Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety the international treaty governing movements of living modified organisms Module 3: Public Education on Biosafety
|
|
|
- Lisa Townsend
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety the international treaty governing movements of living modified organisms Module 3: Public Education on Biosafety Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity
2 Introduction Welcome to the Module on Public Education on Biosafety. This module was developed within the context of Article 23 of the Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety to the Convention on Biological Diversity, which deals with public awareness, education and participation, including access to information, concerning the safe transfer, handling and use of living modified organisms (LMOs). It highlights emerging experiences, good practices and lessons learned by Parties to the Cartagena Protocol. Article 23 of the Cartagena Protocol, requires Parties to promote and facilitate public awareness, education and participation concerning the safe transfer, handling and use of LMOs. Article 22 of the Cartagena Protocol, based on the needs of developing country Parties, in particular the least developed and small island developing States, also indicated that cooperation in capacity-building shall, subject to the different situation, capabilities and requirements of each Party, include scientific and technical training in the proper and safe management of biotechnology, and in the use of risk assessment and risk management for biosafety, and the enhancement of technological and institutional capacities in biosafety. In 2010, the governing body of the Cartagena Protocol the Conference of the Parties serving as the meeting of the Parties to the Cartagena Protocol adopted a programme of work on public awareness, education and participation concerning the safe transfer, handling and use of LMOs for the period Under element 2 of the programme of work, Parties are invited to promote education concerning the safe transfer, handling and use of LMOs through formal academic institutions. This module is designed to contribute to developing the capacity of Parties to implement the public education requirements under Article 23 and 22 of the Cartagena Protocol as well as programme element 2 of the programme of work on public awareness, education and participation. In 2016, the governing body to the Cartagena Protocol extended the programme of work until 2020 and adopted priority activities/areas of the programme of work. Many priority activities note the importance of training and education to further implement Article 23. The module will introduce you to, among other things: the basic concepts of public education; characteristics of education; roles of public authorities and other stakeholders in public education; administrative mechanisms and procedures to integrate biosafety; teaching methods and learning theories; resource guide to academic institutions and training strategy to other educators; and the education strategy to be implemented by government. It will also provide links to relevant academic institutions and case studies as well as provide you with interactive exercises, scenarios and quizzes to allow you to test your knowledge of the content presented. The module is primarily intended for government officials but can also be used in particular by academic institutions and other educators involved in implementing the Cartagena Protocol at the national level, particularly those responsible for managing or promoting public education and training initiatives regarding LMOs. It will be developed in collaboration with the United Nations Environment. It complements other e-learning resources on the Cartagena Protocol, including the "Introductory e-course to the Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety" developed by UN Environment in collaboration with the Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity, and the e-learning modules on public access to biosafety information and public participation regarding LMOs. The module is suitable for beginners and intermediate level practitioners. On average, it will take your approximately 3 hours to complete the entire module. Exercise: Worksheet Expectations The Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety:
3 The module is divided into the following lessons and topics: Structure Topic 1: Key Public Education Elements Lesson 1: The concept of public education Lesson 3: The importance of public education Lesson 4: The context of public education Topic 2: Procedures and practices of public education Lesson 1: Roles and Responsibilities of Relevant Authorities Lesson 2: Administrative procedures and mechanisms for public education Lesson 3: Learning theories and Teaching methods Lesson 4: Good public education practices and lessons learned Topic 3: Planning for Public Education Lesson 1: Key components, steps and monitoring of a resource guide and training strategy Lesson 2: Key components, steps and monitoring of education strategy for governments
4 Introduction In Topic 1, Key Public Education Elements, you will be introduced to concepts, characteristics, the importance and context of public education. Learning Objectives At the end of the topic you should be able to: Describe public education concepts based on relevant international instruments and agreements Describe the characteristics of public education Discuss the importance of public education, including for biosafety issues Discuss the context for public education, including external factors and internal factors Structure This topic consists of the following lessons: Lesson 1: The concept of public education Lesson 3: The importance of public education Lesson 4: The context of public education
5 Lesson 1: The concept of public education This lesson covers the concept, including the general and specific definitions, based on legal instruments and other agreements in public education. The concepts provide a basis for rationale and mechanisms to promote public education of biosafety issues, including a reference to mainstreaming biosafety into other areas. Meaning of public education The concept of public education refers to government education that is entirely or partly funded and overseen. National education systems vary in each country. However, all educational systems promote learning between two or more persons or medium of persons.
6 Lesson 1: The concept of public education General Instruments and Agreements The right to education is a fundamental human right enshrined in Article 26 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, Articles 13 and 14 of the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights and other international agreements and is a component of the broader right to freedom of expression and the right to know. In this regard, in most countries, it is compulsory for the public to participate in the national education system to a certain level. This may not include higher education, however, the Declaration notes that higher education shall be made equally accessible to all, on the basis of capacity, by every appropriate means, and, in particular, by the progressive introduction of free education". Aside from the level of education, governments regulate the national education system in terms of the resources, content and structure based on national legal frameworks. Most countries have national frameworks and other agreements on public education drawn on the principles and provisions of relevant international and/or regional conventions and agreements. These instruments promote and develop the right of every person to enjoy access to education and a number of other standards. The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) sets in place international legal obligations for the right to education. As a result, there are many regional educational agreements. Based on regional and international commitments, most governments then develop and implement specific legal frameworks and other standards. Some of the key international conventions and agreements from UNESCO on public education include: Incheon Declaration and Framework for Action for the implementation of Sustainable Development Goal 4, to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all. It promotes effective learning environments and sustainable development. Recommendation on the Recognition of Studies and Qualifications in Higher Education, which, on a national level, promotes, among other things, efforts to encourage the competent authorities concerned to give recognition to certificates of secondary education and other diplomas necessary for access to higher education, qualifications in higher education, defining procedures for the recognition of partial studies carried out in higher education institutions, preparation at the higher education level for the practice of a profession. It also promotes countries to evaluate a qualification obtained abroad for the purpose of further studies, alleviation of the difficulties encountered by those returning home after having studied abroad and wishing to pursue their studies or practice a profession. Convention on Technical and Vocational Education, which involves all forms and levels of the educational process, including the study of technologies and related sciences and the acquisition of practical skills, know-how, attitudes and understanding relating to occupations in the various sectors of economic and social life. In 2015, the Recommendation concerning Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET), which aims to, among other things, empower individuals and promote employment, decent work and lifelong learning and environmental sustainability. Recommendation on the Development of Adult Education, which aims to contribute to, among other things, developing a critical understanding of major contemporary problems and social changes and the ability to play an active part in the progress of society with a view to achieving social justice. In 2015, an additional agreement was adopted, the Recommendation on Adult Learning and Education, which aims at, among other things, develop the capacity of individuals to think critically and to act with autonomy and a sense of responsibility, reinforce the capacity to deal with and shape the developments taking place in the economy and the world of work, contribute to the creation of a learning society where every individual has an opportunity to learn and fully participate in sustainable development processes and to enhance solidarity among people and communities and enhance awareness for the protection of the environment. Convention against Discrimination in Education, which aims to limit discrimination in education such as based on gender or language. UNESCO s Incheon Declaration and Framework:
7 Lesson 1: The concept of public education Sustainable development and environmental education instruments and agreements In general, environmental education involves learning how the environment functions and the public s relation to ecosystems in order to live sustainably. It is a multi-disciplinary field integrating many topics, such as biology, chemistry, ecology and earth science. The aim is to address the gap in the public s understanding of how to relate to the environment, including participating in resolving environmental challenges. As a result, governments have some experience in developing concepts and other environmental education information for educational institutions. At the same time, educational institutions have some experience in incorporating environmental education having receiving incentives to promote environmental education. In the field of environment and sustainable development, the most relevant international instruments and other agreements include the following: Chapter 36 of Agenda 21, which calls for reorienting education to address sustainable development. International Environmental Education Programme (IEEP) of UNESCO/UNEP, which, among other things, provides every person with opportunities to acquire the knowledge, values, attitudes, commitments and skills needed to protect and improve the environment. The key is that it promotes the linking of educational institutions and specialists in a network. Article 12 of the Convention on Biological Diversity, which requires Parties to the Convention to establish and maintain programmes for scientific and technical education. Article 13 requires Parties to the Convention to promote and encourage understanding of the importance of, and the measures required for, the conservation of biodiversity, as well as its propagation through media, and the inclusion of these topics in educational programmes. Article 23 of the Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety, which requires Parties to the Protocol to promote and facilitate public awareness, education and participation concerning the safe transfer, handling and use of living modified organisms in relation to the conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity, taking also into account risks to human health. In doing so, the Parties shall cooperate, as appropriate, with other States and international bodies. It also requires Parties to endeavor to ensure that public awareness and education encompass access to information on LMOs. In addition, Article 22 of the Protocol, based on the needs of developing country Parties, in particular the least developed and small island developing States, also indicate that cooperation in capacity-building shall, subject to the different situation, capabilities and requirements of each Party, include scientific and technical training in the proper and safe management of biotechnology, and in the use of risk assessment and risk management for biosafety, and the enhancement of technological and institutional capacities in biosafety. Exercise : Questions based on text from the international agreements and reflection of public education of biosafety needs in your country/situation pubiceducation.doc Resources: The Universal Declaration of Human Rights, Agenda 21 (
8 This lesson covers the characteristics of public education, including formal and informal education. It is important to understand these features to take note of the best methods to focus on at each level of education. Regarding biosafety, some countries have experience in offering postgraduate level courses and ad hoc informal training activities. However, in general, there are programmes and ongoing initiatives in informal and formal public education. Formal education Based on legal frameworks and programmes, governments set up mechanisms and procedures for formal education to be facilitated by educational institutions. Formal education differs between countries regarding the structure and content. However, formal education primarily includes schools, colleges and universities, such as at the secondary and higher educational level. Governments recognize qualifications from these academic institutions as formal degrees, diplomas and other certificates. Exercise: education.docx
9 Secondary public education Secondary public education is basic education that governments provide and oversee. This is usually compulsory at adolescence to prepare the public for higher education or to enter the work force. Secondary education mainly includes high schools, gymnasiums, lyceums and middle schools. To be qualified, governments provide accreditation (e.g. certifying educators, content and certificates) and set other standards on the characteristics. A few characteristics to consider for secondary education Educational materials: If topics are not part of the curricula, educational materials could be made available through other means (e.g. libraries, bulletin boards, guidelines, extra-curricula activities, seminars, lectures) Courses and Programmes: Specialized topics are taught as part of courses or a course within a programme such as biosafety taught in a biology course or biosafety taught as part of an environmental degree. The level of integration depends on the national educational system. In general, secondary education teaches theoretical concepts across a broad range of topics and educators usually do not have the opportunity to undergo a pedagogical training to have an in-depth knowledge of all topics. Whole-school approach: Some secondary education has a whole-school approach teaching an overarching topic in all programmes. For example, some educational institutions promote sustainable development/environment education in every programme or course. In this regard, the educational institution has developed certain values (e.g. practices and principles) that support sustainable development or the environment. Partnerships with communities and civil society: Certain secondary educational institutions promote partnerships with communities and civil society. In this regard, partners promote and influence the topics available in educational institutions.
10 Tertiary public education Tertiary (higher) level public education is graduate and post-graduate level education that governments provide and oversee. This is usually non-compulsory for adults to enter the work force. The higher education could include universities, colleges, and technical schools. Governments qualify the education through attainments or level of completion (e.g. accredited certificates, diplomas, or academic degrees) and other characteristics. A few characteristics to consider for higher education Exchange programmes for individuals: Exchange programmes are initiatives for individuals to take courses and programmes in an educational institution that is a partner institution to where the participant is enrolled. The aim is to incorporate understanding of and/or skills gained from different topics into further studies or careers in the same area. The exchange time could be on a short or long term basis on a national or international level. Educational institutions make an agreement with each other (e.g. through a memorandum of understanding), for a national or international programme. The educational institutions are selected by governments decisions on the qualifications (e.g. standards to apply or the grades), duration and other characteristics of education. Good practices: Capacity can be built through financial contributions from developed countries to sponsor participants from developing countries Participants can receive scholarships, loans, fellowships or rewards Foundations dedicated to exchange programmes and other initiatives may assist in the process to sponsor fellowships Courses are offered in a more flexible manner such as during the summer, intensive courses and/or online Expertise, based on skills acquired, can be transferred to other developing countries and economies in transition
11 Joint educational initiatives: Joint educational initiatives in higher education programmes or courses can be funded by developed countries for developing countries to enhance research and capacity Financial, human and technical resources may be shared The initiatives promote transfer of technology and support for capacity-building in developing countries and countries with economies in transition More stakeholders can and are interested in participating (e.g. government officials, civil society, businesses/industries, unions, non-governmental organizations and/or associations) as education could be taken as a continuing education course The quality of related programmes or courses can be enhanced Participants could be provided with an entire or partial degree programme recognized internationally under a certain topic (e.g. bridge program) Government funding may increase as part of improving the country s international relations Scholarships or fellowships are frequently provided Networks of experts can be created with ongoing sharing of information, including research, peer-reviews and advice Increased monitoring and evaluation of content and structure of information as more experts are involved Established academic institutions on a sub-regional, regional and international level and strengthened technical capacities Consultative meetings can be organized regularly, including for donors, to discuss and update curricula, programmes and quality assurance A standard for comparing attainment and performance of scholars could be utilized (e.g. European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System)
12 Courses or Topics Integrated into Course: Courses or topics integrated into courses taught in higher education are part of an entire programme or other degree-related attainment. The courses or topics integrated into courses may be integrated by educational institutions in a more flexible manner. For biosafety, these may be included in degrees in biodiversity, sustainable development, biology, biotechnology, legal aspects and science. However, governments approve the integration and other characteristics of the education. Good practices Educational materials are usually standardized to be used in many fields Initiatives for integrating topics in to courses result in enhanced public understanding of the importance of the specific topic and partnerships with key stakeholders (e.g. decision-makers and educators) The courses or topics integrated into courses are designed and planned for specific programmes (e.g. law, environment, health). Educational institutions offering related courses or topics integrated into courses (e.g. biodiversity, sustainable development, science) are more open to integrating courses or topics integrated into courses Participants learn the interlinkages between biosafety and other fields Participants bring the knowledge and understanding into other areas/topics
