 The effect of raising water temperature on sugar dissolution Water temperature description Refrigerated Room temperature Hot (from kettle) Boiling (Bunsen burner) Measured water temperature ( C) Time taken for sugar cube to completely dissolve (s) Graphing Draw a graph of your data. Make sure that it has an appropriate title and all axes are labelled correctly. The y axis will be used for the factor that is being measured. What type of variable is this? The x axis will be used for the factor that is being changed. What type of variable is this? 25
14 Science Inquiry Skills Conclusion Write a statement that answers your question for investigation. (Claim) (Hint: describe what happens to the time taken for the sugar to dissolve as the temperature of the water increases.) Support your claim with a summary of your evidence. (Evidence) Explain your results using the relevant scientific concepts. (Reasoning) 26
15 Analysing data Processing data Science Inquiry Skills Planning and conducting Questioning and Predicting SASTA Year 8 Practical Workbook 2017 Science Inquiry Skills Assessment Rubric Sweet Cuppa Achievement Standard A B C D E Students identify and construct questions and problems that they can investigate scientifically. Constructs a clear and correctly formatted question that can be investigated scientifically. Makes a justified prediction. Constructs correctly formatted question that can be investigated scientifically. Makes a valid prediction. Constructs a question that can be investigated scientifically. Makes a logical prediction. With guidance, constructs a question that can be investigated scientifically. Makes a simple prediction. Uses question given investigation question. Does not make a prediction or makes an irrelevant or unclear prediction. Students identify variables to be changed, measured and controlled. Accurately identifies the independent and dependent variables, including their units of measure where appropriate. Provides a comprehensive list of factors that need to be controlled to ensure the reliability of data collected. Accurately identifies the independent and dependent variables, including their units of measure where appropriate. Lists a range of factors that need to be controlled to ensure the reliability of data collected. Identifies the independent and dependent variables. Lists several factors that need to be controlled to ensure the reliability of data collected. Identifies, with guidance, the independent and dependent variables. Acknowledges the need for a fair test by listing one factor to be controlled. Lists variables without identifying the independent, dependent and controlled variables. Students construct representations of their data. Accurately organises and records data and observations, giving appropriate detail. Accurately records data and observations. Records data and observations. Records data and observation simply.. Uses provided tables to organise and record data and observations with some inaccuracies. Constructs an appropriate graph with an accurate title incorporating the variables, labels and measurements for the axes, an incremental scale and accurate plotting of data. Constructs an appropriate graph with an accurate title incorporating the variables, labels and measurements for the axes, an incremental scale and plotting of data. Constructs a graph with a title, axes labels and measurements for the axes, an incremental scale and accurate plotting of data. Constructs a simple graph with some inaccuracies and/or key features omitted. Partially constructs a simple graph with many inaccuracies and/or key features omitted. Students use representations to reveal and analyse patterns and trends in data and observations. Critically and logically examines data to identify patterns and trends. Logically examines data to identify patterns and trends. Examines data to identify patterns and trends. Identifies simple patterns in data. Has attempted to identify some trends in the data. Recognises simple patterns in data. Has not independently identified any trends in the data. 27
16 Communicating SASTA Year 8 Practical Workbook 2017 Science Inquiry Skills Assessment Rubric Sweet Cuppa Achievement Standard A B C D E Students use patterns and trend in data and observations when justifying their conclusions. Critically analyses data, making connections with relevant scientific concepts to formulate an accurate conclusion based on evidence. Analyses data, making connections with relevant scientific concepts, to formulate logical conclusions. Analyses data and their connections with scientific concepts, to formulate simple conclusions. Draws a conclusion that does not accurately relate to the data. If provided, the conclusion is unclear and unconnected to the data. Students use appropriate language and representations to communicate science ideas, procedures and findings in a range of text types. Concisely and coherently uses appropriate scientific language and representations to communicate science ideas, methods and findings in a range of text types Coherently uses appropriate scientific language and representations to communicate science ideas, methods and findings in a range of text types Uses appropriate language and representations to communicate science ideas, methods and findings in a range of text types Uses everyday language and representations to communicate simple science ideas, methods and findings Limited use of language and representations. Ineffective communication of ideas and results. 28
17 Biological sciences Practical 6 Fantastic yeast Background Yeast is a micro-organism that breaks down sugars to release energy in order for it to survive and grow. When there is oxygen in their environment (aerobic environment), they break the sugar down into carbon dioxide and water. Unlike us, yeast can survive in an environment without oxygen (anaerobic environment). When sugar is broken down in an anaerobic environment, the products are alcohol (ethanol) and carbon dioxide. Purpose To explore the metabolism of yeast by planning and carrying out an investigation into the effects of temperature on cell activity. The yeast will give off bubbles of carbon dioxide gas as it respires (breaks down the sugar and produces energy). The better the conditions are for respiration, the more gas is produced. This production of gas will be used as a measure of cell activity. Materials These materials will be available to each group as well as a hot water bath and a refrigerator. 3 conical flasks (100 ml) 3 beakers (250 ml) 3 balloons (equal size) rubber bands packet of dried yeast hot tap water 3 teaspoons of glucose spatula electronic balance thermometer stirring rod measuring cylinders (100 and 250 ml From the information given in the Purpose, identify the variables in this investigation and construct a question for investigation. Independent variable Dependent variable Question for investigation What happens to (dependent variable) When we change (independent variable) Controlled factors 52
18 Biological sciences Prediction Procedure Design a procedure that will generate data/observations that will help you answer your question for investigation. Make sure you consider: How you will set up your equipment. What temperatures you will use and how you will measure them. How you will measure the yeast. How you will collect and measure the gas. How long you will leave each flask (must be more than 30 mins). How you will record your results. 53
19 Biological sciences Results Record your results below: Draw a labelled scientific diagram of the 3 conical flasks and their contents after fermentation. Conclusion Write a statement that answers your question for investigation. (Claim) Support your claim with a summary of your evidence. (Evidence) Explain your results using the relevant scientific concepts. (Reasoning) 54
20 Biological sciences Evaluation 1. Explain why the balloon could be used to indicate that fermentation had occurred. 2. Discuss any differences that were noticed in the rate of fermentation of the glucose at different temperatures. 3. The data collected in this experiment was qualitative. Explain what this means and then comment on why quantitative data would be more useful. 4. Devise and describe an experimental system that might allow you to collect quantitative (number) data for this experiment instead (Include a labelled diagram to help you with your description). 55