13 Stand-alone Programmes: Stand-alone programmes offer an entire degree on one topic. Educational institutions may decide and/or propose the sub-topics under the programme. These could include a Bachelor s, Master s or PhD level programme. Based on this, the national government qualifies the programmes through degrees or diplomas and other characteristics of the educational programme. Good practice Funding is secured and the sustainability of the education is long-term Standards on quality control and assessment can easily be set in place Governments can enhance planning and support for job opportunities related to the topic of the programme As the duration is longer, the programme is able to provide educational materials in a more impartial manner, such as considering pros and cons in science and technology Educational materials in different sub-topics can be developed and taught to more stakeholders A balanced curriculum including many sub-topics (e.g. biosafety law, socio-economic considerations) can be taught, enhancing the understanding and skills of participants in many fields A mechanism is usually set up to facilitate continued communication, coordination and networking among scholars. For example, an alumni network can be established among participants to improve understanding, promote employment and other support There could be permanent resource persons to assist in education and training The long duration provides room for flexible teaching methods and use of more learning theories An internship programme could be better facilitated with collaboration between governments, business, civil society, farmers and other stakeholders Similar programmes are easier to set up in other national and local universities and other educational institutions Credentials of educators (e.g. professors) can be set in place More background information and preparations for researchers and other scholars can be provided on a regular-basis The long-term duration may enhance political will to further support education Link to academic-accredited programmes and courses:
14 Informal education As a response to promoting education to reach more stakeholders, governments set up procedures or temporary plans for informal education. Informal education differs vastly in countries. However, informal education tends to be initiatives involving participants who have not undergone formal education on certain topics. These could include workshops/conferences or seminars on a national and/or local level (e.g. community centers, in government and in other places). In addition, informal education usually involves vocational and other training activities. In general, governments recognize such initiatives as non-accredited education or training that may lead to a qualification. A few characteristics to consider for informal education: Vocational and practical training promotes work-based learning, including continuous training and professional development Educational centers, associations, training institutes and other civil society carry out educational activities to support government More stakeholders that are not part of the educational system are trained (e.g. policy-makers, risk assessors, customs officers, consumer groups, NGOs, biosafety staff, technicians, researchers, media) There are limited prerequisites for the education (e.g. requirement to have a past science degree) Independent decision can be taken as the Ministry of Education and other decision-makers related to education may be less involved in deciding on the qualifications and other requirements Enhance direct collaboration between local government and communities Innovative forms of informal education may reduce the funding to promote public education (e.g. promoting educational groups, networks/discussion groups, online tools, community education) The education and training uses teaching methods that are more practical than theoretical (e.g. apprenticeships and inviting the public to visit fields and/or labs) Opportunities to join initiatives with organizations and institutions on regional and international levels Exercise: education.docx Resource: Capacity-building database at
15 Lesson 3: The importance of public education This lesson highlights the importance of public education. It is also the rationale and purpose of promoting public education. In general, public education can lead to: Increased public understanding of relevant issues Acceptance and trust of final decisions in government Increased employment in specific fields. Education is important to national economies, both as an industry in its own right, and as a source of trained and educated personnel for the rest of the economy. A public with higher education tend to have a lower unemployment rate. In this regard, the cost is also less on training for the employer as staff members have better skills. Increased understanding of the importance of adopting and implementing national, regional and international instruments and agreements Opportunities for women and local communities (e.g. indigenous peoples) to learn about relevant issues Effective public participation through informed public inputs on relevant issues Reduced funding needed for training at the workplace Education is a prerequisite for further information sharing Specific to biosafety, public education can lead to: Nonpartisan and impartial education and training to understand issues related to biosafety Impartial analysis and research in biotechnology (e.g. development of biotechnology in a safe manner) Enhanced understanding of biosafety by stakeholders in related fields Increased collaboration and support of biosafety issues at the international, regional and national levels Fostered South-South and North-South cooperation on biosafety issues Long-term and comprehensive education and training Improved research, studies and/or capacity to conduct risk assessments of LMOs and/or laboratory detection of LMOs Enhanced implementation of the National Biosafety Frameworks (NBFs), legal frameworks and biosafety policies and guidelines Opportunity to increase the understanding of benefits and concerns of new developments such as synthetic biology Strengthened human resource capacities, including biosafety experts (e.g. researchers) in government, academic institutions, civil society and among women, indigenous peoples and local communities and other stakeholders to assist in implementing the Protocol Improved access to training materials on biosafety Sustainable source of funding for other capacity-building projects Improved laboratory equipment and facilities for biosafety field research and training Improved funding from regional and international sources of biosafety education and training
16 Lesson 4: Context of Public Education The effectiveness of promoting public education regarding LMOs is often influenced by social, cultural, economic, technological, and political factors and circumstances. Thus, governments need to carefully identify and consider the different contexts when promoting public education. Among other things, they need to analyze the external and internal factors. External factors: The historical context of the development and planning of public education The existing national and local government education agencies, including the structures, the legislative or other frameworks such as educational legal frameworks, institutions and international commitments The decision-making process, including roles and responsibilities and allocation of budget decisions, of the national educational system. This includes a system of decentralized or centralized decisions. The national education systems, such as structures, contents in curricula, practices, as well as the roles and responsibilities of various stakeholders The existing social, cultural, economic, technological and political factors that may affect public education (e.g. number of languages, the majority of the public s age group, illiteracy level, urbanization level, gender equality, number of indigenous and local communities, technological availability) Educational requirements (e.g. content, teaching methods, structure, class size, school facilities, composition of textbooks, level of gender equality, special programmes of marginalized groups) Financial support for education (e.g. level of funded public education, educator-preparation programmes, workshops, vocational training, extra-curricula activity, using new technologies) Level of environment and sustainable development integrated in public education A system of making available research in science and technology Civil society, associations and other stakeholders on a national, regional and international level offering education or training on biosafety
17 Lesson 4: Context of Public Education Internal factors: Established educational programmes, courses or other training activities on biosafety The skills, competencies and experiences of staff to develop and/or integrate public education in biosafety (e.g. technological skills, developing educational materials) Allocated funding for educational projects for biosafety Biosafety integrated and harmonized into biodiversity, environment and sustainable development education, including the related frameworks and mechanisms Existing relation with stakeholders to adopt and implement legal frameworks on biosafety related to education Biosafety educational mechanism and procedure in place (e.g. advisory boards on biosafety education and relations with academia) Efforts in training-of-trainers and other similar activities The availability of human resources to promote public education Existing joint national, regional and international educational initiatives in biosafety Number of biosafety experts Existing public awareness and education initiatives to various stakeholders (e.g. women, indigenous peoples and local communities, and customs officials, ministries, media and researchers) Number of educational materials on biosafety, including their translation into local languages Collaboration on professional exchange programmes and fellowships on biosafety National and sub-national (local) libraries with biosafety materials and educational events on biosafety Collaboration with sub-regional, regional and/or international networks on education and training in biosafety or general education networks
2 di 7 29/06/
 2 di 7 29/06/2011 9.09 Preamble The General Conference of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, meeting at Paris from 17 October 1989 to 16 November 1989 at its twenty-fifth
2 di 7 29/06/2011 9.09 Preamble The General Conference of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, meeting at Paris from 17 October 1989 to 16 November 1989 at its twenty-fifth
VOCATIONAL QUALIFICATION IN YOUTH AND LEISURE INSTRUCTION 2009
 Requirements for Vocational Qualifications VOCATIONAL QUALIFICATION IN YOUTH AND LEISURE INSTRUCTION 2009 Regulation 17/011/2009 Publications 2013:4 Publications 2013:4 Requirements for Vocational Qualifications
Requirements for Vocational Qualifications VOCATIONAL QUALIFICATION IN YOUTH AND LEISURE INSTRUCTION 2009 Regulation 17/011/2009 Publications 2013:4 Publications 2013:4 Requirements for Vocational Qualifications
The Isett Seta Career Guide 2010
 The Isett Seta Career Guide 2010 Our Vision: The Isett Seta seeks to develop South Africa into an ICT knowledge-based society by encouraging more people to develop skills in this sector as a means of contributing
The Isett Seta Career Guide 2010 Our Vision: The Isett Seta seeks to develop South Africa into an ICT knowledge-based society by encouraging more people to develop skills in this sector as a means of contributing
Note: Principal version Modification Amendment Modification Amendment Modification Complete version from 1 October 2014