21 Processing data Science Inquiry Skills Planning and Conducting Questioning and Predicting SASTA Year 8 Practical Workbook 2017 Biological sciences Assessment Rubric Fantastic yeast Achievement Standard A B C D E Students identify and construct questions and problems that they can investigate scientifically. Constructs a clear a correctly formatted (or identifies a) question that can be investigated scientifically. Makes a justified prediction. Constructs a correctly formatted (or identifies a) question that can be investigated scientifically. Makes a valid prediction. Constructs a (or identifies a) question that can be investigated scientifically. Makes a logical prediction. With guidance, constructs (or identifies) a question that can be investigated scientifically. Makes a simple prediction. Uses given investigation question. Does not make a prediction or makes an irrelevant or unclear prediction. Students design field or experimental procedures. Constructs a detailed and logical step-by-step procedure. Gives a diagram where required. The procedure is the most suitable and can be replicated. Constructs a clear and logical step-by-step procedure. Gives a diagram where required. The procedure is appropriate and can be replicated. Constructs a simple stepby-step procedure. Gives a diagram where required. Constructs an incomplete and/or simple procedure with some key steps omitted. If provided, the procedure is disorganised, unclear and/or omits large parts. Students identify variables to be changed, measured and controlled. Accurately identifies the independent and dependent variables, including their units of measure where appropriate. Accurately identifies the independent and dependent variables, including their units of measure where appropriate. Identifies the independent and dependent variables. Identifies, with guidance, the independent and dependent variables. Lists variables without identifying the independent, dependent and controlled variables. Provides a comprehensive list of factors that need to be controlled to ensure the reliability of data collected. Lists a range of factors that need to be controlled to ensure the reliability of data collected. Lists several factors that need to be controlled to ensure the reliability of data collected. Acknowledges the need for a fair test by listing one factor to be controlled. Students construct representations of their data. Accurately organises and records data and observations, giving appropriate detail. Constructs a data table that incorporates the independent and dependent variables and uses appropriate conventions and formats such as column and row headings. Includes the most suitable units. Accurately records data and observations. Constructs a data table that incorporates the independent and dependent variables and uses appropriate conventions and formats such as column and row headings. Includes units. Records data and observations. Constructs a data table that uses appropriate conventions and formats such as column and row headings. Uses provided tables to organise and record data and observations simply. Uses provided tables to organise and record data and observations with some inaccuracies. 56
22 Communicating Evaluating Processes Analysing data SASTA Year 8 Practical Workbook 2017 Biological sciences Assessment Rubric Fantastic yeast Achievement Standard A B C D E Students use representations to reveal and analyse patterns and trends in data and observations. Critically and logically examines data to identify patterns and trends. Logically examines data to identify patterns and trends. Examines data to identify patterns and trends. Identifies simple patterns in data. Has attempted to identify some trends in the data. Recognises simple patterns in data. Has not independently identified any trends in the data. Students use patterns and trend in data and observations when justifying their conclusions. Critically analyses data, making connections with relevant scientific concepts to formulate an accurate conclusion based on evidence. Analyses data, making connections with relevant scientific concepts, to formulate logical conclusions. Analyses data and their connections with scientific concepts, to formulate simple conclusions. Draws a conclusion that does not accurately relate to the data.. If provided, the conclusion is unclear and unconnected to the data. Students explain how modifications to procedures could improve the quality of their data. Reviews the method. Provides relevant, specific suggestions for modifying the procedure. Thoroughly explains how these modifications will improve the quality of the data. Reviews the method. Provides a relevant, specific suggestion for modifying the procedure. Explains how this modification will improve the quality of the data. Reviews the method. Provides a reasonable suggestion for modifying the procedure. Explains how this modification could improve the quality of the data. States that the procedure could be improved, but the suggestion provided is not related to the purpose of the investigation. States that the procedure could be improved. Students use appropriate language and representations to communicate science ideas, procedures and findings in a range of text types. Concisely and coherently uses appropriate scientific language and representations to communicate science ideas, methods and findings in a range of text types Coherently uses appropriate scientific language and representations to communicate science ideas, methods and findings in a range of text types Uses appropriate language and representations to communicate science ideas, methods and findings in a range of text types Uses everyday language and representations to communicate simple science ideas, methods and findings Limited use of language and representations. Ineffective communication of ideas and results. 57
Creating Coherent Inquiry Projects to Support Student Cognition and Collaboration in Physics
 Creating Coherent Inquiry Projects to Support Student Cognition and Collaboration in Physics 6 Douglas B. Clark, Arizona State University S. Raj Chaudhury, Christopher Newport University As a physics teacher,
Creating Coherent Inquiry Projects to Support Student Cognition and Collaboration in Physics 6 Douglas B. Clark, Arizona State University S. Raj Chaudhury, Christopher Newport University As a physics teacher,
INSTRUCTIONAL FOCUS DOCUMENT Grade 5/Science
 Exemplar Lesson 01: Comparing Weather and Climate Exemplar Lesson 02: Sun, Ocean, and the Water Cycle State Resources: Connecting to Unifying Concepts through Earth Science Change Over Time RATIONALE:
Exemplar Lesson 01: Comparing Weather and Climate Exemplar Lesson 02: Sun, Ocean, and the Water Cycle State Resources: Connecting to Unifying Concepts through Earth Science Change Over Time RATIONALE:
Science Fair Project Handbook
 Science Fair Project Handbook IDENTIFY THE TESTABLE QUESTION OR PROBLEM: a) Begin by observing your surroundings, making inferences and asking testable questions. b) Look for problems in your life or surroundings
Science Fair Project Handbook IDENTIFY THE TESTABLE QUESTION OR PROBLEM: a) Begin by observing your surroundings, making inferences and asking testable questions. b) Look for problems in your life or surroundings
Getting Started with TI-Nspire High School Science
 Getting Started with TI-Nspire High School Science 2012 Texas Instruments Incorporated Materials for Institute Participant * *This material is for the personal use of T3 instructors in delivering a T3
Getting Started with TI-Nspire High School Science 2012 Texas Instruments Incorporated Materials for Institute Participant * *This material is for the personal use of T3 instructors in delivering a T3
Grade 2: Using a Number Line to Order and Compare Numbers Place Value Horizontal Content Strand
 Grade 2: Using a Number Line to Order and Compare Numbers Place Value Horizontal Content Strand Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS): (2.1) Number, operation, and quantitative reasoning. The student
Grade 2: Using a Number Line to Order and Compare Numbers Place Value Horizontal Content Strand Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS): (2.1) Number, operation, and quantitative reasoning. The student
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15
 Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments Plants Are Producers... 17 Producing a Producer... 19 The Part Plants Play...
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scientific Inquiry... 11 Assembling Rubber Band Books... 15 Organisms and Environments Plants Are Producers... 17 Producing a Producer... 19 The Part Plants Play...