 Note: The following curriculum is a consolidated version. It is legally non-binding and for informational purposes only. The legally binding versions are found in the University of Innsbruck Bulletins
Note: The following curriculum is a consolidated version. It is legally non-binding and for informational purposes only. The legally binding versions are found in the University of Innsbruck Bulletins
Assessment and national report of Poland on the existing training provisions of professionals in the Healthcare Waste Management industry REPORT: III
 Assessment and national report of Poland on the existing training provisions of professionals in the Healthcare Waste Management industry REPORT: III DEVELOPING AN EU STANDARDISED APPROACH TO VOCATIONAL
Assessment and national report of Poland on the existing training provisions of professionals in the Healthcare Waste Management industry REPORT: III DEVELOPING AN EU STANDARDISED APPROACH TO VOCATIONAL
Referencing the Danish Qualifications Framework for Lifelong Learning to the European Qualifications Framework
 Referencing the Danish Qualifications for Lifelong Learning to the European Qualifications Referencing the Danish Qualifications for Lifelong Learning to the European Qualifications 2011 Referencing the
Referencing the Danish Qualifications for Lifelong Learning to the European Qualifications Referencing the Danish Qualifications for Lifelong Learning to the European Qualifications 2011 Referencing the
Regional Bureau for Education in Africa (BREDA)
 United Nations Education, Scientific and Cultural Organization Regional Bureau for Education in Africa (BREDA) Regional Conference on Higher Education in Africa (CRESA) 10-13 November 2008 Preparatory
United Nations Education, Scientific and Cultural Organization Regional Bureau for Education in Africa (BREDA) Regional Conference on Higher Education in Africa (CRESA) 10-13 November 2008 Preparatory
European Higher Education in a Global Setting. A Strategy for the External Dimension of the Bologna Process. 1. Introduction
 European Higher Education in a Global Setting. A Strategy for the External Dimension of the Bologna Process. 1. Introduction The Bologna Declaration (1999) sets out the objective of increasing the international
European Higher Education in a Global Setting. A Strategy for the External Dimension of the Bologna Process. 1. Introduction The Bologna Declaration (1999) sets out the objective of increasing the international
Programme Specification. BSc (Hons) RURAL LAND MANAGEMENT
 Programme Specification BSc (Hons) RURAL LAND MANAGEMENT D GUIDE SEPTEMBER 2016 ROYAL AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY, CIRENCESTER PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION BSc (Hons) RURAL LAND MANAGEMENT NB The information contained
Programme Specification BSc (Hons) RURAL LAND MANAGEMENT D GUIDE SEPTEMBER 2016 ROYAL AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY, CIRENCESTER PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION BSc (Hons) RURAL LAND MANAGEMENT NB The information contained
FACULTY OF PSYCHOLOGY
 FACULTY OF PSYCHOLOGY STRATEGY 2016 2022 // UNIVERSITY OF BERGEN STRATEGY 2016 2022 FACULTY OF PSYCHOLOGY 3 STRATEGY 2016 2022 (Adopted by the Faculty Board on 15 June 2016) The Faculty of Psychology has
FACULTY OF PSYCHOLOGY STRATEGY 2016 2022 // UNIVERSITY OF BERGEN STRATEGY 2016 2022 FACULTY OF PSYCHOLOGY 3 STRATEGY 2016 2022 (Adopted by the Faculty Board on 15 June 2016) The Faculty of Psychology has
World Data on Education Données mondiales de l éducation Datos Mundiales de Educación. VII Ed. 2010/11 IBE/2011/CP/WDE/AI
 World Data on Education Données mondiales de l éducation Datos Mundiales de Educación VII Ed. 2010/11 IBE/2011/CP/WDE/AI Armenia Updated version, August 2011. Principles and general objectives of education
World Data on Education Données mondiales de l éducation Datos Mundiales de Educación VII Ed. 2010/11 IBE/2011/CP/WDE/AI Armenia Updated version, August 2011. Principles and general objectives of education
HARPER ADAMS UNIVERSITY Programme Specification
 HARPER ADAMS UNIVERSITY Programme Specification 1 Awarding Institution: Harper Adams University 2 Teaching Institution: Askham Bryan College 3 Course Accredited by: Not Applicable 4 Final Award and Level:
HARPER ADAMS UNIVERSITY Programme Specification 1 Awarding Institution: Harper Adams University 2 Teaching Institution: Askham Bryan College 3 Course Accredited by: Not Applicable 4 Final Award and Level:
Education in Armenia. Mher Melik-Baxshian I. INTRODUCTION
 Education in Armenia Mher Melik-Baxshian I. INTRODUCTION Education has always received priority in Armenia a country that has a history of literacy going back 1,600 years. From the very beginning the school
Education in Armenia Mher Melik-Baxshian I. INTRODUCTION Education has always received priority in Armenia a country that has a history of literacy going back 1,600 years. From the very beginning the school
Programme Specification. MSc in International Real Estate
 Programme Specification MSc in International Real Estate IRE GUIDE OCTOBER 2014 ROYAL AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY, CIRENCESTER PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION MSc International Real Estate NB The information contained
Programme Specification MSc in International Real Estate IRE GUIDE OCTOBER 2014 ROYAL AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY, CIRENCESTER PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION MSc International Real Estate NB The information contained
LAW ON HIGH SCHOOL. C o n t e n t s
 LAW ON HIGH SCHOOL C o n t e n t s I BASIC PROVISIONS... 101 The Scope (Article 1)... 101 Aims (Article 2)... 101 Types of High Schools (Article 3)... 101 The Duration of Education (Article 4)... 101 The
LAW ON HIGH SCHOOL C o n t e n t s I BASIC PROVISIONS... 101 The Scope (Article 1)... 101 Aims (Article 2)... 101 Types of High Schools (Article 3)... 101 The Duration of Education (Article 4)... 101 The
CONSULTATION ON THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE COMPETENCY STANDARD FOR LICENSED IMMIGRATION ADVISERS
 CONSULTATION ON THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE COMPETENCY STANDARD FOR LICENSED IMMIGRATION ADVISERS Introduction Background 1. The Immigration Advisers Licensing Act 2007 (the Act) requires anyone giving advice
CONSULTATION ON THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE COMPETENCY STANDARD FOR LICENSED IMMIGRATION ADVISERS Introduction Background 1. The Immigration Advisers Licensing Act 2007 (the Act) requires anyone giving advice
A European inventory on validation of non-formal and informal learning
 A European inventory on validation of non-formal and informal learning Finland By Anne-Mari Nevala (ECOTEC Research and Consulting) ECOTEC Research & Consulting Limited Priestley House 12-26 Albert Street
A European inventory on validation of non-formal and informal learning Finland By Anne-Mari Nevala (ECOTEC Research and Consulting) ECOTEC Research & Consulting Limited Priestley House 12-26 Albert Street
INSTRUCTION MANUAL. Survey of Formal Education
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Survey of Formal Education Montreal, January 2016 1 CONTENT Page Introduction... 4 Section 1. Coverage of the survey... 5 A. Formal initial education... 6 B. Formal adult education...
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Survey of Formal Education Montreal, January 2016 1 CONTENT Page Introduction... 4 Section 1. Coverage of the survey... 5 A. Formal initial education... 6 B. Formal adult education...
Dakar Framework for Action. Education for All: Meeting our Collective Commitments. World Education Forum Dakar, Senegal, April 2000
 Dakar Framework for Action Education for All: Meeting our Collective Commitments Text adopted by the World Education Forum Dakar, Senegal, 26-28 April 2000 Dakar Framework for Action Education for All:
Dakar Framework for Action Education for All: Meeting our Collective Commitments Text adopted by the World Education Forum Dakar, Senegal, 26-28 April 2000 Dakar Framework for Action Education for All:
Guidelines for the Use of the Continuing Education Unit (CEU)
 Guidelines for the Use of the Continuing Education Unit (CEU) The UNC Policy Manual The essential educational mission of the University is augmented through a broad range of activities generally categorized
Guidelines for the Use of the Continuing Education Unit (CEU) The UNC Policy Manual The essential educational mission of the University is augmented through a broad range of activities generally categorized
Conditions of study and examination regulations of the. European Master of Science in Midwifery
 Conditions of study and examination regulations of the European Master of Science in Midwifery Midwifery Research and Education Unit Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Hannover Medical School September
Conditions of study and examination regulations of the European Master of Science in Midwifery Midwifery Research and Education Unit Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Hannover Medical School September
TRAVEL & TOURISM CAREER GUIDE. a world of career opportunities
 TRAVEL & TOURISM CAREER GUIDE CULTURE, ARTS, TOURISM, HOSPITALITY & SPORT SECTOR EDUCATION & TRAINING AUTHORITY (CATHSSETA) a world of career opportunities (011) 217 0600 www.cathsseta.org.za 1 Newton
TRAVEL & TOURISM CAREER GUIDE CULTURE, ARTS, TOURISM, HOSPITALITY & SPORT SECTOR EDUCATION & TRAINING AUTHORITY (CATHSSETA) a world of career opportunities (011) 217 0600 www.cathsseta.org.za 1 Newton
GENERAL INFORMATION STUDIES DEGREE PROGRAMME PERIOD OF EXECUTION SCOPE DESCRIPTION LANGUAGE OF STUDY CODE DEGREE
 Curriculum 1 (7) GENERAL INFORMATION DEGREE PROGRAMME PERIOD OF EXECUTION SCOPE DESCRIPTION LANGUAGE OF STUDY CODE DEGREE Master's Degree Programme in Health Care and Social Services Development and Management
Curriculum 1 (7) GENERAL INFORMATION DEGREE PROGRAMME PERIOD OF EXECUTION SCOPE DESCRIPTION LANGUAGE OF STUDY CODE DEGREE Master's Degree Programme in Health Care and Social Services Development and Management
California Professional Standards for Education Leaders (CPSELs)
 Standard 1 STANDARD 1: DEVELOPMENT AND IMPLEMENTATION OF A SHARED VISION Education leaders facilitate the development and implementation of a shared vision of learning and growth of all students. Element
Standard 1 STANDARD 1: DEVELOPMENT AND IMPLEMENTATION OF A SHARED VISION Education leaders facilitate the development and implementation of a shared vision of learning and growth of all students. Element
Abstract. Janaka Jayalath Director / Information Systems, Tertiary and Vocational Education Commission, Sri Lanka.
 FEASIBILITY OF USING ELEARNING IN CAPACITY BUILDING OF ICT TRAINERS AND DELIVERY OF TECHNICAL, VOCATIONAL EDUCATION AND TRAINING (TVET) COURSES IN SRI LANKA Janaka Jayalath Director / Information Systems,
FEASIBILITY OF USING ELEARNING IN CAPACITY BUILDING OF ICT TRAINERS AND DELIVERY OF TECHNICAL, VOCATIONAL EDUCATION AND TRAINING (TVET) COURSES IN SRI LANKA Janaka Jayalath Director / Information Systems,
Did we get to the right train?