Properties of materials before and after change
 SCIENCE YEARS 1 TO 10 SOURCEBOOK MODULE SCIENCE MIDDLE PRIMARY Level F 1 2 3 4 5 6 B6 Properties of materials before and after change Strand Natural and Processed Materials Key concept Patterns of interactions
SCIENCE YEARS 1 TO 10 SOURCEBOOK MODULE SCIENCE MIDDLE PRIMARY Level F 1 2 3 4 5 6 B6 Properties of materials before and after change Strand Natural and Processed Materials Key concept Patterns of interactions
2016 Warren STEM Fair. Monday and Tuesday, April 18 th and 19 th, 2016 Real-World STEM
 2016 Warren STEM Fair Monday and Tuesday, April 18 th and 19 th, 2016 Real-World STEM Tonight s Goal We will examine the different parts of the STEM Fair process (Scientific Method) in order for you to
2016 Warren STEM Fair Monday and Tuesday, April 18 th and 19 th, 2016 Real-World STEM Tonight s Goal We will examine the different parts of the STEM Fair process (Scientific Method) in order for you to
Characteristics of Functions
 Characteristics of Functions Unit: 01 Lesson: 01 Suggested Duration: 10 days Lesson Synopsis Students will collect and organize data using various representations. They will identify the characteristics
Characteristics of Functions Unit: 01 Lesson: 01 Suggested Duration: 10 days Lesson Synopsis Students will collect and organize data using various representations. They will identify the characteristics
Quality teaching in NSW public schools:
 Quality teaching in NSW public schools: Continuing the discussion about assessment practice 2nd edn. State of NSW, Department of Education and Training Professional Learning and Leadership Development
Quality teaching in NSW public schools: Continuing the discussion about assessment practice 2nd edn. State of NSW, Department of Education and Training Professional Learning and Leadership Development
Stacks Teacher notes. Activity description. Suitability. Time. AMP resources. Equipment. Key mathematical language. Key processes
 Stacks Teacher notes Activity description (Interactive not shown on this sheet.) Pupils start by exploring the patterns generated by moving counters between two stacks according to a fixed rule, doubling
Stacks Teacher notes Activity description (Interactive not shown on this sheet.) Pupils start by exploring the patterns generated by moving counters between two stacks according to a fixed rule, doubling
Paper 2. Mathematics test. Calculator allowed. First name. Last name. School KEY STAGE TIER
 259574_P2 5-7_KS3_Ma.qxd 1/4/04 4:14 PM Page 1 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 5 7 2004 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you
259574_P2 5-7_KS3_Ma.qxd 1/4/04 4:14 PM Page 1 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 5 7 2004 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you
Mathematics Scoring Guide for Sample Test 2005
 Mathematics Scoring Guide for Sample Test 2005 Grade 4 Contents Strand and Performance Indicator Map with Answer Key...................... 2 Holistic Rubrics.......................................................
Mathematics Scoring Guide for Sample Test 2005 Grade 4 Contents Strand and Performance Indicator Map with Answer Key...................... 2 Holistic Rubrics.......................................................
Office: CLSB 5S 066 (via South Tower elevators)
 Syllabus BI417/517 Mammalian Physiology Course Number: Bi 417 ~ Section 001 / CRN 60431 BI 517 ~ Section 001 / CRN 60455 Course Title: Mammalian Physiology Credits: 4 Term/Year: Spring 2016 Meeting Times:
Syllabus BI417/517 Mammalian Physiology Course Number: Bi 417 ~ Section 001 / CRN 60431 BI 517 ~ Section 001 / CRN 60455 Course Title: Mammalian Physiology Credits: 4 Term/Year: Spring 2016 Meeting Times:
Montana Content Standards for Mathematics Grade 3. Montana Content Standards for Mathematical Practices and Mathematics Content Adopted November 2011
 Montana Content Standards for Mathematics Grade 3 Montana Content Standards for Mathematical Practices and Mathematics Content Adopted November 2011 Contents Standards for Mathematical Practice: Grade
Montana Content Standards for Mathematics Grade 3 Montana Content Standards for Mathematical Practices and Mathematics Content Adopted November 2011 Contents Standards for Mathematical Practice: Grade
Grade 6: Correlated to AGS Basic Math Skills
 Grade 6: Correlated to AGS Basic Math Skills Grade 6: Standard 1 Number Sense Students compare and order positive and negative integers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. They find multiples and
Grade 6: Correlated to AGS Basic Math Skills Grade 6: Standard 1 Number Sense Students compare and order positive and negative integers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. They find multiples and
Scientific Method Investigation of Plant Seed Germination
 Scientific Method Investigation of Plant Seed Germination Learning Objectives Building on the learning objectives from your lab syllabus, you will be expected to: 1. Be able to explain the process of the
Scientific Method Investigation of Plant Seed Germination Learning Objectives Building on the learning objectives from your lab syllabus, you will be expected to: 1. Be able to explain the process of the
LESSON PLANS: AUSTRALIA Year 6: Patterns and Algebra Patterns 50 MINS 10 MINS. Introduction to Lesson. powered by
 Year 6: Patterns and Algebra Patterns 50 MINS Strand: Number and Algebra Substrand: Patterns and Algebra Outcome: Continue and create sequences involving whole numbers, fractions and decimals. Describe
Year 6: Patterns and Algebra Patterns 50 MINS Strand: Number and Algebra Substrand: Patterns and Algebra Outcome: Continue and create sequences involving whole numbers, fractions and decimals. Describe
Math Grade 3 Assessment Anchors and Eligible Content
 Math Grade 3 Assessment Anchors and Eligible Content www.pde.state.pa.us 2007 M3.A Numbers and Operations M3.A.1 Demonstrate an understanding of numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among
Math Grade 3 Assessment Anchors and Eligible Content www.pde.state.pa.us 2007 M3.A Numbers and Operations M3.A.1 Demonstrate an understanding of numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among
Mathematics Success Level E
 T403 [OBJECTIVE] The student will generate two patterns given two rules and identify the relationship between corresponding terms, generate ordered pairs, and graph the ordered pairs on a coordinate plane.
T403 [OBJECTIVE] The student will generate two patterns given two rules and identify the relationship between corresponding terms, generate ordered pairs, and graph the ordered pairs on a coordinate plane.
Unit: Human Impact Differentiated (Tiered) Task How Does Human Activity Impact Soil Erosion?
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Rendezvous with Comet Halley Next Generation of Science Standards
 Next Generation of Science Standards 5th Grade 6 th Grade 7 th Grade 8 th Grade 5-PS1-3 Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties. MS-PS1-4 Develop a model that
Next Generation of Science Standards 5th Grade 6 th Grade 7 th Grade 8 th Grade 5-PS1-3 Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties. MS-PS1-4 Develop a model that
Functional Maths Skills Check E3/L x
 Functional Maths Skills Check E3/L1 Name: Date started: The Four Rules of Number + - x May 2017. Kindly contributed by Nicola Smith, Gloucestershire College. Search for Nicola on skillsworkshop.org Page
Functional Maths Skills Check E3/L1 Name: Date started: The Four Rules of Number + - x May 2017. Kindly contributed by Nicola Smith, Gloucestershire College. Search for Nicola on skillsworkshop.org Page
Contents. Foreword... 5
 Contents Foreword... 5 Chapter 1: Addition Within 0-10 Introduction... 6 Two Groups and a Total... 10 Learn Symbols + and =... 13 Addition Practice... 15 Which is More?... 17 Missing Items... 19 Sums with
Contents Foreword... 5 Chapter 1: Addition Within 0-10 Introduction... 6 Two Groups and a Total... 10 Learn Symbols + and =... 13 Addition Practice... 15 Which is More?... 17 Missing Items... 19 Sums with
MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm
 MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm Why participate in the Science Fair? Science fair projects give students
MADERA SCIENCE FAIR 2013 Grades 4 th 6 th Project due date: Tuesday, April 9, 8:15 am Parent Night: Tuesday, April 16, 6:00 8:00 pm Why participate in the Science Fair? Science fair projects give students
Physical Versus Virtual Manipulatives Mathematics
 Physical Versus Free PDF ebook Download: Physical Versus Download or Read Online ebook physical versus virtual manipulatives mathematics in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Engineering Haptic
Physical Versus Free PDF ebook Download: Physical Versus Download or Read Online ebook physical versus virtual manipulatives mathematics in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Engineering Haptic
Statistical Analysis of Climate Change, Renewable Energies, and Sustainability An Independent Investigation for Introduction to Statistics
 5/22/2012 Statistical Analysis of Climate Change, Renewable Energies, and Sustainability An Independent Investigation for Introduction to Statistics College of Menominee Nation & University of Wisconsin
5/22/2012 Statistical Analysis of Climate Change, Renewable Energies, and Sustainability An Independent Investigation for Introduction to Statistics College of Menominee Nation & University of Wisconsin
EDEXCEL FUNCTIONAL SKILLS PILOT TEACHER S NOTES. Maths Level 2. Chapter 4. Working with measures
 EDEXCEL FUNCTIONAL SKILLS PILOT TEACHER S NOTES Maths Level 2 Chapter 4 Working with measures SECTION G 1 Time 2 Temperature 3 Length 4 Weight 5 Capacity 6 Conversion between metric units 7 Conversion
EDEXCEL FUNCTIONAL SKILLS PILOT TEACHER S NOTES Maths Level 2 Chapter 4 Working with measures SECTION G 1 Time 2 Temperature 3 Length 4 Weight 5 Capacity 6 Conversion between metric units 7 Conversion
Friction Stops Motion
 activity Friction Stops Motion BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade Quarter Activity SC.C... The student understands that the motion of an object can be described and measured. SC.H...
activity Friction Stops Motion BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade Quarter Activity SC.C... The student understands that the motion of an object can be described and measured. SC.H...
Cal s Dinner Card Deals
 Cal s Dinner Card Deals Overview: In this lesson students compare three linear functions in the context of Dinner Card Deals. Students are required to interpret a graph for each Dinner Card Deal to help
Cal s Dinner Card Deals Overview: In this lesson students compare three linear functions in the context of Dinner Card Deals. Students are required to interpret a graph for each Dinner Card Deal to help
GCSE Mathematics B (Linear) Mark Scheme for November Component J567/04: Mathematics Paper 4 (Higher) General Certificate of Secondary Education
 GCSE Mathematics B (Linear) Component J567/04: Mathematics Paper 4 (Higher) General Certificate of Secondary Education Mark Scheme for November 2014 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge
GCSE Mathematics B (Linear) Component J567/04: Mathematics Paper 4 (Higher) General Certificate of Secondary Education Mark Scheme for November 2014 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge
Physics 270: Experimental Physics
 2017 edition Lab Manual Physics 270 3 Physics 270: Experimental Physics Lecture: Lab: Instructor: Office: Email: Tuesdays, 2 3:50 PM Thursdays, 2 4:50 PM Dr. Uttam Manna 313C Moulton Hall umanna@ilstu.edu
2017 edition Lab Manual Physics 270 3 Physics 270: Experimental Physics Lecture: Lab: Instructor: Office: Email: Tuesdays, 2 3:50 PM Thursdays, 2 4:50 PM Dr. Uttam Manna 313C Moulton Hall umanna@ilstu.edu
Primary National Curriculum Alignment for Wales
 Mathletics and the Welsh Curriculum This alignment document lists all Mathletics curriculum activities associated with each Wales course, and demonstrates how these fit within the National Curriculum Programme
Mathletics and the Welsh Curriculum This alignment document lists all Mathletics curriculum activities associated with each Wales course, and demonstrates how these fit within the National Curriculum Programme
AGS THE GREAT REVIEW GAME FOR PRE-ALGEBRA (CD) CORRELATED TO CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS
 AGS THE GREAT REVIEW GAME FOR PRE-ALGEBRA (CD) CORRELATED TO CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS 1 CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS: Chapter 1 ALGEBRA AND WHOLE NUMBERS Algebra and Functions 1.4 Students use algebraic
AGS THE GREAT REVIEW GAME FOR PRE-ALGEBRA (CD) CORRELATED TO CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS 1 CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS: Chapter 1 ALGEBRA AND WHOLE NUMBERS Algebra and Functions 1.4 Students use algebraic
Unit 2. A whole-school approach to numeracy across the curriculum
 Unit 2 A whole-school approach to numeracy across the curriculum 50 Numeracy across the curriculum Unit 2 Crown copyright 2001 Unit 2 A whole-school approach to numeracy across the curriculum Objectives
Unit 2 A whole-school approach to numeracy across the curriculum 50 Numeracy across the curriculum Unit 2 Crown copyright 2001 Unit 2 A whole-school approach to numeracy across the curriculum Objectives
PROJECT LEARNING TREE 4 th grade Language Arts Correlation to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
 PROJECT LEARNING TREE 4 th grade Language Arts Correlation/TEKS Language Arts Students are expected to: Activity 4.3A summarize and explain the lesson or message of a work of fiction as its theme 18, 89
PROJECT LEARNING TREE 4 th grade Language Arts Correlation/TEKS Language Arts Students are expected to: Activity 4.3A summarize and explain the lesson or message of a work of fiction as its theme 18, 89
Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 assessment
 Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 assessment www.cityandguilds.com September 2015 Version 1.0 Marking scheme ONLINE V2 Level 2 Sample Paper 4 Mark Represent Analyse Interpret Open Fixed S1Q1 3 3 0
Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 assessment www.cityandguilds.com September 2015 Version 1.0 Marking scheme ONLINE V2 Level 2 Sample Paper 4 Mark Represent Analyse Interpret Open Fixed S1Q1 3 3 0
Physical Features of Humans
 Grade 1 Science, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Physical Features of Humans Overview Number of instructional days: 11 (1 day = 20 30 minutes) Content to be learned Observe, identify, and record the external features
Grade 1 Science, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Physical Features of Humans Overview Number of instructional days: 11 (1 day = 20 30 minutes) Content to be learned Observe, identify, and record the external features
Name Class Date. Graphing Proportional Relationships
 Name Class Date Practice 5-1 Graphing Proportional Relationships 5-1 Graphing Proportional Relationships 1. An electronics store has a frequent shopper program. The buyer earns 4 points for every movie
Name Class Date Practice 5-1 Graphing Proportional Relationships 5-1 Graphing Proportional Relationships 1. An electronics store has a frequent shopper program. The buyer earns 4 points for every movie
Table of Contents. This descriptive guide will assist you in integrating the DVD science and education content into your instructional program.