 Did we get to the right train? Seija Mahlamäki-Kultanen Dean, HAMK School of Professional Teacher Education Adjunct Professor seija.mahlamaki-kultanen@hamk.fi Finland joined European Union 1995 What are
Did we get to the right train? Seija Mahlamäki-Kultanen Dean, HAMK School of Professional Teacher Education Adjunct Professor seija.mahlamaki-kultanen@hamk.fi Finland joined European Union 1995 What are
2007 No. xxxx EDUCATION, ENGLAND. The Further Education Teachers Qualifications (England) Regulations 2007
 Please note: these Regulations are draft - they have been made but are still subject to Parliamentary Approval. They S T A T U T O R Y I N S T R U M E N T S 2007 No. xxxx EDUCATION, ENGLAND The Further
Please note: these Regulations are draft - they have been made but are still subject to Parliamentary Approval. They S T A T U T O R Y I N S T R U M E N T S 2007 No. xxxx EDUCATION, ENGLAND The Further
ACCREDITATION STANDARDS
 ACCREDITATION STANDARDS Description of the Profession Interpretation is the art and science of receiving a message from one language and rendering it into another. It involves the appropriate transfer
ACCREDITATION STANDARDS Description of the Profession Interpretation is the art and science of receiving a message from one language and rendering it into another. It involves the appropriate transfer
AUTHORITATIVE SOURCES ADULT AND COMMUNITY LEARNING LEARNING PROGRAMMES
 AUTHORITATIVE SOURCES ADULT AND COMMUNITY LEARNING LEARNING PROGRAMMES AUGUST 2001 Contents Sources 2 The White Paper Learning to Succeed 3 The Learning and Skills Council Prospectus 5 Post-16 Funding
AUTHORITATIVE SOURCES ADULT AND COMMUNITY LEARNING LEARNING PROGRAMMES AUGUST 2001 Contents Sources 2 The White Paper Learning to Succeed 3 The Learning and Skills Council Prospectus 5 Post-16 Funding
Productive partnerships to promote media and information literacy for knowledge societies: IFLA and UNESCO s collaborative work
 Productive partnerships to promote media and information literacy for knowledge societies: IFLA and UNESCO s collaborative work Dr. Maria-Carme Torras IFLA Governing Board Member; library director, Bergen
Productive partnerships to promote media and information literacy for knowledge societies: IFLA and UNESCO s collaborative work Dr. Maria-Carme Torras IFLA Governing Board Member; library director, Bergen
Curriculum for the Academy Profession Degree Programme in Energy Technology
 Curriculum for the Academy Profession Degree Programme in Energy Technology Version: 2016 Curriculum for the Academy Profession Degree Programme in Energy Technology 2016 Addresses of the institutions
Curriculum for the Academy Profession Degree Programme in Energy Technology Version: 2016 Curriculum for the Academy Profession Degree Programme in Energy Technology 2016 Addresses of the institutions
Higher Education Review (Embedded Colleges) of Navitas UK Holdings Ltd. Hertfordshire International College
 Higher Education Review (Embedded Colleges) of Navitas UK Holdings Ltd April 2016 Contents About this review... 1 Key findings... 2 QAA's judgements about... 2 Good practice... 2 Theme: Digital Literacies...
Higher Education Review (Embedded Colleges) of Navitas UK Holdings Ltd April 2016 Contents About this review... 1 Key findings... 2 QAA's judgements about... 2 Good practice... 2 Theme: Digital Literacies...
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES RECOMMENDATION OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL
 EN EN EN COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 9.4.2008 COM(2008) 180 final 2008/0070 (COD) RECOMMENDATION OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL on the establishment of the European
EN EN EN COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 9.4.2008 COM(2008) 180 final 2008/0070 (COD) RECOMMENDATION OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL on the establishment of the European
International Experts Meeting on REORIENTING TVET POLICY TOWARDS EDUCATION FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Berlin, Germany. Country Paper THAILAND
 Country Paper THAILAND INNOVATIVE PRACTICE IN TVET TOWARDS EDUCATION FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT IN THAILAND DR. (MS.) SIRIRAK RATCHUSANTI SENIOR ADVISOR FOR VOCATIONAL EDUCATION STANDARD (BUSINESS & HOSPITALITY),
Country Paper THAILAND INNOVATIVE PRACTICE IN TVET TOWARDS EDUCATION FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT IN THAILAND DR. (MS.) SIRIRAK RATCHUSANTI SENIOR ADVISOR FOR VOCATIONAL EDUCATION STANDARD (BUSINESS & HOSPITALITY),
Lincoln School Kathmandu, Nepal
 ISS Administrative Searches is pleased to announce Lincoln School Kathmandu, Nepal Seeks Elementary Principal Application Deadline: October 30, 2017 Visit the ISS Administrative Searches webpage to view
ISS Administrative Searches is pleased to announce Lincoln School Kathmandu, Nepal Seeks Elementary Principal Application Deadline: October 30, 2017 Visit the ISS Administrative Searches webpage to view
22/07/10. Last amended. Date: 22 July Preamble
 03-1 Please note that this document is a non-binding convenience translation. Only the German version of the document entitled "Studien- und Prüfungsordnung der Juristischen Fakultät der Universität Heidelberg
03-1 Please note that this document is a non-binding convenience translation. Only the German version of the document entitled "Studien- und Prüfungsordnung der Juristischen Fakultät der Universität Heidelberg
UPPER SECONDARY CURRICULUM OPTIONS AND LABOR MARKET PERFORMANCE: EVIDENCE FROM A GRADUATES SURVEY IN GREECE
 UPPER SECONDARY CURRICULUM OPTIONS AND LABOR MARKET PERFORMANCE: EVIDENCE FROM A GRADUATES SURVEY IN GREECE Stamatis Paleocrassas, Panagiotis Rousseas, Vassilia Vretakou Pedagogical Institute, Athens Abstract
UPPER SECONDARY CURRICULUM OPTIONS AND LABOR MARKET PERFORMANCE: EVIDENCE FROM A GRADUATES SURVEY IN GREECE Stamatis Paleocrassas, Panagiotis Rousseas, Vassilia Vretakou Pedagogical Institute, Athens Abstract
Sharing Information on Progress. Steinbeis University Berlin - Institute Corporate Responsibility Management. Report no. 2
 Sharing Information on Progress - Institute Corporate Responsibility Management Report no. 2 Berlin, March 2013 2 Renewal of the commitment to PRME As an institution of higher education involved in Principles
Sharing Information on Progress - Institute Corporate Responsibility Management Report no. 2 Berlin, March 2013 2 Renewal of the commitment to PRME As an institution of higher education involved in Principles
3 of Policy. Linking your Erasmus+ Schools project to national and European Policy
 1 2 3 of Policy Linking your Erasmus+ Schools project to national and European Policy 1 2 what is policy? Policy is the set of values and objectives that guide the work of organisations or bodies. This
1 2 3 of Policy Linking your Erasmus+ Schools project to national and European Policy 1 2 what is policy? Policy is the set of values and objectives that guide the work of organisations or bodies. This
Special Educational Needs Policy (including Disability)
 Special Educational Needs Policy (including Disability) To be reviewed annually Chair of Governors, Lyn Schlich Signed January 2017 East Preston Infant School SPECIAL EDUCATION NEEDS [SEN] POLICY CONTENTS
Special Educational Needs Policy (including Disability) To be reviewed annually Chair of Governors, Lyn Schlich Signed January 2017 East Preston Infant School SPECIAL EDUCATION NEEDS [SEN] POLICY CONTENTS
2013/Q&PQ THE SOUTH AFRICAN QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY
 2013/Q&PQ THE SOUTH AFRICAN QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY Policy and Criteria for the Registration of Qualifications and Part Qualifications on the National Qualifications Framework Compiled and produced by:
2013/Q&PQ THE SOUTH AFRICAN QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY Policy and Criteria for the Registration of Qualifications and Part Qualifications on the National Qualifications Framework Compiled and produced by:
Nottingham Trent University Course Specification
 Nottingham Trent University Course Specification Basic Course Information 1. Awarding Institution: Nottingham Trent University 2. School/Campus: Nottingham Business School / City 3. Final Award, Course
Nottingham Trent University Course Specification Basic Course Information 1. Awarding Institution: Nottingham Trent University 2. School/Campus: Nottingham Business School / City 3. Final Award, Course
UNIVERSITY OF THESSALY DEPARTMENT OF EARLY CHILDHOOD EDUCATION POSTGRADUATE STUDIES INFORMATION GUIDE
 UNIVERSITY OF THESSALY DEPARTMENT OF EARLY CHILDHOOD EDUCATION POSTGRADUATE STUDIES INFORMATION GUIDE 2011-2012 CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTION 3 A. BRIEF PRESENTATION OF THE MASTER S PROGRAMME 3 A.1. OVERVIEW
UNIVERSITY OF THESSALY DEPARTMENT OF EARLY CHILDHOOD EDUCATION POSTGRADUATE STUDIES INFORMATION GUIDE 2011-2012 CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTION 3 A. BRIEF PRESENTATION OF THE MASTER S PROGRAMME 3 A.1. OVERVIEW
DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCES
 Department of Social Sciences Operations Manual 1 (12) DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCES Operations Manual 1.0 Department of Social Sciences Operations Manual 2 (12) CHANGE PAGE This is the change page of
Department of Social Sciences Operations Manual 1 (12) DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCES Operations Manual 1.0 Department of Social Sciences Operations Manual 2 (12) CHANGE PAGE This is the change page of
M.S. in Environmental Science Graduate Program Handbook. Department of Biology, Geology, and Environmental Science
 M.S. in Environmental Science Graduate Program Handbook Department of Biology, Geology, and Environmental Science Welcome Welcome to the Master of Science in Environmental Science (M.S. ESC) program offered
M.S. in Environmental Science Graduate Program Handbook Department of Biology, Geology, and Environmental Science Welcome Welcome to the Master of Science in Environmental Science (M.S. ESC) program offered
Chiltern Training Ltd.