 Bill Nye the Science Guy Comets & Meteors 1. Implementation Guide........................................ 2 9 This descriptive guide will assist you in integrating the DVD science and education content
Bill Nye the Science Guy Comets & Meteors 1. Implementation Guide........................................ 2 9 This descriptive guide will assist you in integrating the DVD science and education content
Going to School: Measuring Schooling Behaviors in GloFish
 Name Period Date Going to School: Measuring Schooling Behaviors in GloFish Objective The learner will collect data to determine if schooling behaviors are exhibited in GloFish fluorescent fish. The learner
Name Period Date Going to School: Measuring Schooling Behaviors in GloFish Objective The learner will collect data to determine if schooling behaviors are exhibited in GloFish fluorescent fish. The learner
Answers: Year 4 Textbook 3 Pages 4 10
 Answers: Year 4 Textbook Pages 4 Page 4 1. 729 2. 8947. 6502 4. 2067 5. 480 6. 7521 > 860 7. 85 > 699 8. 9442< 9852 9. 4725 > 4572. 8244 < 9241 11. 026 < 211 12. A number between 20 and 4800 1. A number
Answers: Year 4 Textbook Pages 4 Page 4 1. 729 2. 8947. 6502 4. 2067 5. 480 6. 7521 > 860 7. 85 > 699 8. 9442< 9852 9. 4725 > 4572. 8244 < 9241 11. 026 < 211 12. A number between 20 and 4800 1. A number
Spinners at the School Carnival (Unequal Sections)
 Spinners at the School Carnival (Unequal Sections) Maryann E. Huey Drake University maryann.huey@drake.edu Published: February 2012 Overview of the Lesson Students are asked to predict the outcomes of
Spinners at the School Carnival (Unequal Sections) Maryann E. Huey Drake University maryann.huey@drake.edu Published: February 2012 Overview of the Lesson Students are asked to predict the outcomes of
Maryland Science Voluntary State Curriculum Grades K-6
 A Correlation of 2006 to the Maryland Science Voluntary State Curriculum Grades K-6 O/S-60 Introduction This document demonstrates how Scott Foresman Science meets the Maryland Science Voluntary State
A Correlation of 2006 to the Maryland Science Voluntary State Curriculum Grades K-6 O/S-60 Introduction This document demonstrates how Scott Foresman Science meets the Maryland Science Voluntary State
Lab 1 - The Scientific Method
 Lab 1 - The Scientific Method As Biologists we are interested in learning more about life. Through observations of the living world we often develop questions about various phenomena occurring around us.
Lab 1 - The Scientific Method As Biologists we are interested in learning more about life. Through observations of the living world we often develop questions about various phenomena occurring around us.
SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE
 FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York Le REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION LIVING ENVIRONMENT Wednesday, June 19, 2002 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Directions
FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York Le REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION LIVING ENVIRONMENT Wednesday, June 19, 2002 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Directions
Extending Place Value with Whole Numbers to 1,000,000
 Grade 4 Mathematics, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Extending Place Value with Whole Numbers to 1,000,000 Overview Number of Instructional Days: 10 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to Be Learned Recognize that a digit
Grade 4 Mathematics, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1 Extending Place Value with Whole Numbers to 1,000,000 Overview Number of Instructional Days: 10 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to Be Learned Recognize that a digit
Teaching a Laboratory Section
 Chapter 3 Teaching a Laboratory Section Page I. Cooperative Problem Solving Labs in Operation 57 II. Grading the Labs 75 III. Overview of Teaching a Lab Session 79 IV. Outline for Teaching a Lab Session
Chapter 3 Teaching a Laboratory Section Page I. Cooperative Problem Solving Labs in Operation 57 II. Grading the Labs 75 III. Overview of Teaching a Lab Session 79 IV. Outline for Teaching a Lab Session
Environmental Science: Earth s Resources (National 3) level 3 (6 SCQF credit points)
 Environmental Science: Earth s Resources (National 3) SCQF: level 3 (6 SCQF credit points) Unit code: H24R 73 Unit outline The general aim of this Unit is to develop skills of scientific inquiry, investigation
Environmental Science: Earth s Resources (National 3) SCQF: level 3 (6 SCQF credit points) Unit code: H24R 73 Unit outline The general aim of this Unit is to develop skills of scientific inquiry, investigation
For information only, correct responses are listed in the chart below. Question Number. Correct Response
 THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK 4GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST JUNE 207 WRITTEN TEST FOR TEACHERS ONLY SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Note: All schools (public, nonpublic, and charter) administering
THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK 4GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST JUNE 207 WRITTEN TEST FOR TEACHERS ONLY SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE Note: All schools (public, nonpublic, and charter) administering
Teachers Guide Chair Study
 Certificate of Initial Mastery Task Booklet 2006-2007 School Year Teachers Guide Chair Study Dance Modified On-Demand Task Revised 4-19-07 Central Falls Johnston Middletown West Warwick Coventry Lincoln
Certificate of Initial Mastery Task Booklet 2006-2007 School Year Teachers Guide Chair Study Dance Modified On-Demand Task Revised 4-19-07 Central Falls Johnston Middletown West Warwick Coventry Lincoln
This scope and sequence assumes 160 days for instruction, divided among 15 units.
 In previous grades, students learned strategies for multiplication and division, developed understanding of structure of the place value system, and applied understanding of fractions to addition and subtraction
In previous grades, students learned strategies for multiplication and division, developed understanding of structure of the place value system, and applied understanding of fractions to addition and subtraction
PROJECT MARS A curriculum-linked project based learning unit for Year 9 using The Mars Lab. Version 2.04
 PROJECT www.themarslab.org MARS A curriculum-linked project based learning unit for Year 9 using The Mars Lab. Version 2.04 Project Based Learning: Creating a compelling reason to need to know science
PROJECT www.themarslab.org MARS A curriculum-linked project based learning unit for Year 9 using The Mars Lab. Version 2.04 Project Based Learning: Creating a compelling reason to need to know science
Probability and Statistics Curriculum Pacing Guide
 Unit 1 Terms PS.SPMJ.3 PS.SPMJ.5 Plan and conduct a survey to answer a statistical question. Recognize how the plan addresses sampling technique, randomization, measurement of experimental error and methods
Unit 1 Terms PS.SPMJ.3 PS.SPMJ.5 Plan and conduct a survey to answer a statistical question. Recognize how the plan addresses sampling technique, randomization, measurement of experimental error and methods
TRAFFORD CHILDREN S THERAPY SERVICE. Motor Skills Checklist and Advice for Children in PRIMARY & SECONDARY Schools. Child s Name.Dob. Age.