 Chiltern Training Ltd. Information Breakfast Session Agenda: Breakfast and Networking. Welcome Chiltern Training Courses Information Presentation. Evaluation and Networking. Chiltern Training Ltd Independent
Chiltern Training Ltd. Information Breakfast Session Agenda: Breakfast and Networking. Welcome Chiltern Training Courses Information Presentation. Evaluation and Networking. Chiltern Training Ltd Independent
E-Learning project in GIS education
 E-Learning project in GIS education MARIA KOULI (1), DIMITRIS ALEXAKIS (1), FILIPPOS VALLIANATOS (1) (1) Department of Natural Resources & Environment Technological Educational Institute of Grete Romanou
E-Learning project in GIS education MARIA KOULI (1), DIMITRIS ALEXAKIS (1), FILIPPOS VALLIANATOS (1) (1) Department of Natural Resources & Environment Technological Educational Institute of Grete Romanou
Programme Specification
 Programme Specification Awarding Body/Institution Teaching Institution Queen Mary, University of London Queen Mary, University of London Name of Final Award and Programme Title MSc Accounting and Finance
Programme Specification Awarding Body/Institution Teaching Institution Queen Mary, University of London Queen Mary, University of London Name of Final Award and Programme Title MSc Accounting and Finance
EUROPEAN UNIVERSITIES LOOKING FORWARD WITH CONFIDENCE PRAGUE DECLARATION 2009
 EUROPEAN UNIVERSITIES LOOKING FORWARD WITH CONFIDENCE PRAGUE DECLARATION 2009 Copyright 2009 by the European University Association All rights reserved. This information may be freely used and copied for
EUROPEAN UNIVERSITIES LOOKING FORWARD WITH CONFIDENCE PRAGUE DECLARATION 2009 Copyright 2009 by the European University Association All rights reserved. This information may be freely used and copied for
Quality in University Lifelong Learning (ULLL) and the Bologna process
 Quality in University Lifelong Learning (ULLL) and the Bologna process The workshop will critique various quality models and tools as a result of EU LLL policy, such as consideration of the European Standards
Quality in University Lifelong Learning (ULLL) and the Bologna process The workshop will critique various quality models and tools as a result of EU LLL policy, such as consideration of the European Standards
Qualification Guidance
 Qualification Guidance For awarding organisations Award in Education and Training (QCF) Updated May 2013 Contents Glossary... 2 Section 1 Introduction 1.1 Purpose of this document... 3 1.2 How to use this
Qualification Guidance For awarding organisations Award in Education and Training (QCF) Updated May 2013 Contents Glossary... 2 Section 1 Introduction 1.1 Purpose of this document... 3 1.2 How to use this
TABLE OF CONTENTS. By-Law 1: The Faculty Council...3
 FACULTY OF SOCIAL SCIENCES, University of Ottawa Faculty By-Laws (November 21, 2017) TABLE OF CONTENTS By-Law 1: The Faculty Council....3 1.1 Mandate... 3 1.2 Members... 3 1.3 Procedures for electing Faculty
FACULTY OF SOCIAL SCIENCES, University of Ottawa Faculty By-Laws (November 21, 2017) TABLE OF CONTENTS By-Law 1: The Faculty Council....3 1.1 Mandate... 3 1.2 Members... 3 1.3 Procedures for electing Faculty
GUIDE TO EVALUATING DISTANCE EDUCATION AND CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION
 GUIDE TO EVALUATING DISTANCE EDUCATION AND CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION A Publication of the Accrediting Commission For Community and Junior Colleges Western Association of Schools and Colleges For use in
GUIDE TO EVALUATING DISTANCE EDUCATION AND CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION A Publication of the Accrediting Commission For Community and Junior Colleges Western Association of Schools and Colleges For use in
Loyalist College Applied Degree Proposal. Name of Institution: Loyalist College of Applied Arts and Technology
 College and Program Information 1.0 Submission Cover 1.1 College Information Name of Institution: Loyalist College of Applied Arts and Technology Title of Program: Bachelor of Applied Arts (Human Services
College and Program Information 1.0 Submission Cover 1.1 College Information Name of Institution: Loyalist College of Applied Arts and Technology Title of Program: Bachelor of Applied Arts (Human Services
Master s Programme in European Studies
 Programme syllabus for the Master s Programme in European Studies 120 higher education credits Second Cycle Confirmed by the Faculty Board of Social Sciences 2015-03-09 2 1. Degree Programme title and
Programme syllabus for the Master s Programme in European Studies 120 higher education credits Second Cycle Confirmed by the Faculty Board of Social Sciences 2015-03-09 2 1. Degree Programme title and
Mandatory Review of Social Skills Qualifications. Consultation document for Approval to List
 Mandatory Review of Social Skills Qualifications Consultation document for Approval to List February 2015 Prepared by: National Qualifications Services on behalf of the Social Skills Governance Group 1
Mandatory Review of Social Skills Qualifications Consultation document for Approval to List February 2015 Prepared by: National Qualifications Services on behalf of the Social Skills Governance Group 1
ESTONIA. spotlight on VET. Education and training in figures. spotlight on VET
 Education and training in figures Upper secondary students (ISCED 11 level 3) enrolled in vocational and general % of all students in upper secondary education, 14 GERAL VOCATIONAL 1 8 26.6 29.6 6.3 2.6
Education and training in figures Upper secondary students (ISCED 11 level 3) enrolled in vocational and general % of all students in upper secondary education, 14 GERAL VOCATIONAL 1 8 26.6 29.6 6.3 2.6
Studies Arts, Humanities and Social Science Faculty
 BA English Literature and Film For students entering Part 1 in 2014/5 Awarding Institution: Teaching Institution: Relevant QAA subject Benchmarking group(s): Faculty: Programme length: Date of specification:
BA English Literature and Film For students entering Part 1 in 2014/5 Awarding Institution: Teaching Institution: Relevant QAA subject Benchmarking group(s): Faculty: Programme length: Date of specification:
Drs Rachel Patrick, Emily Gray, Nikki Moodie School of Education, School of Global, Urban and Social Studies, College of Design and Social Context
 Learning and Teaching Investment Fund final report Building Capacity Through Partnerships: Embedding Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander cultures, histories and perspectives at the School, College and
Learning and Teaching Investment Fund final report Building Capacity Through Partnerships: Embedding Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander cultures, histories and perspectives at the School, College and
University of Toronto
 University of Toronto OFFICE OF THE VICE PRESIDENT AND PROVOST Governance and Administration of Extra-Departmental Units Interdisciplinarity Committee Working Group Report Following approval by Governing
University of Toronto OFFICE OF THE VICE PRESIDENT AND PROVOST Governance and Administration of Extra-Departmental Units Interdisciplinarity Committee Working Group Report Following approval by Governing
General study plan for third-cycle programmes in Sociology
 Date of adoption: 07/06/2017 Ref. no: 2017/3223-4.1.1.2 Faculty of Social Sciences Third-cycle education at Linnaeus University is regulated by the Swedish Higher Education Act and Higher Education Ordinance
Date of adoption: 07/06/2017 Ref. no: 2017/3223-4.1.1.2 Faculty of Social Sciences Third-cycle education at Linnaeus University is regulated by the Swedish Higher Education Act and Higher Education Ordinance
Position Statements. Index of Association Position Statements
 ts Association position statements address key issues for Pre-K-12 education and describe the shared beliefs that direct united action by boards of education/conseil scolaire fransaskois and their Association.
ts Association position statements address key issues for Pre-K-12 education and describe the shared beliefs that direct united action by boards of education/conseil scolaire fransaskois and their Association.