 TRAFFORD CHILDREN S THERAPY SERVICE Motor Skills Checklist and Advice for Children in PRIMARY & SECONDARY Schools Child s Name.Dob. Age. Class / year.. School... Tel Date screening checklist completed:.
TRAFFORD CHILDREN S THERAPY SERVICE Motor Skills Checklist and Advice for Children in PRIMARY & SECONDARY Schools Child s Name.Dob. Age. Class / year.. School... Tel Date screening checklist completed:.
Algebra 1, Quarter 3, Unit 3.1. Line of Best Fit. Overview
 Algebra 1, Quarter 3, Unit 3.1 Line of Best Fit Overview Number of instructional days 6 (1 day assessment) (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Analyze scatter plots and construct the line of best
Algebra 1, Quarter 3, Unit 3.1 Line of Best Fit Overview Number of instructional days 6 (1 day assessment) (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Analyze scatter plots and construct the line of best
OVERVIEW OF CURRICULUM-BASED MEASUREMENT AS A GENERAL OUTCOME MEASURE
 OVERVIEW OF CURRICULUM-BASED MEASUREMENT AS A GENERAL OUTCOME MEASURE Mark R. Shinn, Ph.D. Michelle M. Shinn, Ph.D. Formative Evaluation to Inform Teaching Summative Assessment: Culmination measure. Mastery
OVERVIEW OF CURRICULUM-BASED MEASUREMENT AS A GENERAL OUTCOME MEASURE Mark R. Shinn, Ph.D. Michelle M. Shinn, Ph.D. Formative Evaluation to Inform Teaching Summative Assessment: Culmination measure. Mastery
Common Core State Standards
 Common Core State Standards Common Core State Standards 7.NS.3 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. Mathematical Practices 1, 3, and 4 are aspects
Common Core State Standards Common Core State Standards 7.NS.3 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. Mathematical Practices 1, 3, and 4 are aspects
Numeracy Medium term plan: Summer Term Level 2C/2B Year 2 Level 2A/3C
 Numeracy Medium term plan: Summer Term Level 2C/2B Year 2 Level 2A/3C Using and applying mathematics objectives (Problem solving, Communicating and Reasoning) Select the maths to use in some classroom
Numeracy Medium term plan: Summer Term Level 2C/2B Year 2 Level 2A/3C Using and applying mathematics objectives (Problem solving, Communicating and Reasoning) Select the maths to use in some classroom
Paper Reference. Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1380 Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Foundation Tier. Monday 6 June 2011 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 1 3 8 0 1 F Paper Reference(s) 1380/1F Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1380 Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Foundation Tier Monday 6 June 2011 Afternoon Time: 1 hour
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 1 3 8 0 1 F Paper Reference(s) 1380/1F Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1380 Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Foundation Tier Monday 6 June 2011 Afternoon Time: 1 hour
FOR TEACHERS ONLY. The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING/PHYSICS
 PS P FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING/PHYSICS Thursday, June 21, 2007 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE
PS P FOR TEACHERS ONLY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING/PHYSICS Thursday, June 21, 2007 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING GUIDE
Interpreting Graphs Middle School Science
 Middle School Free PDF ebook Download: Download or Read Online ebook interpreting graphs middle school science in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database. Rain, Rain, Go Away When the student council
Middle School Free PDF ebook Download: Download or Read Online ebook interpreting graphs middle school science in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database. Rain, Rain, Go Away When the student council
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL
 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL PART ONE: SHORT-ANSWER
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL LEAVING CERTIFICATE 2008 MARKING SCHEME GEOGRAPHY HIGHER LEVEL PART ONE: SHORT-ANSWER
Math-U-See Correlation with the Common Core State Standards for Mathematical Content for Third Grade
 Math-U-See Correlation with the Common Core State Standards for Mathematical Content for Third Grade The third grade standards primarily address multiplication and division, which are covered in Math-U-See
Math-U-See Correlation with the Common Core State Standards for Mathematical Content for Third Grade The third grade standards primarily address multiplication and division, which are covered in Math-U-See
Dublin City Schools Mathematics Graded Course of Study GRADE 4
 I. Content Standard: Number, Number Sense and Operations Standard Students demonstrate number sense, including an understanding of number systems and reasonable estimates using paper and pencil, technology-supported
I. Content Standard: Number, Number Sense and Operations Standard Students demonstrate number sense, including an understanding of number systems and reasonable estimates using paper and pencil, technology-supported
This document has been produced by:
 year 9 This document has been produced by: The All Wales ESDGC Officer Group to support schools introducing the National Literacy and Numeracy Framework through ESDGC activities. With support from: Developing
year 9 This document has been produced by: The All Wales ESDGC Officer Group to support schools introducing the National Literacy and Numeracy Framework through ESDGC activities. With support from: Developing
Mathematics Success Grade 7
 T894 Mathematics Success Grade 7 [OBJECTIVE] The student will find probabilities of compound events using organized lists, tables, tree diagrams, and simulations. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] Simple probability,
T894 Mathematics Success Grade 7 [OBJECTIVE] The student will find probabilities of compound events using organized lists, tables, tree diagrams, and simulations. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] Simple probability,
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 5: HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS
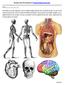 SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 5: HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS NAME: This booklet is an in-class assignment; you must complete all pages during the class work periods provided. You must use full sentences for all sections
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 5: HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS NAME: This booklet is an in-class assignment; you must complete all pages during the class work periods provided. You must use full sentences for all sections
BIOL 2421 Microbiology Course Syllabus:
 BIOL 2421 Microbiology Course Syllabus: Northeast Texas Community College exists to provide responsible, exemplary learning opportunities. Dr. Brenda Deming Office: Math/Science Building, Office I Phone:
BIOL 2421 Microbiology Course Syllabus: Northeast Texas Community College exists to provide responsible, exemplary learning opportunities. Dr. Brenda Deming Office: Math/Science Building, Office I Phone:
What the National Curriculum requires in reading at Y5 and Y6
 What the National Curriculum requires in reading at Y5 and Y6 Word reading apply their growing knowledge of root words, prefixes and suffixes (morphology and etymology), as listed in Appendix 1 of the
What the National Curriculum requires in reading at Y5 and Y6 Word reading apply their growing knowledge of root words, prefixes and suffixes (morphology and etymology), as listed in Appendix 1 of the
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 2 Test Remediation Work Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Provide an appropriate response. 1) High temperatures in a certain
Ch 2 Test Remediation Work Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Provide an appropriate response. 1) High temperatures in a certain
Applied Science Double Award GCSE. Students Guide
 Applied Science Double Award GCSE Students Guide WJEC CBAC APPLIED SCIENCE DOUBLE AWARD GCSE STUDENTS GUIDE This booklet has been produced for the use of students following the WJEC GCSE Applied Science
Applied Science Double Award GCSE Students Guide WJEC CBAC APPLIED SCIENCE DOUBLE AWARD GCSE STUDENTS GUIDE This booklet has been produced for the use of students following the WJEC GCSE Applied Science
Student s Edition. Grade 6 Unit 6. Statistics. Eureka Math. Eureka Math
 Student s Edition Grade 6 Unit 6 Statistics Eureka Math Eureka Math Lesson 1 Lesson 1: Posing Statistical Questions Statistics is about using data to answer questions. In this module, the following four
Student s Edition Grade 6 Unit 6 Statistics Eureka Math Eureka Math Lesson 1 Lesson 1: Posing Statistical Questions Statistics is about using data to answer questions. In this module, the following four
MASTER S THESIS GUIDE MASTER S PROGRAMME IN COMMUNICATION SCIENCE
 MASTER S THESIS GUIDE MASTER S PROGRAMME IN COMMUNICATION SCIENCE University of Amsterdam Graduate School of Communication Kloveniersburgwal 48 1012 CX Amsterdam The Netherlands E-mail address: scripties-cw-fmg@uva.nl
MASTER S THESIS GUIDE MASTER S PROGRAMME IN COMMUNICATION SCIENCE University of Amsterdam Graduate School of Communication Kloveniersburgwal 48 1012 CX Amsterdam The Netherlands E-mail address: scripties-cw-fmg@uva.nl
5.1 Sound & Light Unit Overview
 5.1 Sound & Light Unit Overview Enduring Understanding: Sound and light are forms of energy that travel and interact with objects in various ways. Essential Question: How is sound energy transmitted, absorbed,
5.1 Sound & Light Unit Overview Enduring Understanding: Sound and light are forms of energy that travel and interact with objects in various ways. Essential Question: How is sound energy transmitted, absorbed,
Mathematics process categories
 Mathematics process categories All of the UK curricula define multiple categories of mathematical proficiency that require students to be able to use and apply mathematics, beyond simple recall of facts
Mathematics process categories All of the UK curricula define multiple categories of mathematical proficiency that require students to be able to use and apply mathematics, beyond simple recall of facts
Fourth Grade. Reporting Student Progress. Libertyville School District 70. Fourth Grade
 Fourth Grade Libertyville School District 70 Reporting Student Progress Fourth Grade A Message to Parents/Guardians: Libertyville Elementary District 70 teachers of students in kindergarten-5 utilize a
Fourth Grade Libertyville School District 70 Reporting Student Progress Fourth Grade A Message to Parents/Guardians: Libertyville Elementary District 70 teachers of students in kindergarten-5 utilize a
Curriculum Design Project with Virtual Manipulatives. Gwenanne Salkind. George Mason University EDCI 856. Dr. Patricia Moyer-Packenham
 Curriculum Design Project with Virtual Manipulatives Gwenanne Salkind George Mason University EDCI 856 Dr. Patricia Moyer-Packenham Spring 2006 Curriculum Design Project with Virtual Manipulatives Table
Curriculum Design Project with Virtual Manipulatives Gwenanne Salkind George Mason University EDCI 856 Dr. Patricia Moyer-Packenham Spring 2006 Curriculum Design Project with Virtual Manipulatives Table
Statewide Framework Document for:
 Statewide Framework Document for: 270301 Standards may be added to this document prior to submission, but may not be removed from the framework to meet state credit equivalency requirements. Performance
Statewide Framework Document for: 270301 Standards may be added to this document prior to submission, but may not be removed from the framework to meet state credit equivalency requirements. Performance
AP Statistics Summer Assignment 17-18
 AP Statistics Summer Assignment 17-18 Welcome to AP Statistics. This course will be unlike any other math class you have ever taken before! Before taking this course you will need to be competent in basic
AP Statistics Summer Assignment 17-18 Welcome to AP Statistics. This course will be unlike any other math class you have ever taken before! Before taking this course you will need to be competent in basic
Lesson M4. page 1 of 2
 Lesson M4 page 1 of 2 Miniature Gulf Coast Project Math TEKS Objectives 111.22 6b.1 (A) apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace; 6b.1 (C) select tools, including
Lesson M4 page 1 of 2 Miniature Gulf Coast Project Math TEKS Objectives 111.22 6b.1 (A) apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace; 6b.1 (C) select tools, including
Facing our Fears: Reading and Writing about Characters in Literary Text
 Facing our Fears: Reading and Writing about Characters in Literary Text by Barbara Goggans Students in 6th grade have been reading and analyzing characters in short stories such as "The Ravine," by Graham
Facing our Fears: Reading and Writing about Characters in Literary Text by Barbara Goggans Students in 6th grade have been reading and analyzing characters in short stories such as "The Ravine," by Graham
The Ontario Curriculum
 The Ontario Curriculum GRADE 1 checklist format compiled by: The Canadian Homeschooler using the current Ontario Curriculum Content Introduction... Page 3 Mathematics... Page 4 Language Arts... Page 9
The Ontario Curriculum GRADE 1 checklist format compiled by: The Canadian Homeschooler using the current Ontario Curriculum Content Introduction... Page 3 Mathematics... Page 4 Language Arts... Page 9
EQuIP Review Feedback
 EQuIP Review Feedback Lesson/Unit Name: On the Rainy River and The Red Convertible (Module 4, Unit 1) Content Area: English language arts Grade Level: 11 Dimension I Alignment to the Depth of the CCSS
EQuIP Review Feedback Lesson/Unit Name: On the Rainy River and The Red Convertible (Module 4, Unit 1) Content Area: English language arts Grade Level: 11 Dimension I Alignment to the Depth of the CCSS
Pre-AP Geometry Course Syllabus Page 1
 Pre-AP Geometry Course Syllabus 2015-2016 Welcome to my Pre-AP Geometry class. I hope you find this course to be a positive experience and I am certain that you will learn a great deal during the next