James H. Williams, Ed.D. CICE, Hiroshima University George Washington University August 2, 2012
 James H. Williams, Ed.D. jhw@gwu.edu CICE, Hiroshima University George Washington University August 2, 2012 Very poor country, but rapidly growing economy Access has improved, especially at primary Lower
James H. Williams, Ed.D. jhw@gwu.edu CICE, Hiroshima University George Washington University August 2, 2012 Very poor country, but rapidly growing economy Access has improved, especially at primary Lower
University of the Arts London (UAL) Diploma in Professional Studies Art and Design Date of production/revision May 2015
 Programme Specification Every taught course of study leading to a UAL award is required to have a Programme Specification. This summarises the course aims, learning outcomes, teaching, learning and assessment
Programme Specification Every taught course of study leading to a UAL award is required to have a Programme Specification. This summarises the course aims, learning outcomes, teaching, learning and assessment
Implementation Regulations
 Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences of Leiden University & Faculty of Applied Sciences of Delft University of Technology Implementation Regulations for the MSc in NanoScience Corresponding to the
Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences of Leiden University & Faculty of Applied Sciences of Delft University of Technology Implementation Regulations for the MSc in NanoScience Corresponding to the
REGULATIONS RELATING TO ADMISSION, STUDIES AND EXAMINATION AT THE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF SOUTHEAST NORWAY
 REGULATIONS RELATING TO ADMISSION, STUDIES AND EXAMINATION AT THE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF SOUTHEAST NORWAY Authorisation: Passed by the Joint Board at the University College of Southeast Norway on 18 December
REGULATIONS RELATING TO ADMISSION, STUDIES AND EXAMINATION AT THE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF SOUTHEAST NORWAY Authorisation: Passed by the Joint Board at the University College of Southeast Norway on 18 December
EUA Quality Culture: Implementing Bologna Reforms
 UNIVERSITY OF TAMPERE FINLAND EUA Quality Culture: Implementing Bologna Reforms 1. What is my university s concept of a quality reform with respect to the Bologna process? Note: as for detailed specification
UNIVERSITY OF TAMPERE FINLAND EUA Quality Culture: Implementing Bologna Reforms 1. What is my university s concept of a quality reform with respect to the Bologna process? Note: as for detailed specification
Delaware Performance Appraisal System Building greater skills and knowledge for educators
 Delaware Performance Appraisal System Building greater skills and knowledge for educators DPAS-II Guide for Administrators (Assistant Principals) Guide for Evaluating Assistant Principals Revised August
Delaware Performance Appraisal System Building greater skills and knowledge for educators DPAS-II Guide for Administrators (Assistant Principals) Guide for Evaluating Assistant Principals Revised August
Doctor in Engineering (EngD) Additional Regulations
 UCL Academic Manual 2016-17 Chapter 8: Derogations and Variations Doctor in Engineering (EngD) Additional Regulations Contact: Lizzie Vinton, Assessment Regulations and Governance Manager, Academic Services,
UCL Academic Manual 2016-17 Chapter 8: Derogations and Variations Doctor in Engineering (EngD) Additional Regulations Contact: Lizzie Vinton, Assessment Regulations and Governance Manager, Academic Services,
Davidson College Library Strategic Plan
 Davidson College Library Strategic Plan 2016-2020 1 Introduction The Davidson College Library s Statement of Purpose (Appendix A) identifies three broad categories by which the library - the staff, the
Davidson College Library Strategic Plan 2016-2020 1 Introduction The Davidson College Library s Statement of Purpose (Appendix A) identifies three broad categories by which the library - the staff, the
5 Early years providers
 5 Early years providers What this chapter covers This chapter explains the action early years providers should take to meet their duties in relation to identifying and supporting all children with special
5 Early years providers What this chapter covers This chapter explains the action early years providers should take to meet their duties in relation to identifying and supporting all children with special
Knowledge for the Future Developments in Higher Education and Research in the Netherlands
 Knowledge for the Future Developments in Higher Education and Research in the Netherlands Don F. Westerheijden Contribution to Vision Seminar Higher education and Research 2030 Helsinki, 2017-06-14 How
Knowledge for the Future Developments in Higher Education and Research in the Netherlands Don F. Westerheijden Contribution to Vision Seminar Higher education and Research 2030 Helsinki, 2017-06-14 How
The EQF Referencing report of the Kosovo NQF for General Education, VET and Higher Education
 EQF Referencing Report of the Kosovo Qualifications Framework Editor: Teuta Danuza Authors of the report: Teuta Danuza, Furtuna Mehmeti and Blerim Saqipi Authors of the 2014 version: Teuta Danuza, Anton
EQF Referencing Report of the Kosovo Qualifications Framework Editor: Teuta Danuza Authors of the report: Teuta Danuza, Furtuna Mehmeti and Blerim Saqipi Authors of the 2014 version: Teuta Danuza, Anton
HEALTH SERVICES ADMINISTRATION
 Assessment of Library Collections Program Review HEALTH SERVICES ADMINISTRATION Tony Schwartz Associate Director for Collection Management April 13, 2006 Update: the main additions to the health science
Assessment of Library Collections Program Review HEALTH SERVICES ADMINISTRATION Tony Schwartz Associate Director for Collection Management April 13, 2006 Update: the main additions to the health science
Interview on Quality Education
 Interview on Quality Education President European University Association (EUA) Ultimately, education is what should allow students to grow, learn, further develop, and fully play their role as active citizens
Interview on Quality Education President European University Association (EUA) Ultimately, education is what should allow students to grow, learn, further develop, and fully play their role as active citizens
Bachelor of International Hospitality Management, BA IHM. Course curriculum National and Institutional Part
 Bachelor of International Hospitality Management, BA IHM Course curriculum 2016-2018 August 2016 0 INDHOLD 1. curriculum framework... 4 1.1. Objective of the study programme... 4 1.2. Title and duration...
Bachelor of International Hospitality Management, BA IHM Course curriculum 2016-2018 August 2016 0 INDHOLD 1. curriculum framework... 4 1.1. Objective of the study programme... 4 1.2. Title and duration...
THE QUEEN S SCHOOL Whole School Pay Policy
 The Queen s Church of England Primary School Encouraging every child to reach their full potential, nurtured and supported in a Christian community which lives by the values of Love, Compassion and Respect.
The Queen s Church of England Primary School Encouraging every child to reach their full potential, nurtured and supported in a Christian community which lives by the values of Love, Compassion and Respect.
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION
 PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION 1 Awarding Institution Newcastle University 2 Teaching Institution Newcastle University 3 Final Award MSc 4 Programme Title Digital Architecture 5 UCAS/Programme Code 5112 6 Programme
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION 1 Awarding Institution Newcastle University 2 Teaching Institution Newcastle University 3 Final Award MSc 4 Programme Title Digital Architecture 5 UCAS/Programme Code 5112 6 Programme
Status of the MP Profession in Europe
 Status of the MP Profession in Europe John Damilakis, MSc, PhD Prof. of Medical Physics Faculty of Medicine University of Crete, Greece IOMP Chair, E&T Committee EFOMP Vice-President (2014) Basic education:
Status of the MP Profession in Europe John Damilakis, MSc, PhD Prof. of Medical Physics Faculty of Medicine University of Crete, Greece IOMP Chair, E&T Committee EFOMP Vice-President (2014) Basic education:
Bachelor of Engineering in Biotechnology
 Study Programme for the degree Bachelor of Engineering in Biotechnology Center for Engineering, University College Absalon September 2017 Content Content... 1 Preface... 4 Part 1 Facts about the programme...
Study Programme for the degree Bachelor of Engineering in Biotechnology Center for Engineering, University College Absalon September 2017 Content Content... 1 Preface... 4 Part 1 Facts about the programme...
Henley Business School at Univ of Reading
 MSc in Corporate Real Estate For students entering in 2012/3 Awarding Institution: Teaching Institution: Relevant QAA subject Benchmarking group(s): Faculty: Programme length: Date of specification: Programme
MSc in Corporate Real Estate For students entering in 2012/3 Awarding Institution: Teaching Institution: Relevant QAA subject Benchmarking group(s): Faculty: Programme length: Date of specification: Programme
TEACHING QUALITY: SKILLS. Directive Teaching Quality Standard Applicable to the Provision of Basic Education in Alberta
 Standards of Teaching Practice TEACHING QUALITY: SKILLS BASED ON: Policy, Regulations and Forms Manual Section 4 Ministerial Orders and Directives Directive 4.2.1 - Teaching Quality Standard Applicable
Standards of Teaching Practice TEACHING QUALITY: SKILLS BASED ON: Policy, Regulations and Forms Manual Section 4 Ministerial Orders and Directives Directive 4.2.1 - Teaching Quality Standard Applicable
No educational system is better than its teachers
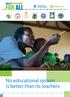 No educational system is better than its teachers Investment in quality educators has a very high multiplier effect: every good teacher benefits an entire class, year after year, and when those bettereducated
No educational system is better than its teachers Investment in quality educators has a very high multiplier effect: every good teacher benefits an entire class, year after year, and when those bettereducated
A planned program of courses and learning experiences that begins with exploration of career options
 14-2 - 2012 A planned program of courses and learning experiences that begins with exploration of career options Supports basic academic and life skills, and enables achievement of high academic standards,
14-2 - 2012 A planned program of courses and learning experiences that begins with exploration of career options Supports basic academic and life skills, and enables achievement of high academic standards,
State Parental Involvement Plan
 A Toolkit for Title I Parental Involvement Section 3 Tools Page 41 Tool 3.1: State Parental Involvement Plan Description This tool serves as an example of one SEA s plan for supporting LEAs and schools
A Toolkit for Title I Parental Involvement Section 3 Tools Page 41 Tool 3.1: State Parental Involvement Plan Description This tool serves as an example of one SEA s plan for supporting LEAs and schools
PROVIDENCE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE
 BACHELOR OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION (BBA) WITH CO-OP (4 Year) Academic Staff Jeremy Funk, Ph.D., University of Manitoba, Program Coordinator Bruce Duggan, M.B.A., University of Manitoba Marcio Coelho,
BACHELOR OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION (BBA) WITH CO-OP (4 Year) Academic Staff Jeremy Funk, Ph.D., University of Manitoba, Program Coordinator Bruce Duggan, M.B.A., University of Manitoba Marcio Coelho,
Xenia Community Schools Board of Education Goals. Approved May 12, 2014
 Xenia Community Schools of Education Goals Approved May 12, 2014 Pro Tem Priorities Improved Communication Goals Strategies Measureable Actions Timing *Clarify and understand who we serve, how we serve
Xenia Community Schools of Education Goals Approved May 12, 2014 Pro Tem Priorities Improved Communication Goals Strategies Measureable Actions Timing *Clarify and understand who we serve, how we serve
Dual Training at a Glance
 Dual Training at a Glance Dual Training at a Glance 1 Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) Mission: Education Research Overall responsibility for vocational training within the Federal Government
Dual Training at a Glance Dual Training at a Glance 1 Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) Mission: Education Research Overall responsibility for vocational training within the Federal Government
Bachelor of Software Engineering: Emerging sustainable partnership with industry in ODL
 Bachelor of Software Engineering: Emerging sustainable partnership with industry in ODL L.S.K. UDUGAMA, JANAKA LIYANAGAMA Faculty of Engineering Technology The Open University of Sri Lanka POBox 21, Nawala,
Bachelor of Software Engineering: Emerging sustainable partnership with industry in ODL L.S.K. UDUGAMA, JANAKA LIYANAGAMA Faculty of Engineering Technology The Open University of Sri Lanka POBox 21, Nawala,
Guidance on the University Health and Safety Management System
 Newcastle University Safety Office 1 Kensington Terrace Newcastle upon Tyne NE1 7RU Tel 0191 222 6274 University Safety Policy Guidance Guidance on the University Health and Safety Management System Document
Newcastle University Safety Office 1 Kensington Terrace Newcastle upon Tyne NE1 7RU Tel 0191 222 6274 University Safety Policy Guidance Guidance on the University Health and Safety Management System Document
Qs&As Providing Financial Aid to Former Everest College Students March 11, 2015
 Qs&As Providing Financial Aid to Former Everest College Students March 11, 2015 Q. How is the government helping students affected by the closure of Everest College? A. Ontario is providing financial assistance
Qs&As Providing Financial Aid to Former Everest College Students March 11, 2015 Q. How is the government helping students affected by the closure of Everest College? A. Ontario is providing financial assistance
Curricular Reviews: Harvard, Yale & Princeton. DUE Meeting
 Curricular Reviews: Harvard, Yale & Princeton DUE Meeting 3 March 2006 1 Some Numbers for Comparison Undergraduates MIT: 4,066 1,745 engineering majors (plus 169 Course 6 MEng) 876 science majors 128 humanities,
Curricular Reviews: Harvard, Yale & Princeton DUE Meeting 3 March 2006 1 Some Numbers for Comparison Undergraduates MIT: 4,066 1,745 engineering majors (plus 169 Course 6 MEng) 876 science majors 128 humanities,
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION
 PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION 1 Awarding Institution Newcastle University 2 Teaching Institution Newcastle University 3 Final Award M.Sc. 4 Programme Title Industrial and Commercial Biotechnology 5 UCAS/Programme
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION 1 Awarding Institution Newcastle University 2 Teaching Institution Newcastle University 3 Final Award M.Sc. 4 Programme Title Industrial and Commercial Biotechnology 5 UCAS/Programme
Qualification handbook
 Qualification handbook BIIAB Level 3 Award in 601/5960/1 Version 1 April 2015 Table of Contents 1. About the BIIAB Level 3 Award in... 1 2. About this pack... 2 3. BIIAB Customer Service... 2 4. What are
Qualification handbook BIIAB Level 3 Award in 601/5960/1 Version 1 April 2015 Table of Contents 1. About the BIIAB Level 3 Award in... 1 2. About this pack... 2 3. BIIAB Customer Service... 2 4. What are
Council of the European Union Brussels, 4 November 2015 (OR. en)
 Council of the European Union Brussels, 4 November 2015 (OR. en) 13631/15 NOTE From: To: General Secretariat of the Council JEUN 96 EDUC 285 SOC 633 EMPL 416 CULT 73 SAN 356 Permanent Representatives Committee/Council
Council of the European Union Brussels, 4 November 2015 (OR. en) 13631/15 NOTE From: To: General Secretariat of the Council JEUN 96 EDUC 285 SOC 633 EMPL 416 CULT 73 SAN 356 Permanent Representatives Committee/Council
The Netherlands. Jeroen Huisman. Introduction
 4 The Netherlands Jeroen Huisman Introduction Looking solely at the legislation, one could claim that the Dutch higher education system has been officially known as a binary system since 1986. At that
4 The Netherlands Jeroen Huisman Introduction Looking solely at the legislation, one could claim that the Dutch higher education system has been officially known as a binary system since 1986. At that
HE and VET, partnering for ensuring portability of qualifications and permeability among education and training systems
 HE and VET, partnering for ensuring portability of qualifications and permeability among education and training systems Seija Mahlamäki Kultanen Dean, HAMK School of Professional Teacher Education Adjunct
HE and VET, partnering for ensuring portability of qualifications and permeability among education and training systems Seija Mahlamäki Kultanen Dean, HAMK School of Professional Teacher Education Adjunct
I set out below my response to the Report s individual recommendations.
 Written Response to the Enterprise and Business Committee s Report on Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths (STEM) Skills by the Minister for Education and Skills November 2014 I would like to set
Written Response to the Enterprise and Business Committee s Report on Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths (STEM) Skills by the Minister for Education and Skills November 2014 I would like to set
NOVIA UNIVERSITY OF APPLIED SCIENCES DEGREE REGULATIONS TRANSLATION
 NOVIA UNIVERSITY OF APPLIED SCIENCES DEGREE REGULATIONS TRANSLATION The Swedish Degree Regulations are followed in cases of possible interpretation issues. Degree Regulations at Novia UAS confirmed by
NOVIA UNIVERSITY OF APPLIED SCIENCES DEGREE REGULATIONS TRANSLATION The Swedish Degree Regulations are followed in cases of possible interpretation issues. Degree Regulations at Novia UAS confirmed by