Pre-AP Geometry Course Syllabus 2015-2016 Welcome to my Pre-AP Geometry class. I hope you find this course to be a positive experience and I am certain that you will learn a great deal during the next
Sight Word Assessment
 Make, Take & Teach Sight Word Assessment Assessment and Progress Monitoring for the Dolch 220 Sight Words What are sight words? Sight words are words that are used frequently in reading and writing. Because
Make, Take & Teach Sight Word Assessment Assessment and Progress Monitoring for the Dolch 220 Sight Words What are sight words? Sight words are words that are used frequently in reading and writing. Because
Edexcel GCSE. Statistics 1389 Paper 1H. June Mark Scheme. Statistics Edexcel GCSE
 Edexcel GCSE Statistics 1389 Paper 1H June 2007 Mark Scheme Edexcel GCSE Statistics 1389 NOTES ON MARKING PRINCIPLES 1 Types of mark M marks: method marks A marks: accuracy marks B marks: unconditional
Edexcel GCSE Statistics 1389 Paper 1H June 2007 Mark Scheme Edexcel GCSE Statistics 1389 NOTES ON MARKING PRINCIPLES 1 Types of mark M marks: method marks A marks: accuracy marks B marks: unconditional
Lesson 1 Taking chances with the Sun
 P2 Radiation and life Lesson 1 Taking chances with the Sun consider health benefits as well as risks that sunlight presents introduce two ideas: balancing risks and benefits, reducing risks revisit the
P2 Radiation and life Lesson 1 Taking chances with the Sun consider health benefits as well as risks that sunlight presents introduce two ideas: balancing risks and benefits, reducing risks revisit the
TEACHING Simple Tools Set II
 TEACHING GUIDE TEACHING Simple Tools Set II Kindergarten Reading Level ISBN-10: 0-8225-6880-2 Green ISBN-13: 978-0-8225-6880-3 2 TEACHING SIMPLE TOOLS SET II Standards Science Mathematics Language Arts
TEACHING GUIDE TEACHING Simple Tools Set II Kindergarten Reading Level ISBN-10: 0-8225-6880-2 Green ISBN-13: 978-0-8225-6880-3 2 TEACHING SIMPLE TOOLS SET II Standards Science Mathematics Language Arts
Assessment Requirements: November 2017 Grade 5
 1 Assessment Requirements: November 2017 Grade 5 Your son starts his exams on 15 November 2017 Please ensure that he has the following at school EVERY DAY during the assessment week: A complete pencil
1 Assessment Requirements: November 2017 Grade 5 Your son starts his exams on 15 November 2017 Please ensure that he has the following at school EVERY DAY during the assessment week: A complete pencil
Grade 3 Science Life Unit (3.L.2)
 Grade 3 Science Life Unit (3.L.2) Decision 1: What will students learn in this unit? Standards Addressed: Science 3.L.2 Understand how plants survive in their environments. Ask and answer questions to
Grade 3 Science Life Unit (3.L.2) Decision 1: What will students learn in this unit? Standards Addressed: Science 3.L.2 Understand how plants survive in their environments. Ask and answer questions to
Includes Activities for all ages CHALLENGE LEVEL 1. Explore STEM with
 Take Our Daughters And Sons To Work Foundation Activity Guide Includes Activities for all ages CHALLENGE LEVEL 1 Explore STEM with WARNING: These STEM activities have been known to cause extreme excitement.
Take Our Daughters And Sons To Work Foundation Activity Guide Includes Activities for all ages CHALLENGE LEVEL 1 Explore STEM with WARNING: These STEM activities have been known to cause extreme excitement.
CHEM 1105: SURVEY OF GENERAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY COURSE INFORMATION
 CHEM 1105: SURVEY OF GENERAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY Fall 2017 Course: Chemistry 1105 laboratory sections meet: Lab Section 01: Tuesday 6:00 pm 8:50 pm; STC 310 Lab Section 02: Wednesday 6:00 pm 8:50 pm;
CHEM 1105: SURVEY OF GENERAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY Fall 2017 Course: Chemistry 1105 laboratory sections meet: Lab Section 01: Tuesday 6:00 pm 8:50 pm; STC 310 Lab Section 02: Wednesday 6:00 pm 8:50 pm;
Evaluating Statements About Probability
 CONCEPT DEVELOPMENT Mathematics Assessment Project CLASSROOM CHALLENGES A Formative Assessment Lesson Evaluating Statements About Probability Mathematics Assessment Resource Service University of Nottingham
CONCEPT DEVELOPMENT Mathematics Assessment Project CLASSROOM CHALLENGES A Formative Assessment Lesson Evaluating Statements About Probability Mathematics Assessment Resource Service University of Nottingham
KS1 Transport Objectives
 KS1 Transport Y1: Number and Place Value Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals; count in multiples
KS1 Transport Y1: Number and Place Value Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals; count in multiples
All Systems Go! Using a Systems Approach in Elementary Science
 All Systems Go! CAST November Tracey Ramirez Professional Learning Facilitator The Charles A. Dana Center What we do and how we do it The Dana Center collaborates with others locally and nationally to
All Systems Go! CAST November Tracey Ramirez Professional Learning Facilitator The Charles A. Dana Center What we do and how we do it The Dana Center collaborates with others locally and nationally to
PRIMARY ASSESSMENT GRIDS FOR STAFFORDSHIRE MATHEMATICS GRIDS. Inspiring Futures
 PRIMARY ASSESSMENT GRIDS FOR STAFFORDSHIRE MATHEMATICS GRIDS Inspiring Futures ASSESSMENT WITHOUT LEVELS The Entrust Mathematics Assessment Without Levels documentation has been developed by a group of
PRIMARY ASSESSMENT GRIDS FOR STAFFORDSHIRE MATHEMATICS GRIDS Inspiring Futures ASSESSMENT WITHOUT LEVELS The Entrust Mathematics Assessment Without Levels documentation has been developed by a group of
GUIDE CURRICULUM. Science 10
 Science 10 Arts Education Business Education English Language Arts Entrepreneurship Family Studies Health Education International Baccalaureate Languages Mathematics Personal Development and Career Education
Science 10 Arts Education Business Education English Language Arts Entrepreneurship Family Studies Health Education International Baccalaureate Languages Mathematics Personal Development and Career Education
NC Global-Ready Schools
 NC Global-Ready Schools Implementation Rubric August 2017 North Carolina Department of Public Instruction Global-Ready Schools Designation NC Global-Ready School Implementation Rubric K-12 Global competency
NC Global-Ready Schools Implementation Rubric August 2017 North Carolina Department of Public Instruction Global-Ready Schools Designation NC Global-Ready School Implementation Rubric K-12 Global competency
Blank Table Of Contents Template Interactive Notebook
 Blank Template Free PDF ebook Download: Blank Template Download or Read Online ebook blank table of contents template interactive notebook in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Table of Contents
Blank Template Free PDF ebook Download: Blank Template Download or Read Online ebook blank table of contents template interactive notebook in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Table of Contents
